
The traditional healthcare field is beset by systemic issues. Specifically, there is a huge lack of data transparency in clinical research worldwide. This opens the door for corruption, fraud, and administration errors to occur. Moreover, the healthcare industry is fragmented and communication between researchers, analysts, patients, and medical professionals could be drastically improved by the use of blockchain technology.
The use of blockchain in healthcare can help to improve patient outcomes, while also helping to bridge the various entities within the industry, allowing teams across the sector (and the various sub-sectors) to become interoperable in their research and analysis in a trustless, permissionless way.
In the following article, we discuss how the use of blockchain in healthcare can revolutionize the way the industry communicates, and how the many security features of the blockchain can benefit medical institutions, staff, and patients while saving time and money for all involved.
If you want to learn more about potential blockchain use cases in a broad number of sectors, be sure to visit Ivan on Tech Academy. Ivan on Tech Academy is one of the leading platforms for blockchain education, whether it is for enterprise purposes or private education. Enroll today and get 20% off with the special promo code BLOG20!
Paperless Society
Everything seems to be going digital right now; banking, education, media, and many of the day-to-day tasks carried out by employees in many sectors. Furthermore, the COVID-19 coronavirus pandemic only appears to have accelerated the advent of digitalization across industries.
Several aspects of daily business activities are now undertaken without the use of paper – gone are the fax machines, the telephone books, and soon the physical newspaper too.

The use of paper money has been in decline for several years now, with the recent pandemic only accelerating the process. If people are less inclined to use paper bills to transact with, and paper letters to communicate with, it makes sense that soon, many important records will be held digitally.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
Blockchain technology is a form of distributed ledger technology, that is an online, open-source database with real-time information updates. Moreover, blockchains are powered by a network of computers around the globe called nodes. These nodes mathematically verify transactions and place the valid transactions into a block.
Once full, these blocks of valid transactions are then appended to the blockchain. Each transaction in the block is cryptographically hashed to the previous valid transaction, thus the entire blockchain history is securely and mathematically linked together.
Why Blockchain?
Information held on the blockchain is immutable, meaning that it cannot be removed or altered. Blockchains rely on the large network of computers to store data on a distributed ledger, meaning that there is no single-point-of-failure and it is difficult to manipulate or hack.
By recording sensitive information on the blockchain, data can be shared without the risk of breaching confidentiality with the use of public and private keys.
How Blockchain Can Be Used In Healthcare
Crowdsourcing
The recent global pandemic has sparked a wave of innovation in the medical field, changing the way that researchers and analysts can find solutions to some of the most complex medical problems.

IBM recently used blockchain technology for crowdfunding campaigns to help healthcare organizations to find new suppliers quickly and to fund COVID-19 vaccine research, acting as a hub for verifiable virus-related information to be shared safely and transparently.
By bringing developers together using open-source blockchain tools, the entire healthcare industry can harness the power of the greatest minds in the field and allow them to work together, individually distributed, on a common goal.
Medical Records
The blockchain can reduce human error in patient records and medicine as all information held on the blockchain is mathematically verified, not verified by humans. Patient data could also be shared between several parties in an efficient and trustless way through the use of public and private keys.
Patients would have complete ownership of their medical data and history, and only allow access to necessary teams and departments of their choice.
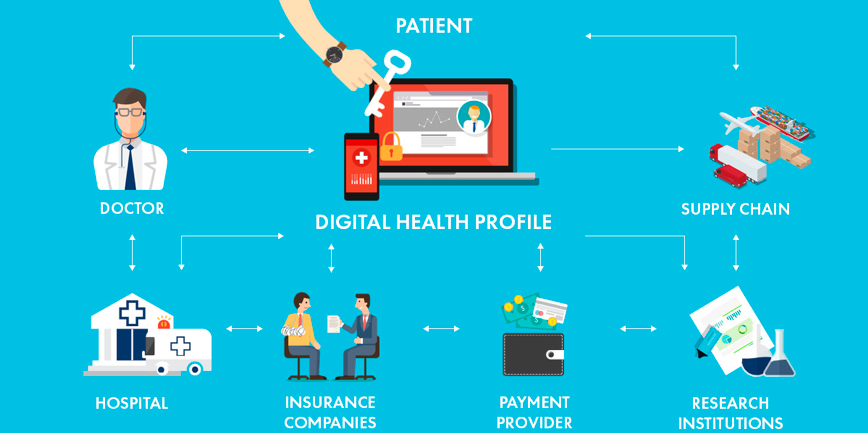
By speeding up the process of sharing data, patients have a faster route to recovery. By reducing the delay between appointments, this could prevent conditions worsening unnecessarily and improve productivity within the healthcare industry.
Patients could also allow access rules for their medical records which could be changed in-line with specific requirements, (such as worsening on-going conditions, or drastic change in a measured health observation) which could be executed by a smart contract. This could drastically improve the efficiency of referrals between departments and medical centers.
Data Security
Patient data security can also be hugely improved with the use of blockchain in healthcare. Doctor-patient confidentiality can be maintained by immutable data held on the blockchain, meaning that sensitive information is only seen by the medical professionals who need to see it and nobody else, while at the same time being easy to access by any authorized parties.
Blockchain technology also presents a strong argument for preventing large-scale hacks within the healthcare industry. Hacking an old-fashioned hospital database comes with significantly fewer challenges than trying to hack a well-protected blockchain network.

