
The launch of the Injective Protocol has caused a wave of headlines and speculative video content across the crypto ecosystem. The project appears to have solid foundations with a credible team of developers and advisors, who have previously worked in large tech or other blockchain projects. The whitepaper for Injective Protocol was released in December 2018, avoiding the ICO hype, successfully receiving funding from venture capital firms, other DeFi platforms, and a public IEO through the Binance Launchpad.
The Injective Protocol team has been busy developing the latest tweaks and updates to ensure quality efficiency with the protocol, evident from the history of activity on their Github profile. Injective Protocol is the first successful project that has been developed and launched through both the Binance Labs and Binance Launchpad. So, what is it that makes Injective Protocol more than just another DEX?
In this article, we’ll explain how the protocol works, the token economic features of the native INJ token, and outline the key distinctions from any other DEX project thus far. Firstly, let’s have a look at Injective Protocol, and the basic functions it serves.
Nevertheless, it can be worth it to preface this with a bit of background on crypto exchanges and decentralized exchanges. Ivan on Tech Academy is your guide to all things cryptocurrency and blockchain-related. As such, we highly encourage you to enroll in Ivan on Tech Academy, to learn more about blockchain and cryptocurrency.
What is a Decentralized Exchange?
There are generally two separate types of crypto exchanges available: centralized exchanges (CEXs) such as Coinbase or Binance, or decentralized exchanges (DEXs), like UniSwap or 1inch Exchange. The fundamental difference between CEXs and DEXs is the custody of the private keys to the funds they hold. CEXs pride themselves on a super easy user experience, where people can buy their first Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies with minimal effort involved. CEXs are great for onboarding newcomers to the industry, however, they do have their drawbacks.
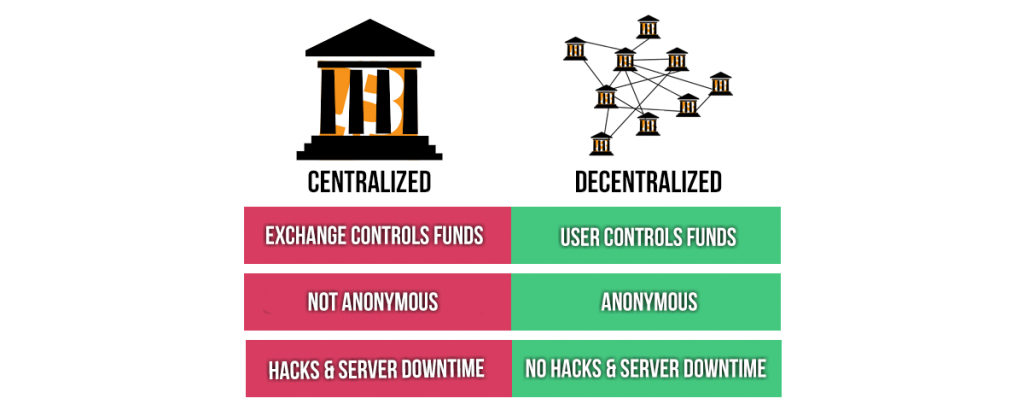
You may have heard the phrase ‘not your keys, not your coins!’ - a frequent saying among crypto users. CEXs are in ownership of the private keys to the funds. This means that users don’t have to worry about the responsibility of storing their wealth. However, problems may arise when the CEO or person in charge of the private keys becomes unavailable for one reason or another. Last year, the CEO of QuadrigaCX passed away in February, and was the only holder of the private key to the funds, meaning that over $145 million worth of assets became frozen in the exchange with no one being able to withdraw from their account.
Decentralized exchanges, on the other hand, are protocols run by a global network of computers, instead of a central governing organization. DEXs allow users to interact with the smart contract on the blockchain directly to trade and swap tokens, masked by a simple attractive graphical user interface, that allows users to navigate and transact with ease.

Interacting with DEXs allows users to have complete ownership of the assets, either stored in a web browser wallet or a cold storage wallet. DEXs allow for ultimate financial freedom having true ownership of wealth.
However, we are still in the early stages of development and as adoption grows, DEXs are showing some teething issues with several hurdles to overcome before DeFi adapts to mainstream use. Despite this, DEXs are becoming more popular than ever.
Current DEX Challenges
The foundation of DeFi is the second-largest cryptocurrency and blockchain, Ethereum, hosting more than 220 decentralized finance applications. Ethereum is only just beginning to phase into its Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, which offers sharding and layer 2 solutions. The progression is slow, and recent months have shown a tremendous increase in users on the platform, resulting in high congestion causing some dispiriting side effects.

