
For many years, crypto taxes have remained a relatively obscure subject to many. During blockchain technology and crypto’s infancy, cryptocurrency adoption was still relatively low. As such, regulatory scrutiny was almost non-existent. As the popularity and adoption of cryptocurrency increased, so too did governments’ interests in taxing this burgeoning asset class. With Bitcoin’s 2020 bull run still fresh in mind, it should come as no surprise that interest in US crypto taxes has increased in recent months. This has prompted concern among crypto investors, as many have little education around the subject. If you are unable to know your potential tax obligations, you could end up facing severe punishments, resulting in a loss of your crypto earnings. Therefore, learning how to calculate US crypto taxes and understanding Form 8949 has never been more important.
In this article, we’re going to dive into US crypto taxes, and what they mean for you as an investor. Even if you’re not based in the United States, crypto taxes have never been more important – and looking at how the US deals with crypto taxes might give you some ideas for what you need to look out for in your own country. Also, we’re going to share some tips to help you avoid getting rekt by crypto taxes. Plus, we’ll show you the best ways to learn how to calculate crypto taxes, and even some information that could help you to fill out the important Form 8949.
As you’ll likely already know, Ivan on Tech Academy is one of the most popular blockchain education platforms. If you’re new to cryptocurrency, check out the Crypto Basics and Blockchain & Bitcoin 101 courses at Ivan on Tech Academy!
Figuring Out Crypto Taxes
Before getting into the crypto tax weeds, however, it’s time for a little disclaimer. This article is not to be considered professional tax advice – rather, this article is for educational purposes and solely aims to help you understand the complexities involved in crypto taxes to make the most informed decisions possible.

Despite what you may have heard, American citizens are required by US law to pay taxes on gains made from cryptocurrency investments. Many millions of dollars have been lost due to a lack of education around crypto taxes.
Figuring out crypto taxes without any advice can end up being a stressful, time-consuming mess. There are several key factors to consider when learning how to calculate crypto taxes. Some of these include the following: How long do you plan on holding your assets? What is your personal tax bracket and how does this affect your realized gains?
These are all important questions. However, to begin to understand US crypto taxes, let’s first look at some of the basic guidelines and rules that crypto investors should consider.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has several means to determine unreported earnings. The 1099 reporting system is used by many popular cryptocurrency exchanges, including Coinbase, Gemini, and Kraken to report any income to the IRS that is not related to a user’s employment.

At the end of each year, both you and the IRS receive a copy of the 1099 forms. Any unreported income declared by crypto exchanges is immediately flagged. From here, you will receive an automated CP2000 letter to alert you of any unreported tax liabilities.
Furthermore, the IRS receives information from blockchain analytics firms to track on-chain movements of funds. This is used to detect nefarious activities such as money laundering and tax fraud.
The IRS has expedited tax compliance measures in recent years, as the discussion around cryptocurrency regulation becomes increasingly pertinent. According to the IRS, by not reporting your crypto gains, you’re committing tax fraud. As such, this can result in fines and even a prison sentence.
US Crypto Taxes Basics
For tax purposes in the US, cryptocurrency is treated as if it is property. As with property such as real estate, crypto investors incur capital gains and capital losses on investments whenever they sell, trade, or give away their crypto. An example of this would be if you purchased 1 BTC at $20,000, and sold it later for $25,000. In this example, you would incur a capital gain of $5,000.