Centralized data silos that exist in the current healthcare model are inefficient, insecure, and often slow down productivity when data sharing is impeded. Blockchain-based Health Information Exchanges can disintermediate the sharing of medical records and patient data by automating access whilst also helping to improve security.
The blockchain allows for information to be shared securely, meaning that researchers could have access to specific parts of a particular set of patients’ data at any given time, scaling the expansion of medical research.
Ivan on Tech Academy has a wealth of blockchain courses for those looking to learn more about blockchain technology and data security. If this interests you, be sure to check out our extensive selection of top-notch courses!
Counterfeit Medical Supplies
The ability to verify proof-of-origin in all supply chains is crucial. In healthcare, it is particularly important to prevent counterfeit products as this can be a huge detriment to patients. Counterfeiting costs the healthcare industry an enormous amount of money each year and can lead to unnecessary illness or even loss of life.
Projects such as Origin Trail are championing supply chain management on the blockchain by ensuring provenance and authenticity in every step of the process.

Medical products can be verified during manufacturing and distribution to ensure that the correct products reach the correct people safely, without tampering.
If an event occurred which would potentially damage or spoil any type of medical supply, this could theoretically be identified in real-time and a replacement sent out automatically, ensuring that nothing potentially dangerous is delivered to medical centers.
Several new start-ups, such as Real Items Company, began using the VeChain blockchain over recent months to verify and tokenize masks and other Covid-19 related PPE. VeChain has also been working towards enhancing drug traceability since 2018.
Tokenized Blood
One of the perhaps most fascinating use cases of blockchain in healthcare is the tokenization of blood with non-fungible tokens.
While fungible tokens such as Ethereum are interchangeable, which means that one ETH in your pocket is the same as 1 ETH in another person’s, non-fungible tokens (or NFTs) can hold unique data relating to a specific subject. NFTs are used to store digital art and can be used in gaming for rare or special in-game items to ensure that they are verifiably scarce and cannot be duplicated or copied.