Lots of users and a small limited TPS (transaction per second) results in high demand for transactions to be verified. Miners will choose transactions with a higher transaction fee as logically this increases profits. For the users though, this means transaction fees are bid higher and higher as more people try to process a transaction.
Alongside the increased gas fees, those who have sent a transaction with an average or smaller gas fee will be waiting a considerably longer time than others in times of high network congestion. In recent months, some transactions have taken over an hour to process.
Although we’ve been promised scaling solutions from Ethereum, we are still waiting, and some users are choosing to switch back to a centralized exchange for faster transactions and a better user experience.
If you want an even greater understanding of the possible hurdles and opportunities of decentralized exchanges, take a closer look at Ivan on Tech Academy. Over 20,000 students have already enrolled in our numerous courses. At the moment, you can get 20% off when joining if you use the exclusive discount code BLOG20. Now it can be your turn to enroll and learn blockchain!
How Injective Protocol Is Different
Below we explain why Injective Protocol is a completely decentralized, interoperable, and permission-less protocol. Users can operate trades, spot, and future derivatives on the Injective Protocol exchange, and create their own derivatives market and trading pairs!

Injective Protocol shows long-term value to the ecosystem with token economics indicating strong price potential (explained later).
As a layer-2 DEX, Injective protocol is unique in that it operates as a cross-chain, interoperable relay chain, and has a completely decentralized infrastructure.
Other DEXs are considered decentralized in terms of the custody of the private keys. The actual infrastructure of the exchange is operated by a centralized team of developers.
Injective Protocol has created an exchange structure that is a public utility, with the network of users personalizing their own derivatives market, alongside having governance and voting rights when holding the INJ token, for future protocol updates.
Injective Protocol was built on Cosmos, with interoperable features of inter-blockchain communication, and a token bridge between Cosmos and Ethereum. For the first time ever, users can trade on an ultimately decentralized exchange, and trade with both Ethereum and Cosmos tokens. This is a tremendous step forward toward a truly interoperable, decentralized web. Due to the layer 2 infrastructure, Injective Protocol promises to be faster and cheaper than other competing DEXs.
How Injective Protocol Works
The Injective Chain is the blockchain backbone of the platform, that plays an incredibly important role in looking after the following key components of the protocol:
Order Books
In keeping with the decentralized nature of the protocol, and to aid in transaction efficiency, the order books are decentralized ‘0x’ based order books. This means that the orders can enable side-chain order relays, with on-chain settlement.
Also, the Injective Protocol is becoming increasingly decentralized as INJ nodes host the censorship-resistant order books.
Trade Execution Coordinator (TEC)
The TEC is an essential protocol that ensures no front-running of orders.
Front-running is when you place an order or bid, and a bot behind the scenes has watched your order being placed, and then jump the queue copying your exact bid, within the space of under a second. Some bots operate as frontrunners on some exchanges and can be very frustrating, often resulting in your order not being processed.
Injective Protocol uses a verifiable delay function, that ensures orders are not being placed ahead of prior orders.
Bi-directional Token Bridge
This is the crucial function that allows users to transfer ERC-20 tokens to and from the INJ chain. The token bridge is built within a ‘peg zone’ in the Cosmos network. (Peg zones are account-based blockchains that bridge zones within the Cosmos ecosystem to and from external blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethererum).
When using the Injective Protocol, the bi-directional token bridge route travels through the following stages from an Ethereum address: firstly through the INJ Peg zone smart contract, secondly the relay service to the ETH bridge module, then via an oracle to the Bank Module (COSMOS address), and in reverse order for Cosmos to Ethereum trades.
EVM Execution Environment
The Ethereum Virtual Machine Execution Environment function allows Ethereum smart contracts to be executed whilst using the Injective Chain. Developers have the opportunity to build Ethereum-based dApps but in a more scalable environment using the PoS consensus algorithm.
Injective Protocol offers the same development experience with Injective EVM when creating decentralized applications, with additional benefits including an increased contract byte code size limit of 100KB.
Smart Contracts performed in EVM environment include:
- TEC
- Bi-directional token bridge
- Staking
- Futures contracts
- ERC20 Token contracts
INJ Token
The token is used to transform the exchange into a “fully decentralized public utility that’s owned and controlled by the community of INJ holders” - injectiveprotocol.com

