
Most people in today’s society have heard of either cryptocurrencies in general, or at least Bitcoin specifically. The crypto market keeps growing, and as of 2020, crypto awareness is arguably bigger than ever before. Along with this surge in public interest, people are also starting to open their eyes to the technology behind cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin. The fundamental technology for cryptocurrencies is blockchain, and this is an essential cog in the crypto machine.
However, even though there’s a large number of people aware of what Bitcoin is, there are still many people who do not know how Bitcoin works or where Bitcoin comes from. Put simply, the process of creating Bitcoin relies on something known as crypto mining, and in this article, we are taking a look at what Bitcoin mining is.
If you feel that you want to learn more about the crypto fundamentals, such as crypto mining, we highly encourage you to enroll in some of the courses available on Ivan on Tech Academy. To mention just a few, the course on the history of money and Bitcoin, as well as the crypto for beginners course, are both excellent starting points!
What are Bitcoin and Crypto?
So, to fully understand what Bitcoin mining is, we must first understand what crypto is. A lot of people already know what cryptocurrencies are, but there are still some people unfamiliar with the basic concept.
Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, are predominantly known for being virtual currencies. Consequently, they represent a form of virtual medium of exchange which effectively allows users to make financial transactions online. In 2009, an anonymous person known as Satoshi Nakamoto first launched Bitcoin, which has since gone on to become the most well-known cryptocurrency.

One of the most important differences between regular fiat currencies and cryptocurrencies is the fact the crypto is decentralized. This means that there is no central authority in the mix that can meddle with or control the system. Since no single person or entity has the power to take control over or rig the system, it also means that the risk for structural fraud is significantly lower.
Blockchain technology is famously the technology underpinning Bitcoin, and Bitcoin subsequently relies on this technology to fully function. Cryptocurrencies use functions known as ”cryptographic functions”, which are also a vital aspect of crypto. Moreover, these functions ensure that the information regarding transactions cannot be falsified. Such cryptographic functions are used to ensure that transactions in the system take place and are recorded.
Once a transaction is made and validated, this information is then stored permanently in a block, hence the name “blockchain”. Whenever a new transaction is made and verified another block forms, containing information confirming the new transaction. Furthermore, when a new block is formed, the new block will contain the cryptographic signature of the previous block, and this signature is known as a hash. Once a transaction is validated and the block forms, it can not retroactively be changed. This ensures that the record is clear and the so-called hash validates everything, ensuring that no one can tamper with the information stored on the blockchain.
What is Bitcoin Mining?
As such, you might be wondering – “where does Bitcoin come from?”. There is more than one way to acquire Bitcoin – some are easier, and some are harder. One easy way is simply to buy Bitcoin using fiat currency. However, the process of purchasing Bitcoin might be complex for people without any technical background. It is also possible to buy Bitcoin using other cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum, and this can be done on a decentralized exchange.
Another way to acquire Bitcoin is to find an employer that pays salaries in the form of Bitcoin. This is not common at all, but there are companies out there that have made the transition of paying their employees in cryptocurrencies. Additionally, although these methods would both allow you to get your hands on Bitcoin, it does not explain where Bitcoin comes from.

To get back to the core of this article, therefore, we are going to take a look at how to create Bitcoin. The crypto-world refers to the process of creating Bitcoin as crypto mining or Bitcoin mining. The term “Bitcoin mining” actually comes from the traditional world of mining since this process somewhat resembles the mining of other metals and commodities. It requires resources and time, and it slowly creates new units – or coins – that anyone mining can take part of. There is also a fixed, or finite amount of Bitcoin out there, and at one point it will be impossible to mine more. This similarly resembles that of, for example, gold or other natural resources which also only exist in finite amounts.
The main reason that Bitcoin mining exists is as an incentive for people to become part of the network to govern, support, and legitimize the system as well as the blockchain. This process is done by a large number of people which means that no single entity controls the system, and this ties back to the decentralized nature of crypto. The miners then receive their compensation for helping out with this process in newly mined Bitcoin.
If you want more basic information about Bitcoin and crypto before diving into Bitcoin mining, Ivan on Tech Academy has got the courses for you. More than 20,000 people are already enrolled in Ivan on Tech Academy, and the Academy keeps producing real-life success stories. Sign up for blockchain courses and get 20% off with the special discount code BLOG20!
So what do Bitcoin miners do?
In technical terms, Bitcoin miners act as “auditors” for the transactions made on the Bitcoin blockchain. They verify previous Bitcoin transactions and the point of this is to keep the users of the system honest. One of the functions that the miners have is actually to prevent the problem of double spending.
Double spending means that one user makes a transaction using the same funds twice. In traditional fiat systems, this is not an issue since the money actually has physical form. If someone takes $2 and buys a bottle of Coca-Cola, they exchange the physical cash and receive the bottle; this means that they are no longer in possession of the two-dollar bill.