Tax rates vary depending on an individual’s personal tax bracket. Also, tax brackets vary depending on if the gains made are long-term or short-term gains. All crypto received as an income are liable for income taxes. This includes income earned through mining, a salary, interest payments, and airdrops. Income tax must be paid on the dollar value of these earnings.
When Do We Pay Crypto Taxes?
Any time a crypto investor is subject to a taxable event, this must be reported. A taxable event is any situation whereby an investor generates and realizes income that results in a tax liability. Taxable events include:
- Crypto-Fiat trades
- Crypto-Crypto trades
- Purchasing goods or services with crypto
- Income earned in crypto (including mining)
However, simply buying and holding crypto in your wallet is not a taxable event. Also, transferring crypto from one wallet to another wallet that you own is not subject to taxation. It is only when crypto-assets are sold, traded, or otherwise disposed of that a taxable event occurs and capital gains and losses are realized.
Form 8949
Capital gains and losses made from crypto trades are reported to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) using Form 8949. Form 8949 is generally used to report the selling and disposal of capital assets, such as stocks, bonds, and cryptocurrency.
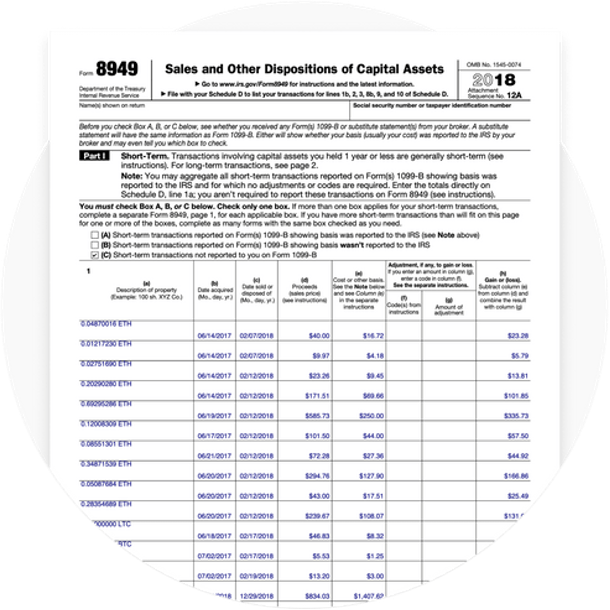
When filling out Form 8949, you must list every cryptocurrency trade, sale, and disposal. Also, you must include information regarding the date that you purchased the asset, the date it was sold, and any gains/losses made. Furthermore, you must also provide the fair market value and the cost basis of your investments (explained below).
Once Form 8949 is completed, you must then calculate your total net profit/loss for the year and declare it to the IRS.
Calculating Crypto Taxes
The following formula can be used to calculate capital gains and losses:
Fair Market Value – Cost Basis = Capital Gain/Loss
- Fair market value is the open-market selling price of an asset denominated in USD.
- Cost basis is the amount of money required to purchase your property (crypto). This takes into account the purchase price of any assets and any fees incurred.
- By subtracting the cost basis from the fair market value, we can ascertain the capital gain/loss.
Capital Gains
Though this may seem relatively simple, when accounting for multiple transactions, things can get complicated. To avoid getting rekt by crypto taxes, traders must keep records of all trades and swaps made. This should also include information regarding cost basis, fair market value, and gains/losses. This can be extremely difficult for high-frequency traders with multiple wallets and exchange accounts. If you are unable to account for this information, you will not be able to accurately report your crypto taxes. Unfortunately for many, this can mean large unexpected losses, which can result in tremendous stress.
If you have earned crypto from mining, staking rewards, or from your job, this is reported as ordinary income. However, if you simply buy, hold, and sell crypto, any income made is reported as capital gains income.
The length of time you hold your crypto assets, and your income tax bracket determines the amount of tax you pay on any crypto income. Naturally, this varies between different types of crypto investors and investment strategies.

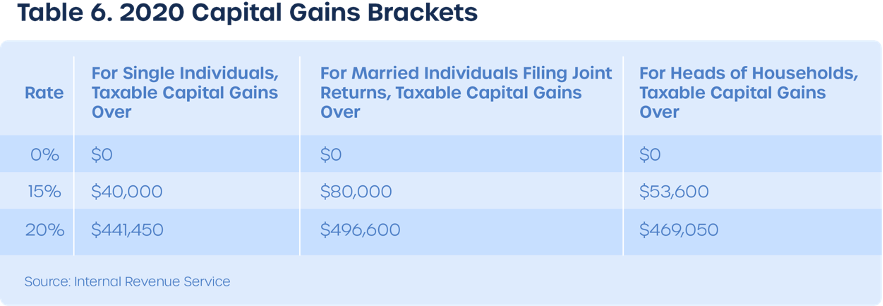
Short Term Capital Gains – Applies to any crypto asset held for less than 12 months. Tax is treated just like income tax earned from your regular job.
Long Term Capital Gains – Applicable to crypto assets held for 12 months or more. Long-term investors are incentivized by the government to hold assets for extended periods. This means that holding crypto over long periods can create tax advantages over short term gains. This is particularly useful for high-net-worth individuals and institutions.
DeFi
The advent of decentralized finance (DeFi) brought several exciting and innovative decentralized applications (dApps) into the crypto space. Interest earned from liquidity provision and lending protocols such as popular DeFi platforms Aave, Compound, and Uniswap is also subject to tax reporting.

