
There appears to be an ever-increasing amount of information to learn about the various blockchain ecosystems. One of the terms that has recently seen an upswing in interest surrounding NFTs. NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) are becoming more established as the crypto sector heats up in what many hope will constitute a 2020 - 2021 bull run. So, what are NFTs?
In properly answering that question, however, we need to take a closer look at what non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, offer. Specifically, NFTs are bringing valuable assets to the blockchain through a wide array of industries including gaming, art, fashion, and real estate.
In this article, we’ll explore some of the key use cases for non-fungible tokens. We’ll also look at some of the latest token standards, how they are implemented, and what gives them value. First and foremost, however, we need to take a look at what blockchain technology actually is.
What is Blockchain Technology?
You may be familiar with blockchain technology and how it works, but if you are new to blockchain, we've briefly explained below why this technology is revolutionary and is taking over the world.
Blockchain technology was effectively popularized back in 2008, with the release of Bitcoin. Moreover, blockchain technology relies on removing central authorities. Instead of having a central entity, organization, or governing body controlling a network from a single server or computer, blockchain technology is decentralized and operates across thousands of computers around the world.
The computers mathematically verify transactions and these actors must all agree that a transaction is valid, before it can then be placed into a block. When a block is full of transactions, it is then appended to the blockchain.

The way the computers mathematically verify transactions includes using data from the previous valid transaction.
This means every transaction is hashed together and becomes incredibly hard to hack, adjust, alter, or remove any information. Information on the blockchain is immutable, meaning it can not be changed, like carving it into stone.
Smart Contracts
The Bitcoin blockchain allows users to send and receive transactions. Put simply, it makes it possible for people to transfer money from party A to party B, and vice versa.
On July 30th, 2015 the Ethereum Network was launched by Vitalik Buterin. The Ethereum network is a decentralized platform that allows anyone to build decentralized applications (dApps) or cryptocurrencies (Ethereum tokens e.g. BAT, VET, OMG) on top of the network.

Vitalik Buterin
Ethereum was the first blockchain to support smart contracts. Smart contracts are pieces of code that deploy movement of money when a specific condition is met.
For example, if you were betting against a friend on a football match:
You can place $20 in a smart contract, and tell the smart contract to go to 2 sports websites after the game to confirm the score.
- If team A wins - Bob gets the money
- If team B wins - Alice gets the money
Smart contracts remove the need for third-party intermediaries, such as brokers or estate agents. Smart contracts are also immutable, once a contract has been deployed it is similar to launching a rocket - it can not be undone.
Since 2015 there are now many more blockchains that support smart contracts such as NEO, Hyperledger, Libra, and Hedera Hashgraph.
What are Fungible Tokens?
If something is fungible, economically speaking, it can be interchangeable with another good or asset for the same value. For example, currency and money can be said to be fungible. A $5 bill in your pocket is worth the same as the $5 bill in my pocket. Likewise, your 2 x $10 bills are worth the same as my single $20 bill.
Gold is also fungible - 1 ounce of pure gold in one country is valued the same as 1 ounce of pure gold in another. Fungibility is written into the code of Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies, which are generally more fungible than gold.
"A fungible good is standardized: each unit of this good has no uniqueness"
What are Non-fungible Tokens?
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are a special type of token which are not interchangeable with other tokens. An NFT has unique characteristics which means that it can not be replaced or exchanged for an identical token.
To tokenize means creating a token, representing a good or an asset.
The token by itself has no value; it gains its value from the good or asset it represents.
NFTs are different to cryptocurrencies, using different token standards and deploying different kinds of smart contracts (explained below).
NFTs are helping to build a new virtual economy on the blockchain which is changing how gamers and art fans interact with their favorite past-times.
Use Cases:
Gaming
Virtual economies have existed in games for many years and are a mainstay in games such as World of Warcraft and Fortnite. Marketplaces, currencies, and in-game items are often the focus of these types of games and are required for players to progress and level up throughout the game.

