
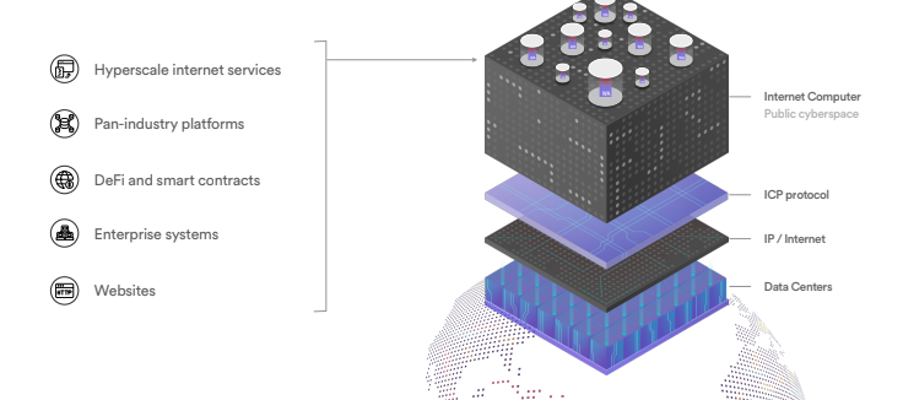
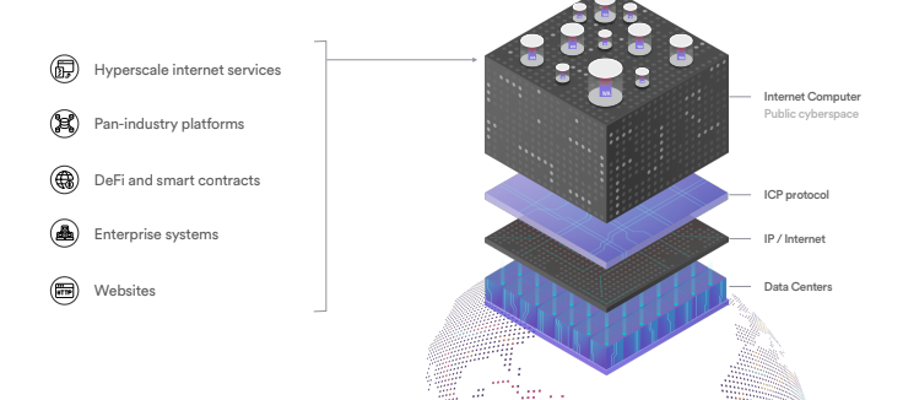
The Internet Computer protocol, created by DFINITY Foundation, has recently launched its long-awaited public mainnet. Moreover, the native Internet Computer Protocol (ICP) token has seen a surge in price action following a successful launch. The Internet Computer is a cryptocurrency project like no other, aiming to recreate the full internet stack. The project aims to build a new decentralized internet paradigm, fully interoperable with other blockchains. To achieve this, the Internet Computer protocol uses smart contract-like ‘canisters’, a specially-designed programming language ‘Motoko’, and a novel ‘Internet Identity’ (II) model, all operated through the decentralized Network Nervous System.
In this article, we are going to dive deep into the Internet Computer protocol and look at the various features that make up the network infrastructure. Also, we’ll look at the background of the project, discovering the history and roles of the DFINITY Foundation. Furthermore, we’ll explore the various use cases for the ICP token, and how it contributes to the Internet Computer ecosystem.
If you’re new to cryptocurrency and would like to learn more about how blockchain operates on a fundamental level, you’ve come to the right place! Ivan on Tech Academy provides all the materials you need, regardless of age, location, or background. Start with our Blockchain & Bitcoin 101 course to discover UTXOs, consensus mechanisms, mining nodes, and much more! Also, our Ethereum 101 course is a great place to start if you’d like to know more about smart contracts, the Ethereum Virtual Machine, and ERC-20 tokens! Join Ivan on Tech Academy today - the world’s largest online blockchain education suite with over 30,000 students!
What is the Internet Computer Protocol?
Blockchains are distributed protocols that operate across the internet. A global orchestration of nodes runs the blockchain networks across the internet. However, there are several aspects of centralization controlling access and utility of the internet itself. This is where the Internet Computer comes in. The Internet Computer protocol removes the centralization of the internet, used by blockchains.

The Internet Computer project aims to ameliorate the entire internet stack, as opposed to just the application or data storage layers. As such, this requires restructuring of sensitive data and protocols. Therefore, unlike most cryptocurrency projects, the majority of the Internet Computer code is not open-source. In addition, access to use the Internet Computer blockchain is permissioned, meaning developers require a private key. Also, developers require “standardized hardware” provided by DFINITY Foundation to access the core blockchain.
