
Hedera Hashgraph was built to provide decentralized governance at scale using the hashgraph consensus mechanism. By harnessing the power and utility of byzantine fault tolerance consensus with the innovative gossip about gossip protocol, Hedera Hashgraph is separating governance from consensus using patented technology. This is thanks to the Hedera Governing Council members, a team of leading companies including the likes of Google, IBM, and Deutsche Bank. Distributed ledger technology (DLT) has become an essential part of many industries. With the use of advanced cryptography, it is now possible for businesses and individuals to safely store data and transact using a trustless, immutable public ledger. However, the hashgraph consensus mechanism has some key distinctions from blockchain consensus. For those who are wondering “what is Hedera Hashgraph?” and “what is the HBAR token?” - let’s find out!
In this article, we’re going to explore the Hedera Hashgraph ecosystem. We’ll discuss the hashgraph consensus mechanism, the HBAR token, and the differences between hashgraph and blockchain technology. Furthermore, we’ll look at some of the exciting use cases for this innovative form of distributed ledger technology (DLT)!
Make sure to see our Distributed Ledger Technology Deep Dive article to understand how this technology operates on a technical level. Moreover, you’ll discover the differences and similarities between blockchain technology and DLT. For a more in-depth learning experience about how blockchain works, see our Blockchain & Bitcoin 101 course at Ivan on Tech Academy! You’ll learn about the process of Proof-of-Work (PoW) mining, the UTXO model, and the value propositions of Bitcoin. Ivan on Tech Academy offers a variety of interactive mediums to suit all learning styles through video-guided tutorials, led by industry experts. Why not try the Academy today with a 14-day money-back guarantee?
What is Hedera Hashgraph?
Hedera Hashgraph is a unique enterprise-grade public ledger that uses hashgraph consensus as an alternative to blockchain consensus mechanisms. Furthermore, Hedera Hashgraph holds the sole patent for the hashgraph technology. The Hedera Hashgraph public ledger is a distributed database. Similar to blockchain networks, Hedera Hashgraph nodes each hold a copy of the ledger, which anyone can write to or read from. However, the Hedera Hashgraph public ledger has some key differences in how it reaches consensus across the network.

