
Many people new to the crypto field can be unsure about the differences between the two biggest cryptocurrencies on the market, Bitcoin and Ethereum. Those that have been in this space a while are beginning to wonder which crypto is the best cryptocurrency for them, as we could possibly be on the cusp of a new 2020/2021 bull run. Therefore, we feel that we should explore the fundamental distinctions between Bitcoin vs Ethereum, the history, and the pros and cons of each crypto asset.
This article breaks down all the major differences between Bitcoin vs Ethereum, and looks at their respective benefits and drawbacks. If you want to go even further into the weeds and learn everything there is to know about Bitcoin and Ethereum, Ivan on Tech Academy is perfect for you. Join over 20,000 existing blockchain alumni and get yourself a highly competitive blockchain education.
Bitcoin vs Ethereum Overview:
Below is a side-by-side table view of Bitcoin vs Ethereum from A to Z Markets.
If you’re not sure what some of these details mean – don’t worry. We will cover the differences between the two largest cryptocurrencies further in the article in a clear and easy-to-understand framework.
| Bitcoin | Ethereum | |
| Founders | Satoshi Nakamoto | Vitalik Buterin |
| Launch Date | January 3, 2009 | July 30, 2015 |
| Hashing Algorithm | SHA-256 | Ethash |
| Block Confirmation Time | 10 minutes approximately | 15 seconds |
| Block Size Limit | 2 MB | 1 MB |
| Block Reward | 6.25 BTC (halves every 210,000 blocks) | 2 ETH per block |
| All-time High | Stacked-based language | $1,432 |
| Circulating Supply | $20,089 | 108,069,207 |
| Market Rank | 1 | 2 |
What is Bitcoin?
The 2008 financial crash has been said to have “broken the global economy“, Satoshi Nakomoto – an unknown developer or group of developers – designed a global digital currency, cryptographically secured through the creation of blockchain technology, to prevent this type of crisis from ever happening again.
Bitcoin is a borderless, censorship-resistant, open-source digital asset, that is used both as a currency and store of wealth. Bitcoin can be accessed anywhere in the world with an internet connection.

Ultimately, on a micro-scale level, Bitcoin is no more than code. Bitcoin is not tangible, and is sometimes referred to as ‘magical invisible coins’. Bitcoin is a revolutionary form of money that can be transferred globally, peer-to-peer, without any third-party intermediaries, e.g. banks.
Bitcoin is arguably the most scarce asset in the universe, with a capped supply of 21 million coins ever to be minted – over 4 million have already been lost through people losing their wallets or keys/passwords to access their wallets. Gold’s scarcity may decrease with Elon Musk suggesting he is going to mine gold on asteroids in space. Scarcity drives demand which increases value.
With the use of blockchain technology, it is now possible to remove trust from every transaction, with all necessary data and information being mathematically verified on the blockchain.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work
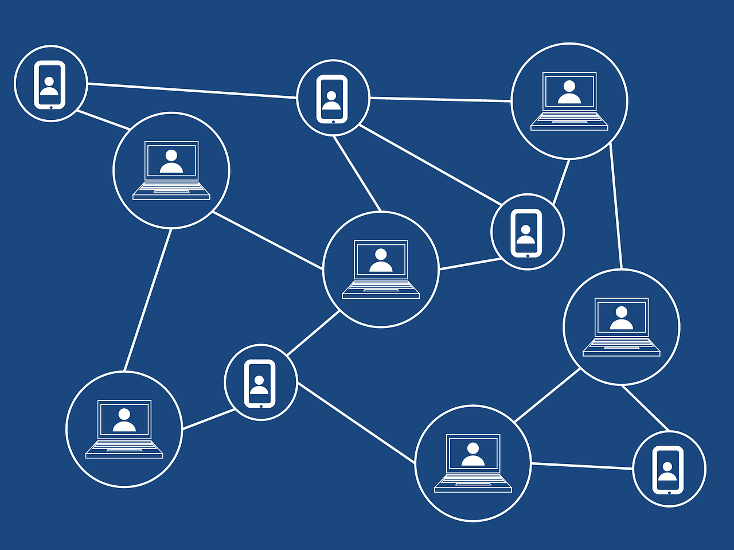
Instead of a central organization or governing body managing the movement and transactions of money, Bitcoin is run by a network of thousands of computers called ‘nodes’.
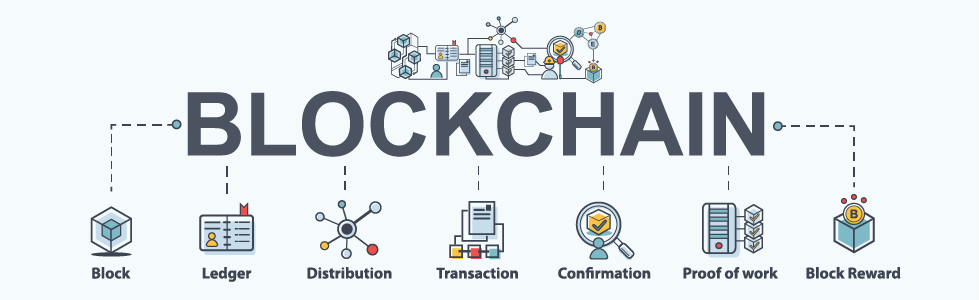
Nodes verify and complete transactions through immensely complex mathematical equations, then store the verified transaction data information in a ‘block’.
When each block is full of verified transactions, it is appended to the blockchain by mining nodes, who then receive freshly minted Bitcoin as a reward.
Each transaction in every block is hashed (cryptographically linked) to the previous valid transaction in the block, through completion of the maths equations. Therefore every single block in the blockchain is cryptographically hashed together, making all of the data immutable – meaning it can not be removed or altered.
Immutability is one of the main attractive qualities of blockchain technology alongside transparency, with the complete history of every transaction and movement of a coin recorded on the blockchain and publically available to view online.
The blockchain can be referred to as distributed ledger technology – an online database that anyone can access, with real-time information updates across the network.
The decentralization and immutability of blockchain are revolutionizing the last analog piece of infrastructure and making it digital. With the use of digital signatures and private keys, blockchain removes trust from the equation when signing documents.
With recent technology updates and innovations over the years, there has not been a suitable and reliable technology that could replace the signing of pen and paper. There are countless legal documents and requirements for businesses that require a paper signature to prove that you agree to something i.e. legal papers, receipt of supplier delivery, exchange of house/other assets.
What Can Bitcoin Do?
The Bitcoin blockchain allows users to send Bitcoin from wallet A to wallet B, peer-to-peer, with no intermediary parties. Each transaction is recorded on the blockchain.
There are different kinds of programming languages available depending on the kind of project you would like to build. The Bitcoin blockchain was created using C++.

