
The growth of Ethereum over recent years has propelled blockchain technology beyond what many thought was possible. As the crypto community eagerly awaits the seemingly ever-delayed Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, many are wondering, could Layer-2 solutions provide the sustainable growth and scaling of the network that is needed?
Successful implementation of Ethereum’s Layer-2 solutions can be said to be important both for the security and overall success of the network, but also the mass adoption of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology. Specifically, scaling solutions are imperative for increased network activity.
Proponents of Ethereum would say that Ethereum is at the forefront of various fields such as payments technology, financial infrastructure, and global enterprise, but with network congestion and gas fees at all-time highs, scaling solutions are highly sought after, as the demand for Ethereum usage far exceeds the capacity of the network.
In this article, we’re going to explore why there is such a huge demand for Ethereum Layer-2 solutions, what the future of cryptocurrency could look like, and we’ll also be taking a look at some of the projects that could help take blockchain scaling to the next level.
Those of you wondering why blockchain scaling is so important for greater blockchain adoption should take a look at all the educational material available on Ivan on Tech Academy. Ivan on Tech Academy is one of the premier blockchain education platforms in the world, and you can enroll right now to learn everything from Ethereum to Technical Analysis.
What is Scalability?
Scalability is all about building a long-term solution for the expansion, adoption, and innovation on the Ethereum network. Scaling involves building a bigger, smarter ecosystem whilst maintaining the security of the network in a way that brings value to everyone without exclusion, and is enjoyable and easy to use. Some of the key areas of Ethereum scalability include:
- Block Size
- Transaction Speed
- Throughput
- Congestion
- Network Fees
- Composability
- Ecosystem Growth
Layer-1
Scaling functions within the Ethereum blockchain itself are commonly known as layer-1 solutions. This includes things such as increased block size and Sharding.
Layer-2
On the second layer, we have off-chain solutions. These take some of the most complex computations outside of the blockchain and execute them using structures built on top of the blockchain, whilst leaving the most crucial and sensitive data on-chain. This can prevent bottlenecks on the blockchain, reduce congestion, and increase throughput. Raiden and Plasma are examples of layer-2 scalability, which we will continue to explore in future articles.
The Ethereum 2.0 Update
The Ethereum 2.0 update can’t come quick enough, and scalability is the number one focus of most Ethereum developers right now. Many projects are now taking matters into their own hands by taking data off-chain to do very quick computations before putting the data back on-chain in a trustless way, immutable manner.

