
Holochain provides foundational technology to allow people to connect with one another, with a choice of what data they share. As such, Holo is creating a bridge platform between users of Holochain and the traditional internet. Also, Holochain is seeing increased adoption welcoming new Holochain applications (hApps), offering developers an efficient and cheaper alternative to blockchains. Moreover, this has been achieved with substantially lower upfront and running costs, instant transaction finality, and without traditional consensus algorithms. All this is possible thanks to Holochain’s distributed hash table (DHT). Also, the Holo token (HOT) reached new all-time-highs recently as the Holochain platform has gained industry-wide recognition.
In this article, we’re going to explore the various elements of the Holochain and Holo ecosystems. We’re going to discuss the different projects using the Holochain platform, making a passive income with Holo, and how the Holo token (HOT) and HoloFuel interoperate. Furthermore, we’ll look at how Holochain is creating a better internet that empowers users with the help of ‘post-blockchain’ technology.
Considering the rapid development of blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT), this industry is still in its infancy. The innovation and creativity in this space are taking crypto and blockchain into new territory seemingly every day! If you’re new to crypto and want to learn how blockchain works on a fundamental level, be sure to check out the Blockchain & Bitcoin 101 course at Ivan on Tech Academy. Following this with the Ethereum 101 course will give you a great insight into the fundamental differences between each blockchain.
Ivan on Tech Academy is the premier blockchain education platform online. With courses covering every area of the industry, curated by our expert team of blockchain specialists, Ivan on Tech Academy is the perfect place to start your crypto journey!
What is Holochain?
Holochain was designed to create a distributed internet built with user autonomy in mind. By changing how we distribute, store, and process data, Holochain is reimagining how this influences our communications. Holochain aims to create “a more human internet”, one where interactions and relationships aren’t dictated or overlooked by centralized entities, and information is not commoditized immorally.

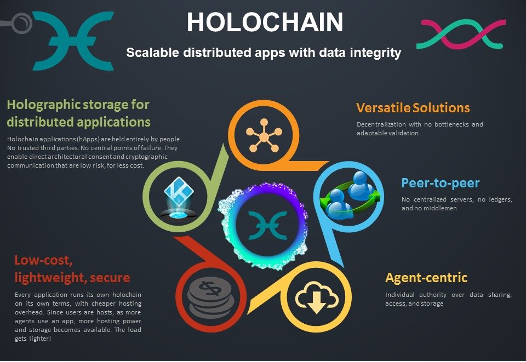
By minimizing corporate control, Holochain is creating an internet that serves individuals, not corporations. Holochain enables people to take control of their own data and online identity while transacting and connecting with applications that meet their needs without being reliant on centralized entities. Also, Holochain makes it easy, fast, and cost-effective to build distributed Holochain applications (hApps).
Furthermore, Holochain uses post-blockchain technology to separate data integrity from data security. This is achieved in a way that uses neither Proof-of-Work (PoW) nor Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanisms (more explained later).
Holochain offers developers the opportunity to quickly and efficiently create fully distributed peer-to-peer web applications. Moreover, with scalability a key focus of Holochain, the protocol can facilitate a global infrastructure compared to that of Twitter or Facebook, without any centralized data centers or storage.
Holochain has created a platform that enables developers to create distributed apps that use the Javascript programming language. If you want to learn how to program your own decentralized applications (dApps), be sure to check out the C++ and Javascript Programming for Blockchain courses at Ivan on Tech Academy. These courses are designed to teach you programming from scratch, regardless of previous experience. Following this, check out the Ethereum Smart Contract Programming courses to learn how to create and deploy your own dApps!
How Does Holochain Work?
The main difference between blockchain technology and Holochain’s use of a distributed hash table (DHT) is the approach in which a transaction is verified and confirmed. With blockchain, all nodes in the network must achieve consensus using a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus algorithm. Although, some variations of Proof-of-Stake (PoS) algorithms only need a majority confirmation from the network to verify a transaction.
However, with a distributed hash table (DHT), the hash-chain approach is ‘agent-centric’. This means that individual nodes themselves can verify and confirm transactions. This is then broadcast to the rest of the network for transparency, with neighboring nodes double-checking the verification.
Scalability is a primary objective in the current blockchain development landscape. As blockchain networks grow with additional nodes, increased energy is needed to confirm transactions. This is a challenge many blockchain developers are looking to resolve, including innovative layer-2 solutions.
Holochain has designed a way to combat this, by sharding distributed hash tables (DHT). This helps by decreasing the transaction load for each node as the network increases in size.
Moreover, the energy required to generate Holo tokens is minuscule compared to that of blockchain technology. For large blockchains such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, the upfront cost of becoming a node or validator is a high barrier to entry for a lot of people. This could be due to the initial hardware or minimum tokens needed to stake. Holochain doesn’t require mining and is capable of operating multiple full nodes on a mobile device.
Holochain is a ‘post-blockchain’ technology that requires no staking and no mining. Therefore Holochain can not be subjected to any majority attacks. Also, this substantially reduces the already-minute risk of bad actors in the network. Users can trust and verify the code on a single node with the added ability to validate counterparty nodes.
DHT (Distributed Hash Table)
Distributed hash table (DHT) technology removes the idea of using distributed ledger technology (DLT) with a decentralized ledger for all nodes to connect to. Rather, Holochain is about having “individual source chains”, and independent node sufficiency. This is an alternative to all nodes needing to be on the network simultaneously. Nodes are validated against each other and checked against their neighbors.
A distributed hash table (DHT) means no Proof-of-Work (PoW), Proof-of-Stake (PoS), or any other consensus mechanism. As a result, there is minimal energy required to produce the Holo token (HOT). Also, the ability to scale through DHT networks is far more efficient than blockchains. The process of sharding DHT is easier and cheaper than sharding blockchains. Moreover, transactions are processed immediately with no risk of bottlenecks or delays.
What is Holo?
Holo is referred to by Holochain as the ‘bridge’ between the mainstream internet world and Holochain. Further to that, Holo allows anyone to use the ‘Holo hosting box’ through the Holo Host application. This runs in the background on users’ computers, to monetize any spare storage or computational power. If people aren’t using their computer to maximum capacity (which, most aren’t) Holo has created an opportunity to earn HoloFuel by becoming a Holo Host.
Holo Hosts earn HoloFuel in exchange for sharing space and computational resources and allowing others to host distributed Holochain applications (hApps) and data. Moreover, Holo Hosts have the choice of which hApps to host, the fees associated with their hosting, plus the priority of applications.
Holo Ecosystem: Centralized or Decentralized?
Holochain itself is a self-sustainable fully distributed platform. However, the team recognizes that to reach mainstream adoption, there will be a slow transition of users from centralized entities to decentralized. This can often be through lack of education and understanding around the technology, or comfort of the familiar, centralized user-experience.
This is where Holo comes in. Holo is designed to be the bridge for users to move from centralized systems to the decentralized, distributed Holochain world. As Holo is a connection between the two, the team recognizes certain aspects of the Holo ecosystem must be centralized.
HoloPorts
HoloPorts are hosting devices also used as a bridge between Holochain applications (hApps) and users from the mainstream web. Both Holo and HoloPorts focus on providing distributed computing power to peer-to-peer hApps, with users being rewarded with HoloFuel.