Designed to address concerns about decentralization, the Hedera network separates governance from consensus to provide a compelling substitute for blockchain consensus. The Hedera governance model is based on the initial model used by National BankAmericard Inc., which later became VISA. The model aims to ensure that the governance structure serves to benefit the network and that no individual member can act in their own interest.
The blockchain landscape is continuously evolving. First, Bitcoin introduced the decentralized infrastructure that would pave the way for Ethereum and other programmable smart contract-enabled blockchains. Now, distributed ledger technology (DLT) has entered its third generation. The Hedera public Proof-of-Stake (PoS) network utilizes hashgraph consensus to achieve the highest possible security using asynchronous Byzantine fault tolerance (ABFT). Not only does this make the Hedera Hashgraph network incredibly robust, but it also allows for super-fast transaction settlement with low fees. Furthermore, transactions on the Hedera network require very little bandwidth compared to many other blockchain-based transactions.
Hashgraph Consensus - Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Hedera is a unique public ledger. It is the only one of its kind to use hashgraph consensus instead of blockchain consensus mechanisms. The hashgraph consensus mechanism verifies transactions fast, with the highest levels of efficiency and security. Furthermore, the Hedera Hashgraph consensus facilitates near-instant finality and ultra-high throughput with low latency, allowing over 10,000 transactions per second (TPS) using the novel “gossip about gossip protocol”, along with virtual voting.
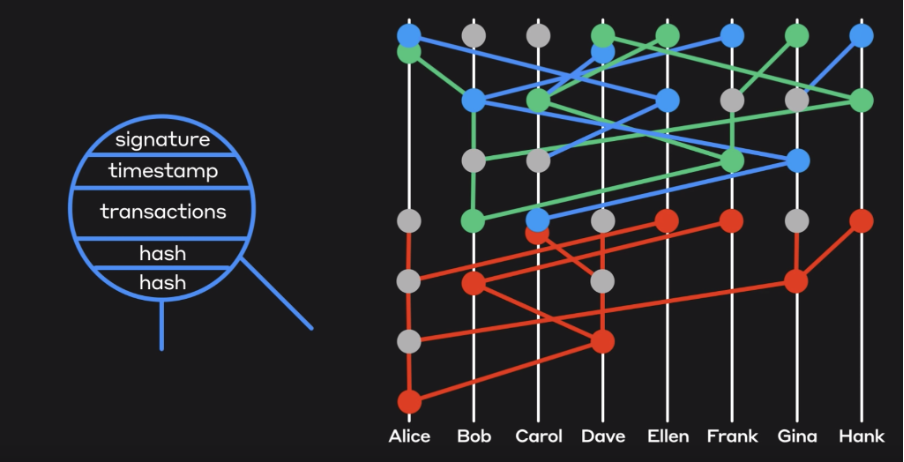
Gossip About Gossip Protocol
A Gossip protocol is a computational procedure or process for peer-to-peer communication based on how epidemics spread. One of the most common use cases for a gossip protocol is in distributed systems to make sure that data is communicated effectively and evenly throughout a group. As with blockchain protocols, when consensus is reached across the Hedera network, all transactions are immutable and transparent. Plus, all transactions are viewable on the public ledger. The gossip about gossip protocol provides a history of the relationship between the information that is broadcast across a network, and how the network reaches consensus. This is achieved using parent hashes that create a directed acyclic graph (DAG) known as a hashgraph.
The Hedera Hashgraph public ledger resides on the mainnet. This is a network made up of nodes. At present, the ledger is permissioned and operated by the Hedera Governing Council. However, in the future, anyone will be able to run a consensus node as the ledger becomes permissionless. Consensus nodes validate and order transactions and store the latest state of the ledger on the network. Also, “mirror nodes” provide a cost-efficient way to query historical data and can be run by anyone.
How does Hashgraph Consensus Work?
Like blockchain, hashgraph is a type of distributed ledger technology (DLT). Hashgraph technology uses directed acyclic graphs to form an asynchronous Byzantine Fault-Tolerant consensus algorithm. Hashgraph technology is patented. However, Hedera Hashgraph is the solely authorized ledger to utilize it.
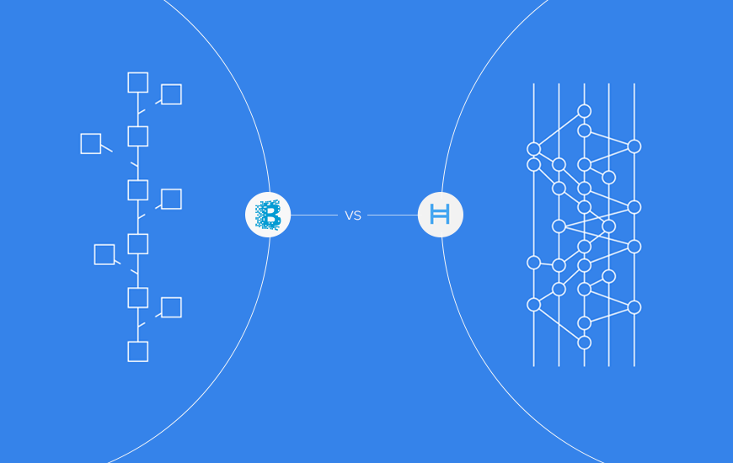
The hashgraph consensus mechanism takes an innovative approach to DLT, working as a system that generates trust. According to Hedera Hashgraph, “a blockchain is like a tree that is continuously pruned as it grows – this pruning is necessary to keep the branches of blocks from growing out of control and to ensure the ledger consists of just one chain of blocks. In hashgraph, rather than pruning new growth, such growth is woven back into the body of the ledger.”
Transactions on blockchains form a continuous string of blocks or containers of transactions. When two blocks are created simultaneously on the same blockchain, the network must decide which chain to pursue, and which to discard. If the network cannot agree on which chain to pursue, the blockchain may have to fork into two separate chains. With hashgraph consensus, each container is retained within the ledger. This means that no transactions are discarded and each “branch” of the ledger can continue to exist. Moreover, because no transactions are dropped, hashgraph is more efficient than blockchain consensus.
Also, blockchains require consensus mechanisms such as Proof-of-Work (PoW) to slow down the network. This is so that new blocks or containers cannot be created before old ones are discarded. However, the hashgraph data structure remains fully intact. It does not need to be slowed down to maintain optimum security, and any member of the network can create containers and transactions at any time.
Why use Hashgraph Consensus?
As all containers of transactions are incorporated into the hashgraph ledger, hashgraph enables complex and powerful mathematical guarantees. This is thanks to Byzantine agreement and fairness. Moreover, unlike many distributed databases, the hashgraph algorithm is byzantine, fast, cost-efficient, ACID compliant, timestamped, and resistant to denial of service (DoS) attacks.
If you want to learn more about cryptography, check out the Cryptography & Privacy Coins course at Ivan on Tech Academy. With a wide range of courses covering every area of the crypto space, Ivan on Tech Academy is the number one online blockchain education suite. Join over 30,000 students today to find your perfect career in crypto!
Our Academy offers students many different programming courses to get started in the blockchain industry, including the Ethereum Smart Contract Programming 101, Bitcoin Programming 101, EOS Programming 101, and Enjin Blockchain Game Development 101 courses! Also, for non-programmers, our Bitcoin Money Revolution and DeFi 101 courses are perfect for an introduction to decentralized finance (DeFi).
Hedera Network Service
Hedera network services consist of a set of application programming interfaces (APIs). These enable users to create accounts, tokens, write to the ledger, and more. Every API call requires a small transaction fee which is determined by the processing power and storage space required. Furthermore, using Hedera software development kits (SDKs), users can easily access APIs in several programming languages.