Recent congestion and corresponding gas fees have hit an all-time-high, surging higher than the December 2017 peak. This has been a concern for some, however, Ethereum 2.0 promises to deliver a range of updates to its protocol, with scaling specifically in mind. Here we have listed the main updates you will see to improve the capacity and flow of Ethereum users.
Block Gas Limits
The debate around block gas limits became much of a focal point of discussion within the Ethereum developer community earlier this year. Specifically, this came to a head with Ethereum miners voting to increase the block gas limit for Ethereum from 10,000,000 to 12,500,000 gas, according to a tweet from the parent company of the Ethermine pool, Bitfly.
The unit of measurement for the amount of computational power used to send a transaction, and interact with smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain, is known as gas. Gas is denominated in very small fractions of ETH, known as Gwei. Therefore, the block gas limit is the threshold of gas that can be spent on the transactions within a specific block on the Ethereum blockchain.
The proposal would allow miners to process 44 transactions per second compared to the current 35 per second average. This would theoretically increase the capacity of the network while reducing fees. Though this might be true, if blocks are not created fast enough, it could result in duplicate blocks being produced and could waste miners’ computational power and energy. As only one of these blocks would be appended to the blockchain, it would result in a loss of time and block rewards.
The increased block size also has the potential to overload nodes across the network and leave weaker nodes vulnerable to attack. For this reason, previous gas limit increases have been approached conservatively.
PoW to PoS
One of the major changes for Ethereum’s update is the consensus algorithm, switching from the current Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake. This will help create a foundation more suited to scaling the Ethereum blockchain.
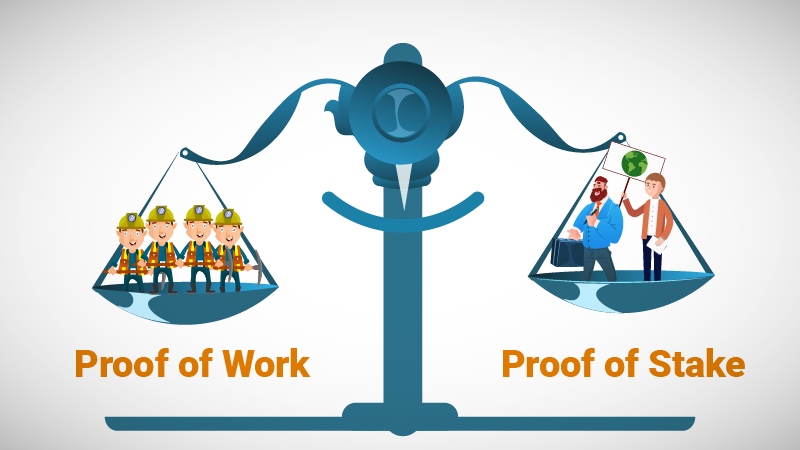
A consensus algorithm is an agreement for all nodes on the network to agree on a transaction becoming valid. The current and most popular consensus algorithm is known as Proof-of-Work.
Proof-of-Work involves using large amounts of computational power from nodes to solve complex mathematical equations, with each node competing to reach the correct answer first.
There are several drawbacks to this algorithm; firstly it requires a large upfront investment cost for the computing equipment required to mine cryptocurrency. Secondly, there is room for manipulation on networks between miners depending on the size of their hash power. A supercomputer with a higher hash rate will be more likely to solve the equation first.
The switch to Proof-of-Stake involves much less hardware and initial upfront costs, with staking nodes or validators required to stake a minimum of 32 ETH. PoS reduces the risk of mining manipulation as the algorithm now randomly chooses a block from the staking pools, with miners placing bets on blocks that are likely to be added to the blockchain.
If a block gets added, the validator receives rewards relative to their bet. PoS is theoretically more secure than PoW by eliminating the risk of 51% attacks. To learn more about the difference between PoW vs PoS, click here!
Sharding
One of the mechanisms used to increase scalability is that of Sharding. Due to the Proof-of-Work consensus algorithm used by the current Ethereum protocol, the introduction of sharding will be in two phases.
Ethereum 2.0 aims to create a total of 1024 shards of the Ethereum blockchain following the initial 64 shards to be created during the launch of Phase 1. Sharding is a form of breaking down large complex amounts of data, into smaller more organized manageable chunks.
Ethereum founder Vitalk Buterin has described the process at Devcon:
“Imagine that Ethereum has been split into thousands of islands. Each island can do its own thing. Each of the islands has its own unique features and everyone belonging on that island i.e. the accounts, can interact with each other AND they can freely indulge in all its features. If they want to contact with other islands, they will have to use some sort of protocol.”
Sharding allows multiple transactions to be verified together at the same time, and aims to speed up the Ethereum transaction speed from <25 transactions per second, to more than 1000x its original throughput.
Enterprise
The Ethereum network is also working hard at integrating layer-2 solutions that serve to benefit businesses, solving some of the key barriers faced by banks and enterprises today.
While some large crypto exchanges such as Kraken move towards becoming a bank, the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade could end up being the backbone of the traditional financial system, providing payments infrastructure to a myriad of businesses and services globally.

Blockchain scaling solutions are paramount if adoption in enterprise is on the cards. Current congestion resulting in longer transfer times and higher fees can be off-putting to an enterprise unsure about the integration of blockchain.
Large corporations are often in communication with vast amounts of other businesses, often requiring a lot of data from multiple servers and sources. Enterprise needs communication efficiency and a pleasant user-experience to gain full traction of blockchain throughout the industry, something this is being worked on by developers across multiple projects.
Below we have listed various projects covering different aspects of scaling solutions both live and operating now, and some that are soon to be launched.
If you want to use blockchain technology in your business or enterprise, you should check out the courses on Ivan on Tech Academy. Join over 20,000 students who have already enrolled in the Academy and find the best blockchain use cases for your enterprise. Right now, you can get 20% off by using the promo code BLOG20!
Blockchain Scaling Solutions
ZK-Rollup
ZK-Rollup was proposed by Barry Whitehat in 2018 and developed alongside Matter Labs and Iden3. As a layer-2 scaling solution, ZK-Rollup allows multiple transactions to be validated by a single on-chain transaction.

Hundreds of transfers are stored using side-chains, which can then be rolled into a single transaction. This reduces the amount of computing and storage required for validating blocks by minimizing the amount of data held within a transaction.
To do this, ZK-Rollup uses zero-knowledge proofs, which is a cryptographic protocol that can validate or confirm the value of a transaction between peers, without any other data of the transaction being visible to those validating it. This is done by validating minuscule fragments of unlinkable information form multiple transactions so that the validity of an assertion is overwhelmingly probable.
Interoperability
Alongside scaling solutions such as transitioning from PoW to PoS and sharding, interoperability is key to growing the blockchain ecosystem. Blockchain interoperability relates to having a seamless exchange process of transactions or data between two or multiple blockchains. If you would like to read a little more in-depth about how interoperability works why blockchain interoperability is needed for mass adoption!
Matic
Beginning as a concept in May 2017, the goal of Matic was to make it easier and cost-efficient to build and deploy decentralized applications securely, with the use of hybrid Proof-of-Stake and Plasma-enabled sidechains.