However, it’s worth noting that Bitcoin itself isn’t written in any specific language. Bitcoin is a distribution of binary data, (where units can be in only two possible states, traditionally 0 and 1 in accordance with the Boolean algebra) that conforms to a particular standard.
The standard can be created and manipulated in any language as long as the result adheres to the same standard.
Why People Use Bitcoin
Bitcoin and blockchain have created a free market of cryptocurrencies, with assets being valued by supply and demand, and no central governing or manipulation of prices.
Since its launch in 2009, the value of 1 Bitcoin has gained over 10,000,000%, and we are still in the very early stages of mass adoption.
However, in Nigeria, small businesses are using Bitcoin as a life-line to keep their businesses and livelihoods afloat, whilst their native currency is being deflated – losing 30% of its purchasing power over the year.

A lot of businesses in Nigeria, Kenya, and South Africa purchase products from international traders, normally completing these transactions in U.S. dollars.
With native currencies being able to purchase fewer dollars each year, and incurring high fees for doing so, using Bitcoin to transact with international suppliers saves money, time and increases efficiency.
Venezuela is another country whose citizens use Bitcoin as a defense from the hyperinflation of their native currency in an attempt to preserve their wealth.
Bitcoin is a secure store of value that is priced by the supply and demand of the market. People have complete ownership and control of their crypto funds that can not be deleted or altered by any central leading party.
Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are the easiest store-of-value assets that you can take across borders.
If you want to learn more about the benefits of Bitcoin, join Ivan on Tech Academy and go from zero to blockchain hero. We offer many Bitcoin courses, including an introduction to Bitcoin and blockchain, and you can get 20% off by using the exclusive promo code BLOG20.
Ethereum
Origin of Ethereum
Vitalik Buterin proposed the Ethereum whitepaper in 2013, aged just 19, and is the founder of the Ethereum network.
Vitalik was fascinated by the decentralized technology powering Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies, and through his infamous thirst for knowledge, started researching about Bitcoin and writing articles before becoming co-founder, and head journalist, of Bitcoin Magazine in 2011.

