Rebranded from “Matic Network” in February 2021, the Polygon chain is a layer-2 network designed to bring mass scalability to Ethereum and interoperability between other blockchains. Retaining the MATIC cryptocurrency ticker, Polygon is evolving into a platform to help developers bring products to market quickly. This is achieved using customizable, modular blockchain network tools and services that harness the power of the Ethereum network, without the drawbacks associated with high transaction fees and network congestion. As such, layer-2 solutions are drawing a lot of attention as the crypto industry looks to expand and interoperate.
Described as “Ethereum’s internet of blockchains”, Polygon has become a compelling alternative for several new up-and-coming projects as the completion of Ethereum 2.0 still lurks somewhere in the distance. This is largely due to the high throughput and low gas fees experienced by users and developers, afforded by Polygon.
In this article, we’re going to explore the Polygon ecosystem architecture and the transition from Matic Network. Also, we’ll look at layer-2 solutions, why we need them, and how they function. Furthermore, we’ll discuss some of the recent partnerships, explore the MATIC token, and its role within the Polygon ecosystem.
Polygon has been made possible thanks to the revolutionary technology introduced via Bitcoin, called blockchain. To understand how blockchain technology works on a foundational level, take a look at the Blockchain & Bitcoin 101 course at Ivan on Tech Academy. Here you’ll gain an insight into the foundational operations of blockchain, and why Bitcoin is here to stay. Moreover, Ivan on Tech Academy is packed full of further exciting courses to educate people in cutting-edge technologies. Try our Ethereum 101 course to learn about the second-largest cryptocurrency and the backbone of decentralized finance (DeFi).

Matic Network Background
Matic Network was created as a layer-2 scaling solution to address the network congestion on the Ethereum blockchain. With the use of Plasma side chains, Matic Network developed an environment that made it easy, cheap, and fast to get decentralized applications (dApps) to market. This was expedited due to high gas fees on Ethereum and an increase in the development of decentralized applications (dApps).
Plasma
Plasma was designed to facilitate off-chain transactions in a fast and cost-effective manner for blockchains. This can be achieved with the use of a “requisite fraud proof verification mechanism” along with Ethereum sidechain state snapshots. Essentially, Matic Network implemented an adapted decentralized iteration of the Plasma platform. It allows Ethereum to scale using Proof-of-Stake (PoS) side chains with low-cost, near-instant transaction settlement and finality.

Matic SDK
The Matic Network SDK (software development kit) makes it easy for developers to create and scale decentralized applications (dApps) on Ethereum quickly and efficiently. This was largely responsible for the immense adoption of the platform, as it created an environment that made it easy for crypto projects to get their products to market.
What is Polygon Network?
Polygon Network is a new name with established foundations and a strong community backing. The Polygon team was among the first to approach innovative off-chain solutions for scaling the Ethereum blockchain. As the popularity and traffic on Ethereum have grown, developers are seeking enterprising avenues for reducing cost and finding a lower barrier to entry, whilst maintaining the security of the Ethereum Network.
Polygon Network’s Challenge
Ethereum is the go-to choice for many blockchain developers. That being said, Etherum has some drawbacks which are still to be addressed in the rollout of Ethereum 2.0. Low throughput, high gas fees, and network congestion create limitations for developers that can hinder progress.
Ethereum has effectively become a victim of its own success. Several smart contract-compatible blockchains have since emerged to circumnavigate these issues while still utilizing the power of the Ethereum ecosystem. However, there is an element of fragmentation across the blockchain landscape as there is no protocol or single framework available to connect these blockchains and little infrastructure to bridge them together in a consistent, reliable manner.
Polygon Network’s Solution
Thankfully, Polygon has developed a layer-2 network for building Ethereum-compatible, interoperable blockchain networks. Polygon’s modular framework for building custom networks allows builders to deploy preset blockchain networks with a single click. Furthermore, Polygon makes it easy for any blockchain to interact with another blockchain, without friction.
Polygon was built for developers, by developers, with scalability in mind. The platform boasts scalable consensus algorithms, bespoke Wasm execution environments, and modular “security as a service” features with industry-standard Ethereum compatibility and functionality. This means that Polygon networks can harness the established technology, standards, languages, and tools to create customizable enterprise-ready blockchain networks.