This can be tricky, particularly when it comes to yield farming. With so many variables across multiple platforms, keeping track of your taxable earnings can become incredibly complex.
Decentralized finance (DeFi) has been a major catalyst in the developments of US crypto regulations. DeFi is changing the financial landscape in a way that will help shape the future of tax laws across the globe. If you’re new to DeFi and want to learn more, be sure to check out the DeFi 101 and DeFi 201 courses at Ivan on Tech Academy!
Trading
Cryptocurrency exchanges such as Coinbase and Binance are unable to keep track of capital gains and losses for their customers. As these exchanges have no way of determining the original price you paid for your crypto (cost basis), it is impossible to know each individual customer’s tax obligations. Furthermore, when assets are removed from exchanges, the exchange is no longer able to establish an accurate cost basis or fair market value for your crypto assets.
As this is mandatory for tax reporting, you cannot rely on your transaction history alone to calculate your crypto taxes. For high-frequency traders, this could be an absolute nightmare if left unchecked.

How To Reduce Crypto Taxes
To preserve wealth, there are several ways cryptocurrency investors can reduce tax obligations. One example of this is tax-loss harvesting. This process involves selling your crypto assets at a loss. By doing this, you can offset tax liabilities related to capital gains. This is often one of the most efficient ways to reduce any crypto gains-related tax burden.
Also, long term capital gains offer substantially lower tax rates than short term gains. If you can hold your crypto assets for longer than a year, this could reduce your overall tax burden. Furthermore, generous crypto holders can give a tax-free crypto gift of up to $15,000 to friends and family – although the recipient will eventually have to pay tax when realizing his or her capital gains. However, to truly minimize crypto taxes, it’s key to understand the nuances of the US crypto tax system. The subject should not be taken lightly. Whether you’re a whale or a newcomer to the crypto space, understanding US crypto taxes should be a serious consideration.
Is There A US Crypto Taxes Course?
By learning how to calculate crypto taxes, you can ensure that you don’t break the law. Also, you can protect your earnings by implementing strategies to minimize your tax burden. Luckily, however, Ivan on Tech Academy will soon launch its very own US crypto tax course. This course will be free to current Ivan on Tech Academy subscribers, or it is available as a stand-alone purchase. As such, there’s never been a better time to enroll in the Academy before the course releases on February 8th!

The Ivan on Tech Academy US Crypto Tax course aims to teach you exactly how to calculate US crypto taxes and identify the necessary forms for reporting different types of crypto taxes. Learn how to establish assets that qualify for long-term capital gains, helping you to save money in the long run and make informed decisions when trading. The course combines three core elements:
- Fundamentals of US Federal Taxation
- Reporting Forms To Know About
- Reading Transactions & Reporting
This course helps you to understand how to report your crypto transactions, how different DeFi earnings are handled, and how crypto taxes work when people lose money to scams. The Ivan on Tech US Crypto Taxes course aims to take you through each process step by step, breaking down the complexities of crypto taxes.
US Crypto Taxes Summary
With increasing regulatory scrutiny across the crypto space, you must take care of your crypto investments. In the future, we can expect to see higher levels of auditing and an increase in criminal prosecutions related to crypto taxes. By learning how to calculate crypto taxes, you can protect your wealth and ensure that your tax burden doesn’t exceed your realized gains.
As enterprise adoption and institutional investment in cryptocurrency continue to accelerate, cryptocurrency regulations are likely to become tighter. Regardless of whether you think increased regulation is a good thing or a bad thing, it’s happening. Instead of putting it off, why not take action now? With a strong crypto tax strategy in place, it doesn’t need to be daunting to file taxes or fill out Form 8949. Enroll in Ivan on Tech Academy to get access to the US crypto taxes course when it launches!