In 2020, the launch of the first decentralized application (dApp) on the Internet Computer was showcased at the annual Davos conference, hosted by the World Economic Forum. The application is an open-source version of LinkedIn, known as LinkedUp. The Internet Computer later released ‘CanCan’, a clone of the popular TikTok social media platform. Amazingly, this was achieved using only 1000 lines of code!
After a staggered launch over four years of development, the Internet Computer public mainnet launched on May 7th, 2021. The periodic element-named updates include Copper, Bronze, Tungsten, and Sodium. The Mercury: Alpha Mainnet first launched in December 2020, before finally, Mercury Beta Mainnet + Genesis launched earlier this month.
DFINITY Foundation
The Internet Computer was founded by Dominic Williams in 2016. However, Williams has been active in the blockchain cryptography space since 2014. The project was originally known as DFINITY, with the Internet Computer being managed and developed by the DFINITY Foundation. The DFINITY Foundation consists of nearly 200 world-class industry experts, with over 15,000 collective research publications, nearly 100,000 academic citations, and over 200 patents filed within the team.
As a global not-for-profit organization with headquarters in Zurich, DFINITY Foundation has research centers in the US, UK, Germany, Palo Alto, and Japan. The leaders in distributed ledger technology and cryptography at DFINITY Foundation are “committed to building advanced experimental technologies to improve the public internet”.
DFINITY Ecosystem
The DFINITY Foundation ecosystem is dedicated to enhancing developer experiences and serving community needs. This is achieved through three main avenues. Firstly, the DFINITY Foundation reserves a “Beacon Fund” for developers building decentralized applications (dApps) and services on the Internet Computer blockchain.

Secondly, the DFINITY Foundation offers an exciting opportunity with the Internet Computer Fellowship program. This is designed for graduate students and educators around blockchain, cryptography, and computer science. Finally, DFINITY Foundation caters to enterprise needs, helping to accelerate businesses using the Internet Computer protocol.
How Does the Internet Computer Protocol Work?
The Internet Computer blockchain is hosted by a series of data centers containing multiple nodes. Different nodes from within different data centers are pooled together and referred to as a ‘subnet’. Each subnet can host its own Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchain by using a unique consensus model referred to as “Threshold Relay”.
A selection of nodes from each subnet is chosen to produce blocks depending on the amount of ICP tokens staked. The subnets operate similarly to the parachains model within Polkadot, allowing developers to build applications on the subnets.
Unlike most cryptocurrency projects and development platforms, the Internet Computer protocol doesn’t offer development opportunities with smart contracts. As an alternative, applications are built using one or more different types of “canisters”. Canisters are similar to smart contracts but with far greater flexibility, development opportunities, and ease of utility. Canisters can automatically upgrade themselves on other subnets and can be used by other developers building different decentralized applications (dApps).
As subnets contain only a few nodes running from within different data centers, the Internet Computer blockchain can process transactions within seconds. This makes the processing time similar to that of the regular centralized internet. Moreover, interacting with canister-based decentralized applications (dApps) on the Internet Computer comes with zero fees. However, transactions on decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols will require a small transaction fee to process requests for lending platforms or decentralized exchanges (DEXs).
Internet Computer Protocol Features
Below we have outlined the key areas of the Internet Computer protocol. Combined, these elements are bringing a new online paradigm of decentralization.
Network Nervous System
The Network Nervous System (NNS) infrastructure is partly composed of canisters operating on the Internet Computer network, in a dedicated governance subnet. These canisters consist of a ‘registry’ canister (tracks data and subnet organization), a ledger canister (keeping records of all transactions and data), and the governance canister (allows ICP token holders to vote on proposals).
The Network Nervous System (NNS) also makes use of ‘Chain Key Technology’. This cryptographic technology allows subnets to communicate with each other through the NNS. Moreover, the NNS can validate all subnet transactions using a master private key.
As the Internet Computer’s backbone, the NNS is responsible for managing the entire Internet Computer protocol stack. The hierarchy displayed from bottom to top is data centers, nodes, subnets, and canisters.
Data Centres: The Network Nervous System (NNS) is responsible for maintaining and choosing new data centers in the network.
Nodes: The nodes layer of the ecosystem plays a crucial role in identifying bad actors in the network. In turn, misbehaving nodes will be removed from the subnets. Additionally, underperforming nodes in the network may also be removed.