With dedicated throughput, independent governance, and a versatile, customizable tech stack, Polygon enhances the user experience by facilitating cost-efficient, near-instant transactions with deterministic transaction finality. Furthermore, this can be transposed across a plethora of blockchain networks with native support for tokens and contract calls to bridge between other networks. Moreover, Polygon enables developers with zero protocol knowledge to create highly customizable and upgradeable networks with short time-to-market that promote interoperability and cross-network collaboration.
What are Layer-2 Solutions?
When it comes to blockchain scaling solutions there are many different options. However, they can generally be categorized into two levels: layer-1 solutions, and layer-2 solutions.
Layer-1 solutions refer to scaling opportunities that facilitate scaling functions within the blockchain itself. Examples of this would be increasing block limits, novel consensus algorithms, and to an extent, sharding.
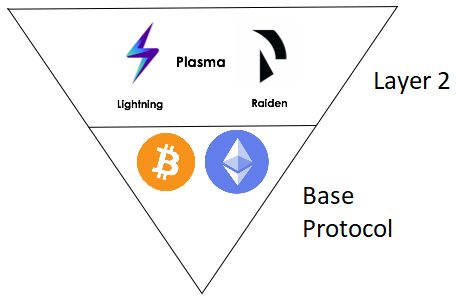
On the other hand, layer-2 scaling solutions refer to off-chain solutions. This involves reducing or removing elements of computational power from the main blockchain, before being executed elsewhere such as on side-chains. This increases throughput on the mainchain alongside the efficiency of computing power across the network. Layer-2 solutions such as Polygon are seeing increased popularity, and are critical to the mass adoption of cryptocurrency.
If you want to buy Polygon (MATIC) safely and securely, but are unsure where to start, check out the Crypto Basics course at Ivan on Tech Academy. Then, if you want to interact with decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms such as those created on Polygon, you would ideally need to understand how to use a web3 wallet such as MetaMask. The Defi 101 course at Ivan on Tech Academy is the perfect place to learn how to navigate some of the most popular DeFi platforms and decentralized wallets.
If you want to dive deeper into the world of DeFi and learn about crypto arbitrage, yield farming, and DeFi hedge funds, be sure to check out the DeFi 201 course at Ivan on Tech Academy, the number one blockchain education suite online!
Polygon Architecture
The Polygon architecture is made up of four distinguished abstract, composable layers. Each layer is responsible for a range of services and functions and can be used for several purposes.
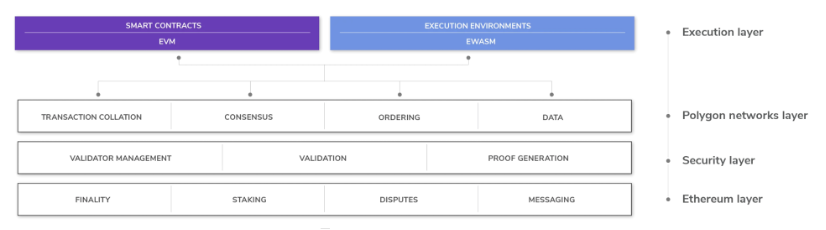
Ethereum Layer
First of all, Polygon chains can opt to use the Ethereum layer. As Ethereum is the most robust programmable blockchain in existence, it’s ideal for the hosting and execution of mission-critical logic. The Ethereum layer operates as a series of smart contracts that are responsible for several functions. These include dispute resolution, checkpointing, message relaying, and staking.
Security Layer
The security layer is a “specialized, non-mandatory layer managing a set of validators that can periodically check the validity of any Polygon chain for a fee”. Furthermore, the security layer serves as a meta-blockchain that operates in parallel to the Ethereum blockchain. This layer takes care of functions such as management of validators, registrations, Polygon chain validation, and rewards.
Moreover, the security layer can exist in several instances and be implemented by multiple entities and organizations. Each security layer can hold its own individual characteristics and can be validated by Ethereum miners and implemented on the Ethereum blockchain.
Polygon Networks Layer
The networks layer is a series of independent blockchain networks that operates to serve its own user base and community. This layer is responsible for block production, local consensus, and collating transactions. Using the Polygon protocol, each network can connect with one another to facilitate the exchange of arbitrary messages.
Execution Layer
When transactions are agreed upon by any of the blockchains within the Polygon network, the execution layer is used for interpreting and executing these transactions. The execution layer is made up of two sublayers; an execution environment that provides plug-and-play virtual machine implementation, and execution logic for each of Polygon’s networks, which is usually written as Ethereum smart contracts.
Polygon Chains
There are two main types of Ethereum compatible blockchain networks supported by Polygon. These are “stand-alone” networks, and networks that use the “security as a service” feature.
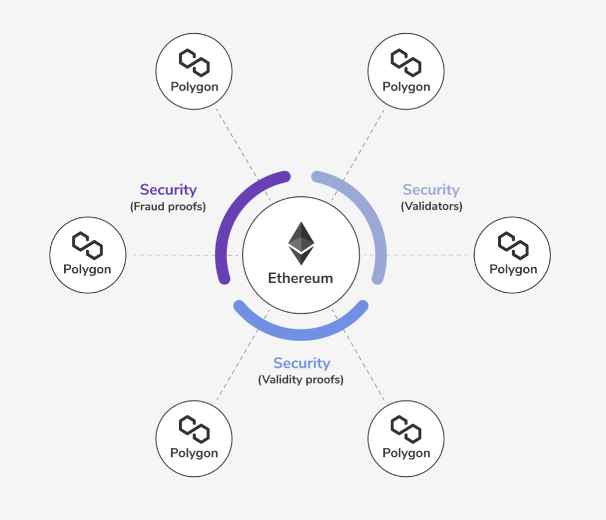
Secured Chains
Rather than creating their own native validator pool, secured chains utilize “security as a service” for their blockchain network validations. This can be achieved via Ethereum using fraud or validity proofs. Alternatively, a reputable validator pool can be used much like the Polkadot “shared security” feature. Although these chains offer higher levels of security, the compromise is reduced autonomy and flexibility.
Matic Plasma is already live on Polygon. In the future, we can also look forward to the implementation of Optimistic Rollups, Validum Chains, and zk Rollups!
Stand-Alone Chains
These Ethereum-compatible chains are fully autonomous blockchain networks. Stand-alone chains are responsible for their own security and validators. Though establishing a validator pool can be challenging, stand-alone chains offer the greatest levels of flexibility and independence. The Matic Proof-of-stake (PoS) chains are up and running, and we can expect to see sidechains, and enterprise chains implemented soon!
Polygon Token (MATIC)
The ERC-20 Polygon token (MATIC) is the base asset of the Polygon ecosystem. Not only is it used for transaction fees, but it is also used for staking to secure the Polygon network. Since the rebrand, the Polygon (MATIC) token has seen incredible price action in line with a huge increase in usage.
The MATIC token has a capped supply of 10 billion tokens, with a current circulating supply of around 5 billion. The Polygon (MATIC) token is available on most popular centralized and decentralized exchanges (DEXs). These include 1inch Exchange, Coinbase Pro, and Binance. Available with both crypto and fiat token pairs, the crypto community is working together to make it simple and easy to buy Polygon (MATIC).