This difference is that HoloPorts are external hardware devices used for redirecting spare computational resources to the Holochain network. HoloPorts are available in three sizes; the HoloPort Nano, the HoloPort, and the HoloPort+. Holo and Holochain are working together to reduce wasted computing capacity by compensating users for sharing capacity with other people around the world.
HoloFuel
HoloFuel is an “asset-backed mutual-credit currency” only available through the exchange of computational power on the Holochain network. The primary purpose of HoloFuel is to reward the Holo Hosts for their input. Holochain’s “mutual-credit accounting system” can facilitate billions of microtransactions per day.

HoloFuel is referred to as “value-stable not value-static”. This means that the price is not pegged to an external currency or commodity. Instead, HoloFuel is valued in computational units; a combination of bandwidth, storage, and processing time. As such, HoloFuel can be understood as a Holochain analog to Ethereum gas. Users will soon be free to sell their HoloFuel on the open market or exchange them for computational power on the network. HoloFuel is the quintessential cog in the machine of sharing distributed computing power across the Holochain network.
Holochain Applications (hApps)
Holochain allows users to interact with, build, and/or host distributed Holochain applications (hApps) on the network. Developers can create hApps using open-source preset modules from libraries and utility classes available through Github. There are a broad range of tools available for developers on offer. These include Rust HDK (Rust Holochain Development Kit), Zome Explorer Tool, Holochain Playground, and HoloJS Wrapper. Others include the Holochain IDE App builder and Holochain RAD Tools Phase 2 (Rapid Application Development) and many more.

For non-developers, Holochain applications (hApps) offer the opportunity to earn a passive income with cryptocurrency. This is achieved through sharing computational resources to power the hApps. Users can provide any spare computational capacity to Holochain applications either through the online HoloHost software or the HoloPort hardware extension, offering a plug-and-play option with pre-installed software.
Overall, the ease of development and computational resource distribution makes Holochain an attractive alternative development platform for applications, compared to other large blockchains. Below we’ve listed just a few of Holochain’s applications (hApps) active on the network.
Current Holochain Applications:
Holochain is a completely distributed open-source network allowing anyone to create Holochain applications (hApps). The team is in the development stages of several official hApps for users to manage data and privacy throughout the Holochain ecosystem. These include DPKI (private keys management tool), HoloChat (peer-to-peer chat tool within the community), and HoloVault (an application displaying how a user's data has been used).