Bitcoin Magazine was an online publication until 2012 when the outlet launched a printed version that can be found in Barnes & Noble and other bookshops. Vitalik was eager to learn as much as he could, so traveled around the world to meet developers and Bitcoin enthusiasts.
During a trip to Israel in 2013, Vitalik came across projects ‘CovertCoins’ and ‘MasterCoin’ whose protocols inspired the programmer. It was this moment he realized that it would be possible to generalize and scale what these protocols were doing by replacing component.
Vitalik envisioned a decentralized platform language that could be capable of solving any mathematical equation programmed (given the time and memory to do so). Following rejection of the presentation of his idea by colleagues and the Bitcoin team, he set out to create it himself.
The whitepaper for Ethereum was released shortly after Vitalik returning from Israel, which attracted a lot of investors and a high-quality team behind Buterin. The Ethereum Network later went live in July 2015.
According to CoinTelegraph, “Vitalik is motivated by his conviction that the powerful people have way too much power in their hands.”
What Can Ethereum Do?
Ethereum explores some of the perceived limitations for developers on the Bitcoin network.
Gavin Wood proposed the programming language Solidity in 2014, which was later developed by the Ethereum project’s Solidity team, led by Christian Reitwiessner.

The Ethereum network is a landscape for developers to build decentralized apps on the blockchain. The network is designed for applications to interact with each other, and build and combine new projects, like Lego.
Ethereum introduced smart contracts, working like programmable money and forming the backbone of decentralized finance, arguably the largest catalyst for the coming bull run.
Smart contracts are pieces of code, that move a specified amount of money, upon certain stated requirements being met. As smart contracts are programmed on the blockchain, they are also immutable.
Deploying a smart contract has been referred to as like setting off a rocket – it’s impossible to undo. There are countless different use cases for smart contracts, including betting, house exchanges, and confirmation of deliveries in supply chains.
The internet revolutionized a lot of different sectors – Amazon changed retail, Uber changed transport, Airbnb changed hotels; decentralized finance is transforming the legacy financial system to open up fairer opportunities to everyone, allowing people to be in complete control of their assets. The Ethereum network could challenge the traditional financial sector with tools such as synthetic assets, lending, borrowing, and mortgages on the blockchain.
Alongside smart contracts and application development, Ethereum is the main blockchain supporting NFTs – non-fungible tokens – that can be used for gaming, licenses, certifications, and is the foundation of the much-loved CryptoKitties.
Ethereum 2.0
On August 4th, 2020 the Ethereum 2.0 testnet was released to developers, who can navigate their way through the update to report any bugs and iron out any kinks. The testnet is named “Medalla” after the Buenos Aires metro stop.

The key difference between Ethereum and Ethereum 2.0 is the consensus algorithm switching from proof of work (PoW) to proof of stake (PoS).
In simple terms, proof of work is a consensus algorithm used by Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies which requires mining nodes to use tremendous amounts of computational power to solve mathematical equations in a process known as hashing. Bitcoin for example uses the SHA-256 algorithm.
SHA-256 stands for Secure Hashing Algorithm and generates a 256 bit (64 characters long) random sequence of letters and numbers (hash) out of any input.
Proof of stake however, requires far less energy and requires node validators to lock up a stake of their tokens in the network and bet on the next block to be appended to the blockchain.
Instead of receiving coins for solving complex equations, nodes receive rewards proportional to their bet.
The heavily anticipated phase 0 of Ethereum 2.0, known as Serenity, was expected to be launched later this year. However, the start of the multi-year transition could begin in 2021.
The change from PoW to PoS creates much more opportunity for growth and scaling, with Ethereum announcing sharding to be a part of the update to help with the current high gas fees on the network due to congestion.
Sharding is splitting the entire Ethereum network into multiple portions called ‘shards’, with each shard containing its own independent state, similar to cities in a country.
Through partitioning large chains (databases) into smaller, faster ones, transactions can be processed in a much faster and more efficient way, preparing for global mass adoption and further large enterprise partnerships. Current partnerships include Amazon, Microsoft, JP Morgan, and Coca-Cola.
Why We Need Bitcoin and Ethereum
Despite the tribalism between the two cryptocurrencies, both can exist in harmony as they serve very different functions. Bitcoin is the most secure payment network and could soon be the world’s most scarce asset. Ethereum on the other hand is a framework for programmable money and is helping to propel the technology towards mass adoption.

Bitcoin vs Ethereum is like apples and oranges. In many ways, Bitcoin would be less likely to achieve mass adoption without Ethereum. Bitcoin is, and probably always will be the number one cryptocurrency, but much of the innovation in the space recently has been thanks to Ethereum and its vast community of developers.
While Ethereum might not be the same store of wealth as Bitcoin, Ethereum is helping to bridge traditional finance with blockchain technology by constantly pushing towards cryptocurrency adoption.
Bitcoin paved the way for this exciting new technology, but Ethereum took the potential of blockchain technology and turned it into more than what Bitcoin could offer.
That being said, however, there will likely never be a serious competitor to Bitcoin, as it is the largest and most secure blockchain, and there are several potential competitors to Ethereum which stand a chance of gaining a substantial portion of the market.
If you find this subject interesting, be sure to check out the many different blockchain, Bitcoin and Ethereum courses available on Ivan on Tech Academy. Start your blockchain education today!