According to CoinGecko, at the time of writing, Polygon (MATIC) has a total market cap value of $1.8 billion, with the MATIC token price sitting at around $0.36.
Polygon Advisors and Partnerships
Polygon has the support of some of the greatest minds in the Ethereum community. These include Ryan Sean Adams of Bankless, Anthony Sassano of EthHub, and The Ethereum Foundation’s Hudson Jameson.
Some projects that had initially intended to launch on Ethereum have since opted to launch on Matic Network/Polygon instead. This is partly due to the extended roll-out of Ethereum 2.0, but also due to the robust platform and community that Matic Network managed to build. Since rebranding to Polygon, several other projects have also jumped on board.
Polygon boasts a wide range of partnerships with crypto projects across every area of the industry. These include SuperFarm, Polymarket, Aavegotchi, Decentral Games, SportX, Easyfi, and Neon District.

Polygon Network and MATIC Token Summary
Before mainstream adoption of cryptocurrency can be truly realized, it must be frictionless and accessible. Furthermore, both developers and users must have access to sleek, simple decentralized apps (dApps) if they are to become widely adopted.
Polygon aims to remedy this by tackling the issues of slow confirmation times and high gas fees. Furthermore, Polygon is at the forefront of interoperability, bringing together several thriving communities for the good of the entire industry.
If creating decentralized applications sounds exciting, but you have no programming experience, Ivan on Tech Academy can provide all the knowledge you need! For those with zero programming background, we’d recommend our Javascript Programming for Blockchain course first. This is the best place to get started before learning the Solidity programming language through the Ethereum Smart Contract Programming 101 course.
From here, your possibilities are endless! You will be equipped with highly sought-after skills, and the opportunity to incorporate these skills in a broad array of crypto career opportunities!
Also, if you haven’t already, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter @Academy_IOT! Here, you can keep up to date with all the latest crypto news and updates! Say hello and let us know which projects you’re watching at the moment!