However, there is the potential risk that someone makes a copy of a digital token such as a Bitcoin and tries to spend the same amount twice. Nevertheless, this is also a problem when it comes to fiat money. If someone has a two-dollar bill and makes an exact copy of that bill, they would have the same serial number, meaning that one of the bills has to be false. So merely by looking at the serial number of a bill, someone can determine if it is a copy or not.
In the Bitcoin system, it is actually the miners that solve this problem. They check transactions to make sure that someone has not spent the same Bitcoin twice. However, this process is, unfortunately, a bit more complicated than it might first sound.
Bitcoin mining conditions
To earn Bitcoin as a miner, two conditions must be met. The first condition is that you will have to verify or validate blocks of 1 MB worth of transaction data. Once someone has verified 1 MB of data, they are eligible to earn a reward in the form of Bitcoin. However, it’s worth mentioning that this 1 MB size cap has become somewhat of a controversy in the community. Some people argue that this block limit is too small, since bigger blocks would mean that the system can process more transactions faster.
Nevertheless, a block of 1 MB of data does not have a set amount of transactions included; it can actually vary. It all depends on how much data each transaction is included in the 1 MB block. Sometimes this could just be one transaction (even though this would be unlikely), meanwhile other times it can be thousands of transactions.
However, once someone has verified 1 MB worth of transactions, they are only ELIGIBLE to earn Bitcoin, it is not a guarantee of a pay-out.

This brings us to the second condition that needs to be met. To earn Bitcoin, the miner must also be the first person to solve a numeric problem. In the crypto community, this is more well-known as “proof of work”.
What is Proof-of-Work?
So, some of you might have heard that this numeric problem, or “proof-of-work”, involves performing challenging mathematics or computations, but this is not entirely true. What the miners are trying to do is come up with a 64-digit hexadecimal number, and which is something better known as a “hash”. Moreover, this hash has to be equal to a target hash. This means that miners are only trying to guess and match the targeted hash.