In addition to the official Holochain applications (hApps) other projects building on Holochain include:
- RedGrid: A project designed to optimize the energy industry through renewable energy integrations, tokenized energy assets, and a smart transaction energy grid.
- Humm: This platform is often considered the distributed version of WordPress, allowing content creators to be financially rewarded for good publications.
- Fairbnb: The name sounds familiar, with this project using a similar model to the traditional model of the global brand ‘Airbnb’. However, this is achieved in a globally distributed, fair manner.
- Producers Token: Designed primarily for the agricultural industry, Producers Token is a project that tokenizes agricultural assets and natural resources. Moreover, the platform provides an exchange for the trading of assets with three main categories. Tokenized assets can either be a service or produce that is currently active, a farm that’s under reconstruction, or an un-operational installation or space.
Holo Token (HOT)
The ERC-20 Holo token (HOT) was first launched during an initial coin offering (ICO) in 2018. HOT tokens were sold as an ‘IOU’ for the redemption of HoloFuel tokens upon launch of the mainnet. Holo tokens are available through several reputable exchanges including Uniswap and Binance. The price has fluctuated greatly from $0.0002 during the March 2020 crash, to $0.0095 in early March 2021. According to CoinGecko, at the time of writing, the HOT token currently sits around $0.007 valued at a $1.2 billion market cap.
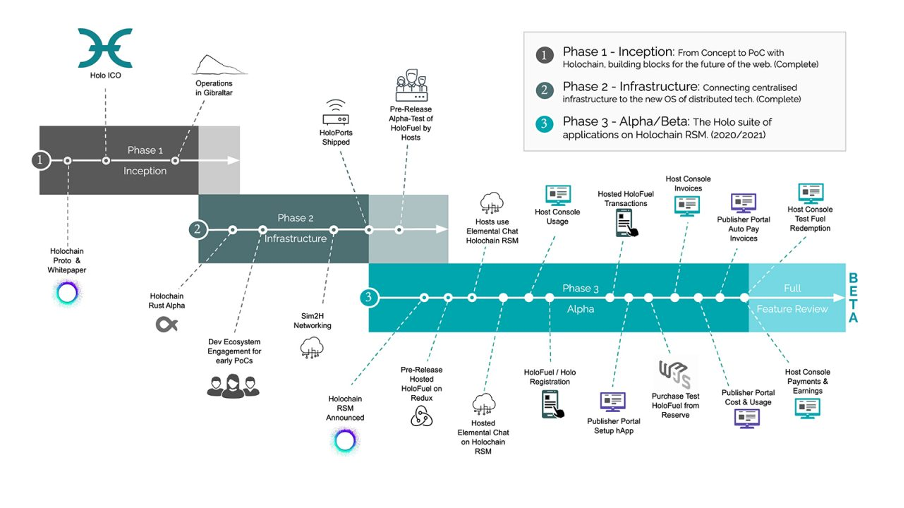
The $20 million of funds raised from the initial coin offering (ICO) was reinvested back into research and development of the Holochain infrastructure. In February 2021, the team announced through their Medium platform, an updated Holochain roadmap for when we can expect to see the launch of the mainnet. Moreover, Holochain enthusiasts are also keen to see the 1:1 token transfer from HOT tokens to HoloFuel tokens.
From Holochain’s most recent roadmap update we can expect to see the ‘Phase 3 - Alpha/Beta’ launch of the Holo suite of applications during the end of Q1 2021. The recent price action of the Holo token (HOT) appears to correlate with the prospect of more exciting updates coming soon!
Holo, Holochain & Holo Token (HOT) Summary
Holochain is presenting a new concept around distributed and decentralized technologies with the introduction of a distributed hash table (DHT). This technology, as marketed by Holochain, is ‘post-blockchain’ technology that makes use of all the advantages of blockchain. Furthermore, this is achieved without the drawbacks of many blockchains, such as high up-front costs, network congestion, and expensive gas fees as a result.
Holo works in conjunction with Holochain as a bridge to connect the distributed Holochain network and the mainstream centralized internet. Moreover, Holo also provides users an opportunity to monetize their spare computer capacity. Users can earn a passive income with crypto, receiving rewards in HoloFuel tokens, redeemable for crypto or computational power.
If you would like to learn how to purchase cryptocurrencies such as the Holo token (HOT), securely with a guided tutorial - look no further! Ivan on Tech Academy can provide you with all you need to know about safely buying and storing cryptocurrencies through our Crypto Basics course! Following this, you will have sufficient confidence to independently purchase your own crypto. If you’d like to take it one step further, see our DeFi 101 course to learn how to navigate web3 wallets on popular decentralized finance (DeFi) applications!