Matic aims to remedy the issues of high gas fees and slow block confirmations while providing a straightforward and intuitive user experience. Matic aims to simplify decentralized financial applications while making them more accessible and enjoyable. Removing the complexity from DeFi is a priority, and it is essential for mass adoption.
The Matic Network enables scaling on Ethereum using an adapted version of Plasma and proof-of-stake based side-chains. This allows less sensitive data to be processed off-chain, reducing congestion, whilst keeping the most important data on-chain.
Matic is a one-stop-shop for DeFi, bringing a wealth of blockchain scaling solutions and interoperability options to the space. With incredibly high throughput, using side-chain tree architecture, Matic is able to process 6500 transactions per second, making for fast, in-expensive transactions
Moreover, the mainnet is now live, with staking and node validations currently in discussion. Matic looks set to play a key role in the development of Ethereum in the coming months.
Loopring
Loopring is a platform for building non-custodial, high-throughput, order book-based exchanges on the Ethereum network with the use of Zero-Knowledge Proofs.

As Loopring is an open-sourced, extensively audited, and non-custodial exchange protocol, it is completely trust-less. Users have complete ownership and control of their assets.
Loopring facilitates highly scalable decentralized exchanges by processing thousands of requests in batches, off-chain to prevent bottlenecking of blockchains with verifiably correct execution via ZKPs.
Having recently been listed on Coinbase, Loopring is moving towards providing a wallet to intersect directly with layer-two applications. Adoption for layer 2 will likely require Metamask compatibility, however, an integrated wallet into layer-two solutions would make decentralized financial applications simpler and less stressful.
The native Loopring token (LRC) still hasn’t received that much attention. The project has a great team, a working model that the market is crying out for.
xDAI Stake
xDAI stable payments blockchain is a blockchain designed for fast and inexpensive transactions of a stable cryptocurrency, for everyday payments and remittances.

xDAI allows users to pay transactions in just one cryptocurrency token, as opposed to the standard ‘Crypto Token Value’ + ETH for Gas.
The xDAI blockchain is a side-chain of the Ethereum blockchain but currently uses the Proof-of-Stake consensus, with the xDai token being used for transactions, payments, and fees. STAKE is used to support the Proof-of-Stake consensus payment layer on the network.
Staking allows block producers (validators and their delegators) to provide transaction consensus and receive staking incentives for honest block production. STAKE is not needed for xDAI payments, and the token value is determined by the marketplace.
Polkadot
One of the co-founding members of the Ethereum Network, and creator of the Solidity programming language, Dr. Gavin Wood, has recently launched one of the largest interoperable projects to date; Polkadot.

The Polkadot ecosystem is created with 4 different types of blockchains.
The relay chain – the backbone of the project that connects all the blockchains like spokes on a bicycle tire. The blockchains that are the spokes in this example are called parachains and parathreads (like the little brother version of a parachain) that come off the relay chain. The blockchains that connect between parachains and parathreads are called bridges.
Polkadot has created an easy-to-use platform for developers to create decentralized applications that are open-source, peer-to-peer, and interoperable with other projects on different blockchains.
Edgeware
One of the projects that have been created based on the Polkadot ecosystem is Edgeware. Moreover, Edgeware is a ‘substrate parachain’ that is a self-upgrading WASM (WebAssembly) smart contract platform and aims to be the easiest way to deploy code to the Polkadot network.
Cosmos
Cosmos is an interoperable ecosystem similar to Polkadot, however, it is much older than Polkadot and still early in adoption phases.

Kava is one of the most popular projects taking the lead for decentralized finance within Cosmos. Kava has recently announced it will be launching Harvest – the world’s first cross-chain money market chain will allow for lending/borrowing options on the Kava platform.
Conclusion
There are different types of blockchain scaling solutions, with various entry levels to suit a variety of people.
It is clear through the variety of current innovations that there is a demand for scaling of the blockchain ecosystem. Once the transitional phases of Ethereum 2.0 are complete, the crypto-community will hear a sigh of relief with the reduction of network congestion and high gas fees.
Projects focusing on blockchain scaling solutions are hot right now, and there are many more in the pipelines. The more efficient cross-chain communication, the faster and smoother the interoperability between blockchains, the sooner mass adoption will arise.
However, there is a lot to learn about blockchain scaling solutions for those interested. Ivan on Tech Academy offers a large number of blockchain courses on crypto fundamentals and blockchain technology in general. Efficient blockchain scaling is heralded as being key to greater blockchain adoption – and blockchain education is just as important to understanding the potential of this technology.