The Injective token, INJ, is the essential component of the community-driven philosophy with a wide variety of use cases to ensure the project has complete self-sustainability and maintains decentralization.
Protocol Governance
A common form of protocol governance for most DeFi tokens is to hold voting rights for changes and updates to the platform.
The Interject Chain core governance process is as follows:
- Proposal Submission (a proposal is submitted to the blockchain with a deposit)
- When the deposit reaches a certain value the proposal is confirmed and open for people to vote
- If the proposal involves a software upgrade, validators will need to signal they are ready to switch to the new upgrade, then once more than 75% of validators have signaled they are ready to switch, their software will automatically flip to the new version
Without community governance, the protocol will become stagnant or centralized, therefore it is paramount to the longevity of the project.
Collateral Backing
Instead of using stable coins for margin and collateral backing like most common DEXs, the INJ token is used as an alternative for the Injective derivatives market.
Injective Protocol has taken a different approach with the use case of their tokens, having INJ locked up in derivatives contracts to ensure margin is met, in addition to being used for collateral backing or insurance pool staking, where stakers earn interest on their locked tokens.
Exchange Fee Value Accrual
This element of the protocol helps to stabilize and maintain a steady price appreciation of the INJ token. The exchange fee value accrual burns any excess tokens that have been accrued after the relayers have been paid.
Burning excess fee tokens reduces the amount of circulating supply of INJ, thus increasing demand.
Security
The Cosmos ecosystem, from where Injective Protocol originates, uses the Proof of Stake Tendermint consensus algorithm. If you’d like to learn more about how Proof of Stake works, see our Proof of Stake vs Proof of Work article here!
Injective Protocol uses a variety of ways to incentivize people to stake their INJ coins through staking rewards, collateral backing, or governance rights. Staking INJ tokens not only increases the strength and security of the network but reduces the circulating supply.
Incentivizing Participation
The INJ tokens are a significant way of introducing active participation on the Injective Protocol, with incentives through liquidity mining, and new features for the specific market maker and relayer incentives. For market makers, you can receive a net positive fee rebate with periodic distributions based on snapshots of your trading activity, to incentivize liquidity.
For the other side of the network, nodes and validators can act as relayers. Relayers are incentivized to originate orders into the shared order book. Nodes that first discover a make order will receive a calculated ratio of the exchange fee as a reward.
Tokenonmics:
The Injective Protocol community has decided on an initial supply of 100,000,000 tokens, with a 7% annual inflation rate that will decrease over time to 2%.
Over time, however, the initial supply of 100,000,000 may decrease with the deflationary burning of excess fess through the exchange fee value accrual mentioned earlier.
Injective Exchange Platform
The above bullish factors for Injective Protocol would be less pertinent without the front-end implementation of the Injective Protocol’s exchange client to create a slick and user-friendly experience. The design is such that it caters to both the newbies to DeFi and the more advanced and experienced traders.

The interface is similar to dYdX and Synthetix, but is a completely decentralized exchange allowing anyone to participate in a fully permissionless way. With the Injective Protocol exchange client being open-source, anyone can host the front end in their own environment.
Injective Protocol is working on creating its own individual version of the front-end, the Injective Exchange, but this is currently under development to be revealed later this year.
Partnerships
Injective Protocol has an impressive list of partnerships that will assist in cross-chain activity, including Elrond, Kava, and recently, Polkadot. Shortly after the Binance IEO listing, INJ was released on Uniswap.

The recent Polkadot collaboration aims to expand cross-chain trading in a decentralized manner and was facilitated by Moonbeam. Moonbeam facilitates Ethereum compatible smart contracts that can be used within the Polkadot ecosystem. This allows for better interoperability between decentralized applications and a bridge between various platforms.
Kava, one of the most popular DeFi lending projects built on Cosmos, partnered with
Injective to add an array of new possibilities in the cross-chain derivatives market that have not been achieved on any other platform. Kava is also part of the Binance ecosystem, meaning that interoperability is easily achieved as the projects work towards a shared goal of making DeFi more accessible.
Conclusion
Injective Protocol has built the first completely interoperable, decentralized exchange across different blockchain ecosystems. The project has outlined a creative balance of supply and demand tokenomics, incentivizing restriction of the circulating supply through staking and collateralized contracts - in addition to the burning of excess fee tokens. Demand will increase from investors, staking rewards, and governance of the platform.
The platform may well be the community’s next favorite go-to DEX, as other decentralized exchanges struggle with congestion and scaling issues. Injective Protocol appears to have pioneered the optimal layer 2, truly decentralized exchange, with protocol fundamentals and token economics ensuring a fully self-sustainable, community DEX for the future.
With that said, the decentralized crypto exchange sector is constantly in flux. As such, you should be sure to keep up-to-date with the industry through Ivan on Tech Academy. Enroll today and supercharge your crypto education with world-class blockchain courses!