Gaming accounts that have excelled through a game can be a hot commodity for those who don’t want to put the time in to unlock bonus features. As such there is quite an underground market for these accounts, which goes largely unregulated.
Blockchain gaming can allow players to securely trade in-game assets and provide a layer of authenticity and verifiability to players.
In addition, blockchain gaming allows for rare items to be traded openly for fiat money safely and securely. NFTs provide a compelling solution for digital ownership of unique or rare in-game items and allow users to generate real-world revenue by utilizing their gaming skills.
Users can also partake in governance to decide the direction of future developments within a game. This gives users the opportunity to design their own virtual world and operate within digitally verifiable in-game marketplaces.
CryptoKitties
CryptoKitties is an online game where you collect, breed, and sell virtual cats and kittens. Each cat has its own genetic identification, just like a human's DNA, created by the 'Genetic Algorithm' or GA.
Users can purchase two cats (a Dame and a Sire) to breed them by simply clicking a button, creating a new unique kitten, with its own GA and identity. No two kitties can be the same.

Some of the genetic variables in these cats include facial expressions, fur design, and even the background color the cat features on.
When the app first launched, it saw so much traffic within the first 3 months that CryptoKitties created congestion on the Ethereum network back in December 2017, with large numbers of users wanting to buy and sell their kittens.
The value various CryptoKitties hold is informed by the scarcity of its' genetic make-up, (i.e. green eyes or blue eyes) which generation of crypto cats it belongs to, (Generation 0 was the first breed of cats when they breed they produce the second generation, and so on and so forth) alongside other factors including how many times a Sire has been used to breed other kittens.
Art
Blockchain technology offers proof of origin and ownership. For digital artists, it is currently very difficult to maintain copyright over their work.
Through NFTs, someone can buy a creation and proudly showcase it in a virtual space knowing the full history of information about the asset. For example, artist details, date of origin, previous owners, and asset value throughout its lifetime.
Artists can also receive a bigger cut of payment for their artwork, removing the need for third-party fees, offering peer-to-peer payments.
Sports
In the sports industry, counterfeit tickets and merchandise are a big issue, and blockchain is helping to eliminate that.
The immutability of blockchain technology prevents counterfeit tickets and collectibles, with tokenized sports game tickets being issued on the blockchain, a perfect use-case for an NFT.
Each ticket is similar, however each one holds unique information to the registered owner of the ticket on the blockchain.
Sports NFTs are also becoming popular with successful athletes becoming tokenized on the blockchain, the value being determined by their performance.
Paper Certificates of Authenticity (CoA) for physical memorabilia are currently being used, however, these can be easily lost or tampered with when the item is resold or transferred over time.

Soon, NFTs will be assigned to physical merchandise such as sweaters or scarves, so that the owner can register and verify the official merch item as theirs, on the blockchain.
Athlete's DNA data
Professional athletes benefit from the use of NFTs as they can be used to securely store their personal medical information on the blockchain. This data could otherwise easily be leaked, and when this occurs it can cost a lot of money!
Any sensitive data that is leaked in professional sports can be a huge detriment; from business arrangements (buying/selling players etc.) to tactical advantages through knowledge of injuries. This can cost a race, a match, a season, or a career.
Ethereum Name Service, Unstoppable domains
The ENS and Unstoppable domains offer crypto addresses as NFTs, for example, myname.eth or myname.crypto.
Your crypto address is similar to your Instagram or Twitter handle, each name must be unique and different. If you have a fairly common name, there may be hundreds of people wanting the same handle name.
Instagram and Twitter ban users from selling their username handle, however with ENS and Unstoppable domains you can buy and sell crypto addresses freely, with more popular names valued at a much higher price than others less in demand.
Identification/Certification
Non-fungible assets hold unique information about a particular good or asset, which makes NFTs a great use case for identification and certifications, or licenses and qualifications to be registered on the blockchain.
Every human being has unique attributes and identification information - NFTs could make your medical history, personal profile, education, and address details go digital, making it much easier for you to be in control of your data.
Media & Entertainment
The entertainment industry has been battling fraud in a massive way, ever since the internet came about. With the introduction of blockchain, each piece of media or film could be appended to the blockchain as a non-fungible token, preventing files from being copied or shared without permission.
The media industry is working on using NFTs to show proof of origin, eliminating 'fake news'.
Real Estate
Work is underway for real-world assets like real estate to be tokenized on the blockchain.