The Hedera Token Service (HTS) enables the configuration, token minting, and management of fungible and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) on Hedera without needing to set up and deploy a smart contract. Also, Hedera network services include a Web3 file service and identity management features.
The HBAR Token
The native HBAR token plays two key roles within the Hedera ecosystem. Firstly, the energy-efficient cryptocurrency is used by developers when logging data and managing fungible and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). The HBAR token is also used to pay for transaction fees and compensate nodes for computational power and bandwidth.

Secondly, HBAR is staked by nodes to secure the Proof-of-Stake public network using weighted voting. Weighted voting makes it extremely costly for potential bad actors to attempt to affect consensus, requiring a stake equal to one-third of the total supply of HBAR. Moreover, this will be physically impossible for the first five years following the release of the token in 2019.
HBAR transactions are incredibly fast, at 10,000 transactions per second (TPS). This is achieved using a single shard on a single ledger without compromise to the security or stability of the network. Also, because hashgraph consensus is computationally light, transaction fees are predictably and consistently very low. On average, HBAR transaction fees cost approximately $0.0001. Furthermore, HBAR token transactions are finalized on-ledger in under five seconds. This makes the HBAR token ideal for micropayments and high-frequency transactions. Moreover, this creates an ideal environment for developers and enterprise-grade distributed ledger applications.
Hedera Governing Council
Hedera is governed by some of the world’s biggest companies, including Google, Boeing, IBM, and LG. This sector-wide group of industry leaders forms the Hedera Governing Council. The Hedera Governing Council members include “up to 39 term-limited and highly diversified organizations and enterprises, reflecting up to 11 unique sectors, academia, and non-profits globally”. Members of the Hedera Governing Council are devoted to the codebase and software direction. Also, responsibilities include maintaining stability and decentralization throughout the Hedera public network.

In the future, it is expected that there will be thousands of nodes supporting the Hedera network and maintaining decentralization. The initial network of nodes will be overseen by the Hedera Governing Council members as the project undergoes testing and continues to scale. Hedera Governing Council members receive a three-year maximum term, and up to two consecutive terms. Furthermore, all members receive an equally weighted vote on network proposals and decisions. Swirlds, the distributed application platform, and creator of the hashgraph consensus mechanism retains a permanent seat. Following the initial selection of members, Swirlds will be replaced with new members by the Hedera Governing Council’s Membership Committee.
To find out how some of the world’s biggest companies are incorporating blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) into their existing systems, be sure to check out the Blockchain for Enterprise course at Ivan on Tech Academy. This course shows you how DLT can revolutionize almost every industry - from the energy sector to fashion, music, and real estate! Following this, why not see how blockchain-based solutions are optimizing global supply chain management with our Origin Trail 101 course? Regardless of experience or background, Ivan on Tech Academy can help you achieve your goals in crypto and blockchain!
What is Hedera Hashgraph? Summary
By reducing computational strain and bandwidth requirements, Hedera Hashgraph is creating a highly scalable, enterprise-grade public ledger that can be used for a variety of applications. Furthermore, as an alternative to blockchain consensus, the hashgraph consensus mechanism is pushing the boundaries of distributed ledger technology (DLT).

The Hedera Governing Council members are establishing a robust, fully decentralized, and energy-efficient public ledger. Plus, the Hedera network enables super-fast, low-cost transactions with the highest levels of security. In the future, we can expect to see an extension of the network as more nodes are introduced. If the Hedera Hashgraph project is successful, it could help pave the way for a new wave of hashgraph-based distributed ledger models.
To discover more about enterprise integration of blockchain technology see our Blockchain Business Masterclass! Ivan on Tech Academy teaches students everything they need to organize and manage a successful blockchain-based project. Also, our FinTech 101 course provides a detailed breakdown of compliance and regulations within the finance and tech industries. Why not start today? Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter @Academy_IOT! We’d love to hear your thoughts on Hedera Hashgraph and the HBAR token!