This might actually not sound too bad, but since it is guesswork and it is actually of a 64-digit hexadecimal number, there are actually trillions of guesses that need to be made. This means that in order to solve one of these problems, someone needs a lot of computing power. So to mine, you need to have a high ”hash rate” which measures how many megahashes per second that a system can process.
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
Aside from “auditing” or simply validating the system in exchange for compensation, Bitcoin miners also serve another critical function. They are still also the reason that new Bitcoin can enter the market. The miners are basically minting new currency, which means that they are the ones responsible for creating new Bitcoin.
At the moment, there are currently just above 18.5 million Bitcoins in existence, and there are approximately 900 new Bitcoins issued every day. However, as mentioned earlier, there is a cap on how many Bitcoins that can exist, and this cap is 21 million. At the rate that Bitcoins are created (taking into account that Bitcoin rewards decrease over time) the last coin will be minted sometime around 2140.
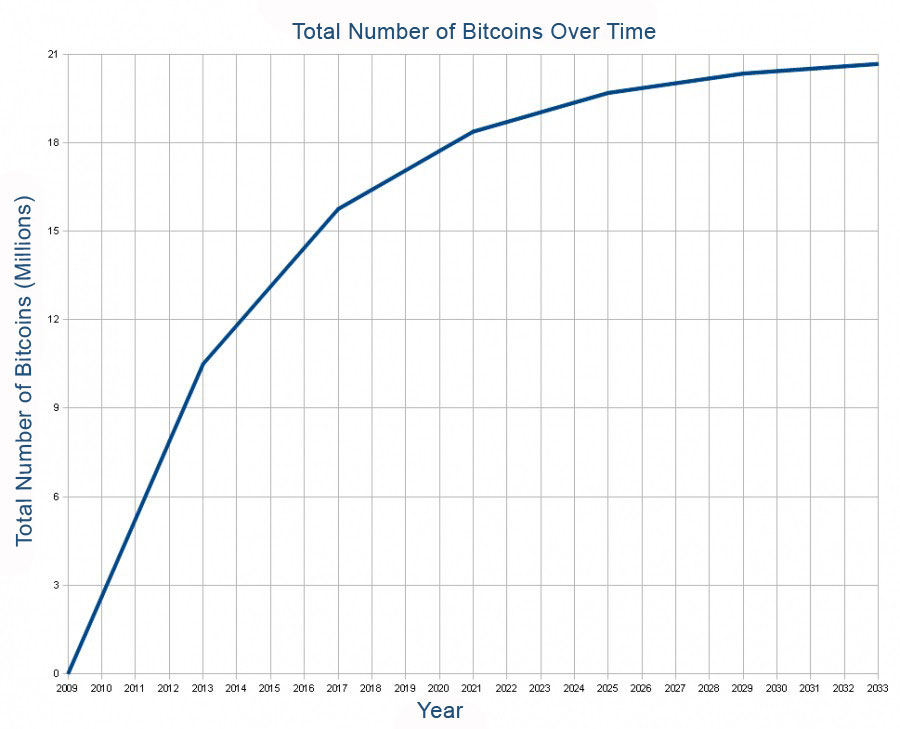
Another interesting number is how many Bitcoins are ultimately lost, and end up being inaccessible. This number could be roughly 3 – 4 million, but this is just a qualified guess. It is hard to calculate the exact number, but it’s possible to speculate based on how long the funds have sat in specific addresses.
How much can you earn from Bitcoin mining?
At the beginning of Bitcoin, in 2009, the verification and proof of work for each block would earn someone 50 BTC per block. However, this halves roughly every fourth year, meaning that in 2012 – 2013, successfully mining one block would result in 25 BTC. This trend has been almost the same meaning that in 2016 one block could result in 12.5 BTC. As of now, in 2020, verifying one block will result in about 6.25 BTC following the Bitcoin halving.
Although mining just a few Bitcoin coins might seem like a small reward, taking the price of Bitcoin into account makes these sums a lot larger. The current price for a Bitcoin reaches $10,755.46, meaning that verifying one block and providing the proof-of-work would result in a payday worth almost $70,000.

These numbers might indicate that the potential for mining Bitcoin is vast, however, this is not the case. The time and resources it takes to mine Bitcoin are huge, and so is the starting investment. The time estimation for mining one Bitcoin is almost 30 days, and the computing power that you need is huge. This also means that the costs for electricity and the hardware/software needed will eat up most of your profit.
Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake
The process of mining cryptocurrencies is resource-intensive, and an alternative to proof of work is proof-of-stake, or “staking”. Staking takes up significantly fewer resources than mining, which makes it a more affordable way of earning money on crypto.
The act of staking revolves around holding cryptocurrencies in a wallet and receiving a reward from this process. This can be done by staking coins directly from a crypto wallet, if the wallet provides that service. Another option is using an exchange that might offer this function.
To understand staking, we must first define what Proof-of-Stake is. Proof of Stake is similar to that of proof of work. The idea behind proof of stake is that people lock (stake) their coins at a specific interval. Then, a protocol assigns someone the right to validate a block. The assigning process is random, but staking more coins enhances the chance of becoming the validator. This means that proof of stake is an alternative method for validating blocks, meaning that we can create coins without having to rely on proof of work.
The most significant benefit of staking is that it does not require the proof of work to validate a block. This means that there is no need to solve the hash-problems, which are resource-intensive. We might therefore be able to conclude that staking is a cheaper and less resource-intensive alternative to mining crypto. This means that more people can participate in the governing of cryptocurrencies. It also means that they can make passive income by simply holding on to their coins.
Nevertheless, Bitcoin uses “proof-of-work” in order to be mined. If you want to learn more about Bitcoin mining, blockchain, and staking, feel free to join the number one blockchain education platform Ivan on Tech Academy for numerous crypto and blockchain courses. Join the crypto industry today!