The EY OpsChain blockchain can record all the data points between blood donation to blood transfusion. From the identification of the donor, temperature of the donation in transit, GPS location points from laboratory to hospital, to finally storing on the medical record of the patient receiving the transfusion.
The blood is tokenized using a barcode that is scanned during the entire process, producing real-time live updates viewable to necessary parties involved.
By tokenizing blood on the blockchain, an inventory of blood donations can be monitored accurately and identify shortages between regions or of specific blood types, while also preventing human error.
The UK-based initiative BloodChain works like a “social blood bank” that allows anyone to join the BloodChain network and donate blood.
This type of innovation, which harnesses AI-based applications, could meet supply and demand in real-time by using data collected on the blockchain to deliver blood to any hospital that might be short of a particular blood-type.
IoT
Healthcare-related wearables have become one of the biggest tech trends in recent years following the introduction of items such as the Fitbit and smartwatches. Technology is tracking everything that we do, from our heart rate, to what we eat and how we feel. This information has helped to form a huge data industry, with companies such as Apple and Facebook recording millions of data points from its users.
As technology and healthcare become increasingly intertwined it is more important than ever that the data gathered by big corporations is secured. Internet of Things, or IoT, is a term that is used to describe a network of interoperating devices and objects that connect via the internet and share data that is gathered by technology without human intervention.
IoT allows medical professionals to monitor patients consistently in a way that would not have been possible just a few years ago, reducing costs and preventing readmissions.
For sensitive data to be transmitted and received securely by devices that are then interpreted by humans, the blockchain plays a key role in ensuring that data is tamper-proof and that the interoperability of devices is optimized.
All kinds of wearable devices can provide a wealth of information to make life easier for patients, physicians, and hospitals, with the blockchain showing the potential to play a key role in the development of this technology.
In the future, IoT could be used to automate administration and several processes within the industry. Blockchain plays a significant role in maintaining the integrity of data which is shared across many different parties.
Sharing Resources
If the recent global health crisis has taught us anything, it is that when under pressure to do so, the healthcare community can effectively pool resources and new information to work towards a common goal. However, these efforts are stifled by outdated and inefficient infrastructure.
Not only does the blockchain provide a great platform for sharing emerging data and new findings, but the technology itself has proven to be a catalyst for building a strong community of dedicated people who can communicate efficiently to find solutions.
Hackathons are commonplace in crypto, with bug bounties and rewards for anyone that can find a bug within a protocols code. Hackathons have spawned countless innovations over the years, with many new exciting crypto projects coming off the back of these events.
The current method of storing patient medical data and their histories is stored in the hospital or doctor’s surgery’s own private individual database, which causes communication issues between different departments and hospitals.
Why We Need Blockchain In Healthcare

Here is an example to illustrate how communication between departments frequently breaks down:
On Wednesday, Bob has investigations done with his General Practitioner (his doctor), who refers him to a specialist for more tests for suspicion of cancer. He doesn’t feel happy waiting for two weeks and decides to go privately, through the cover of his insurance.
However on Thursday, the private surgery has no record of Bob’s investigations with the doctor, so the private doctor repeats the initial blood test and investigations before concluding Bob needs a specialist.
On Friday Bob sees a specialist the next day who confirms his worst fears and advises him he needs an operation. The anesthetist is worried about Bob’s heart condition and needs to see Bob’s medical history before carrying out the operation.
Bob’s doctor surgery is now closed for the weekend and their IT system isn’t compatible with the private hospital’s system. Bob needs to wait 3 days for his surgery to open and a further 2-3 working days to fax across multiple documents before he can have the operation.
Eventually, all documents are aligned and Bob has the operation. Bob has paid for multiple services, some of which the insurance company is now disputing as ‘unnecessary’, but Bob is just happy he has had the operation and is cancer-free.
Ten days later Bob’s wound becomes infected and goes to his local Emergency Department who has no record of his diagnosis, treatment, or medical history. The on-duty doctor administers antibiotics to Bob who then has an allergic reaction resulting in admission to intensive care.
Bob lives to tell the tale, but is out-of-pocket and is being challenged by his insurance company.
Blockchain In Healthcare Conclusion
Blockchain not only has the potential to optimize the healthcare industry but also creates a standard for communications and collaborations that allows for interoperability on a scale never seen before.
However, there are still many obstacles to overcome before blockchain in healthcare becomes mainstream. Many of the practical solutions that have been proposed are yet to be implemented. This means though, that the opportunity to innovate is huge. If you have industry-specific knowledge and knowledge of how blockchain works, you could be a pioneer in your field.
Blockchain can only really progress in the healthcare industry when there is better education and a broader understanding of the technology, and how it can improve all sorts of different procedures.
By choosing to develop blockchain solutions for the healthcare industry you could be at the forefront of an exciting new field, and you don’t need any prior experience in blockchain or programming. Ivan on Tech Academy can equip you with all the relevant blockchain tools and skills necessary to begin planning for implementing blockchain in healthcare.