Subnets: On this level, the Network Nervous System (NNS) plays a slightly more active role, deciding which nodes can form a subnet. The NNS aims to increase the capacity level by generating key shares for nodes. As a requirement for participation, subnets need to already have keys to be able to operate. Therefore, the NNS is responsible for generating subnet keys and sharing these with nodes of a new subnet.
Canisters: The Network Nervous System (NNS) governance body has the responsibility of deciding whether updates to canister management or software updates are required. The NNS can combine nodes to create subnets, and have these connect to other subnets, allowing the Internet Computer protocol to “scale indefinitely”.
Internet Identity
Users require an “Internet Identity” (or “II”, pronounced “eye eyes”) to interact with applications on the Internet Computer. A user can have as many IIs as they like for different use cases or devices. Additionally, a single identity can be used across multiple devices. Each Internet Identity is assigned with an automatic wallet address and is used to sign all transactions within the Internet Computer application ecosystem.
As opposed to remembering or storing a seed phrase or another password, the Internet Identity (II) service enables users to use familiar authentication methods such as facial recognition or a computer password. Moreover, this is achieved anonymously and securely when using an Internet Computer II.
Motoko
Developed by the DFINITY Foundation, Motoko is a new programming language and software development kit (SDK). Designed to be used in conjunction with Internet Computer, the first iteration was released in 2019. Motoko was created to enable as many developers as possible to build robust and sustainable websites, internet services, and enterprise systems with ease. That being said, the Internet Computer supports a multitude of software frameworks.

Furthermore, the DFINITY Foundation is currently building SDKs that can support Rust and C languages. Motoko is an evolving, modern, programming language. In the future, we can expect to see updates to the Motoko compiler and new functionality with the release of each DFINITY Canister SDK.
If you’re interested in learning how to create your own decentralized applications (dApps) but have no programming experience, Ivan on Tech Academy can help you achieve this goal! We offer a range of programming courses to suit all experiences. For our readers with no coding background, start with one of our beginner courses. These are the C++ Programming for Blockchain Developers course and the Javascript Programming for Blockchain Developers course. Here you’ll learn the basics of programming before moving onto one of our range of blockchain programming courses, available at Ivan on Tech Academy. Join today with a 14-day money-back guarantee!
ICP Token
Originally known as the “DFN” token, the Internet Computer Protocol (ICP) token is the lynchpin facilitating decentralized governance and orchestration of the Internet Computer ecosystem. The ICP token has no maximum supply, with a diminishing annual inflation rate starting from 10% per annum. Further, the ICP token holds three main functions.
ICP tokens provide governance rights to holders allowing them to vote on proposals and updates to the protocol through the Network Nervous System (NNS). Moreover, users can earn ICP tokens for participating in the NNS governance voting.
ICP token holders who wish to participate in governance will need to lock up their tokens to do so. The minimum lock-up period is six months and the maximum is eight years! The way the governance protocol operates means, in short, users who lock up ICP tokens for longer periods, receive more voting power.
Another use case for ICP tokens is to reward network participants for honest behavior and upkeep. Finally, the third use case for ICP tokens is to pay for canister gas fees on the network. To do so, tokens are converted into cycles which can then be used to power computations and the running of websites too.
Internet Computer Protocol & ICP Token Summary
The recent launch of the public mainnet has seen huge success. With a fresh approach to blockchain technology uniquely targeting the centralized internet issue, it’s not difficult to see why. Although the technicals under the hood of the project are arguably some of the most complex in the industry. The Network Nervous System (NNS) operates as a decentralized governing body, making use of the canister and subnet infrastructures.

The novel programming language Motoko allows for the development of decentralized applications (dApps) capable of speeds comparable to the traditional centralized web. Also, the evolution of smart contracts creating canisters for development tools increases the efficiency, time, and overall cost of application development.
The ICP token enables the smooth running of the Internet Computer protocol. ICP token holders can receive governing rights, whilst participants of governance proposals are rewarded with ICP tokens. Also, the ICP token extends utility for users and developers to pay for the gas fees on the network when making a transaction. The recent price action of the native token reflects the success of the platform, reaching the top tenth spot in terms of market cap.
Blockchain is one of the fastest-moving, cutting-edge technologies in the tech industry. Moreover, it has been voted as the number one in-demand skill according to LinkedIn. If you’re interested in getting a career in blockchain, Ivan on Tech Academy can help you get there! Check out our Blockchain Business Masterclass course to learn how to manage and organize a blockchain-based project. Also, our FinTech 101 course provides all the information needed to be compliant with regulations within the industry, and ‘wow’ future potential employers! Get started in blockchain at Ivan on Tech Academy! Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter @Academy_IOT! We’d love to know your thoughts about the Internet Computer protocol!