This would allow for smoother transactions when buying/selling the house - removing third-party intermediaries. It would also prevent conflicts over ownership of land and estate assets.
Token Standards
Tokens on Ethereum must follow a set of rules or protocols, complying with different ERC (Ethereum Request for Comment) standards.
The ERC-20 standard is by far the most popular at the moment used for cryptocurrencies, which defines a set of rules that allow the tokens to interact seamlessly with one another in a standardized way.
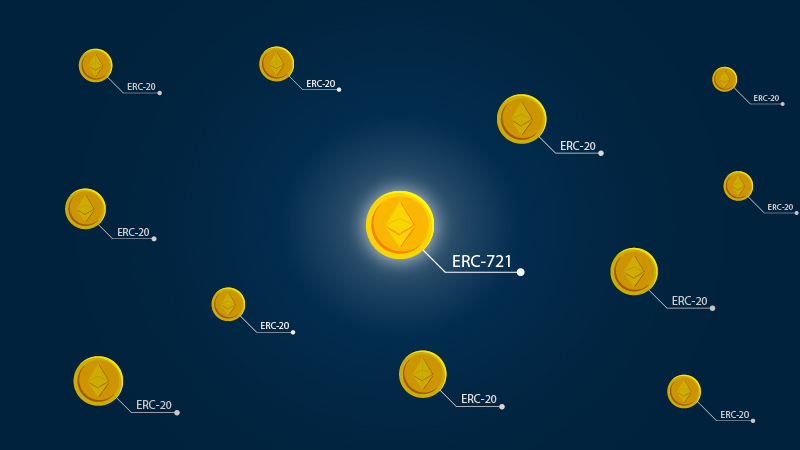
With non-fungible tokens, the blueprint works slightly differently, using the ERC-721 standard allows smart contract code to embed the unique details that make a tokenized asset rare or desirable. This metadata can be stored on or off the blockchain.
This standard does come with some drawbacks though - for example, if Bob wants to exchange his cryptokitties #1, #2, #3, and #4, for Alice’s Cryptokitty #5, it would require 5 different transactions, while this could be completed in one transaction using an ERC-1155 standard.
The ERC-1155 standard allows programmers to develop both fungible and non‑fungible tokens — in gaming, this could be the difference between a shield every player uses and a rare sword only a few people have.
ERC-998 tokens also allow multiple transfers of tokens in one transaction. A selection of ERC-721 tokens can be bundled together, meaning they don’t have to be transferred or sold off individually.
Growth and Adoption
Non-fungible tokens have been around for a long time, however, NFTs have become increasingly popular since a test version of CryptoKitties was unveiled at an Ethereum hackathon, on October 19, 2017.
As the gaming community is generally comprised of tech-savvy individuals, exposure to blockchain technology through gaming should come with less friction than any attempt to overthrow the legacy banking system.
A little over 40% of CryptoKitties users had never owned cryptocurrency until introduced to the game, which indicates the use of NFTs is helping further mass adoption of cryptocurrency.
Although the gaming industry currently has the largest number of active use cases for NFTs, other industries are slowly integrating blockchain and tokenizing their assets. As the adoption of blockchain grows, the use of NFTs will become a secondary on-ramp to new users when choosing a crypto address, or storing personal data on the blockchain. The idea that people will be using blockchain and cryptocurrency in everyday tasks without realizing it, is a great sign for the future of this technology.
Conclusion
Currently, despite an uptick in usage and development, the adoption of NFTs is still relatively slow. The benefits that blockchain brings to gaming are undeniable, however, mainstream adoption still seems a few years away. That being said, the gaming industry seems well equipped for such a transition, which would appear to be a natural one.

NFTs, blockchain, and decentralization are key factors in creating the 'MetaVerse'.
The MetaVerse is a concept that links multiple virtual shared 3D spaces. Almost anything can be tokenized on the blockchain, and open-source decentralized platforms allow everyone to capitalize on these opportunities. An example of this is in-game virtual land ownership Augmented Reality platform, OVRLand allows you to “rent out your virtual land for a fee to advertisers and influencers who wish to use your virtual space as a medium for marketing or distributing their contents.”
Non-fungible tokens appear to be creating a solid foundation for blockchain and cryptocurrency adoption, with a wide spectrum of use cases helping businesses save money on fraud, counterfeit items, copyright issues, and helping people manage their personal data and privacy.





