The blockchain is often known as a “DLT” system. Specifically, DLT stands for distributed ledger technology, and is a digital decentralized system for verifying and recording asset transactions. This means that the system becomes more resilient, as it exists in various places at the same time.
DLT (Distributed Ledger Technology)
Anyone familiar with blockchain technology will likely recognize this definition of DLT. A previous Ivan on Tech Academy article, in which we answer “what is the blockchain”, demonstrates the advantages of distributed ledger technology in various industries. Moreover, this is primarily due to the unique and far-reaching application opportunities of DLTs.

Put simply, a distributed ledger consists of nodes that process and verify items. In doing so, DLTs generate records of various items and reach “consensus”, an agreement, on the items’ validity, or “veracity”.
This means that a DLT ledger is virtually impossible to alter after the fact, or presents an “immutable” ledger. Although these concepts may sounds mundane at first, they promise to revolutionize various types of registries and record-keeping.
Is distributed ledger technology (DLT) society’s next great leap?
The key to humanity’s success is seen by many to be our ability to effectively transfer information. Spreading and preserving information, knowledge and stories allows them to reach other individuals and live on long after us. This lays the very foundation to our civilization – spreading and preserving information means information stops being a zero-sum game.
Ledgers, by definition, store information. Long ago, this took the form of clay tablets, which eventually gave way to paper scrolls. Roughly half a century ago, ledgers began a slow shift towards digitization. This transformation is today well underway, but current electronic ledgers tend to mirror what also exists on paper.

Nevertheless, modern technology allows us to convey electronic information far more efficiently. DLT employs cryptographic techniques, along with algorithms and massive computational power to create ubiquitous digital ledgers for the 21st century.
As such, DLT can be useful in nearly every industry, from transportation to healthcare. However, the perhaps most impactful part of DLT is the advent of DLT trading.
What is DLT trading?
DLT trading constitutes all the different types of trading that involves a distributed ledger system or a blockchain. As such, this naturally includes cryptocurrency trading. However, DLT trading does not primarily focus on how individuals trade cryptocurrencies as an asset.
Rather, DLT trading is more applicable to how banks and institutions trade to transfer large sums across borders and organizations. Moreover, DLT trading is also beginning to make a mark in the world of import and export.
Put simply, DLT trading can be seen as the digitization of various trade finance processes and exchanges. Existing trade finance systems are disconnected, slow and prone to inaccuracies. This is something that can be alleviated through leveraging distributed ledger technology.
Blockchain and DLT in institutional trading
For those who truly want to understand what DLT trading is, it is important to examine the use of blockchain in financial trade. First and foremost, one needs to recognize the impact of cryptocurrencies on the financial world.

Both payments and institutional trading are quickly changing due to the advent of cryptocurrencies. Banks are currently rushing to integrate blockchain systems in their internal work processes and operations.
Moreover, well-known institutions are also shifting towards using cryptocurrencies to transfer funds. The speed and scalability of cryptocurrencies and blockchain is making this an interesting proposition to banks.
A recent study by Business Insider on “Blockchain in Banking 2020” finds that 66% of banks are exploring blockchain payments. Nearly forty percent of banks are also looking to use blockchain, or DLT, for trade finance purposes.
As anyone keeping an eye on the financial sector will know, banks seldom innovate for the sake of innovation. Instead, their eagerness to adopt DLT in their everyday operations comes down to their practical use cases.
Advantages of DLT trading
Distributed ledger technology allows individuals, groups and corporations to create comprehensive and reliable data records. Furthermore, as the case of blockchains demonstrates, these records are immutable – i.e. impossible to alter or forge.
This presents banks and financial trading institutions with a distinctive advantage. Having a reliable record of trades simplifies the process of verifying transactions. What’s more, this makes it possible to backtrack transactions to verify their legitimacy.
Furthermore, trading with cryptocurrencies is distinctly faster than using legacy methods. For example, banks that send payments across national boundaries currently rely on old techniques that are both cumbersome and slow.

The most common way to transfer payments past borders is currently using international wires with the SWIFT payment network. Although practically all banks use SWIFT, many financial trading institutions are looking for alternatives to process payments.
Cryptocurrencies, blockchains and DLT trading presents an interesting alternative that banks are looking into. These new techniques enable financial institutions to quickly transfer large sums of money across borders, with minimal fees.

Consequently, large banks are already trialing the use of blockchains and using cryptocurrencies to transfer funds. For example, banks that have made blockchain forays include well-known actors such as JPMorgan, HSBC, CitiBank and Bank of America.
Furthermore, one should not underestimate the impact of DLT trading’s cost-saving effects. Banks are not only looking to boost the speed with which they conduct payments, they also want to reduce the cost.
Using a blockchain-driven system, such as transferring large sums using cryptocurrencies, have exceptionally low fees. As such, many banks are interested in the technology and its potential use cases.

Nevertheless, DLT trading also brings another interesting advantage for large institutional clients. This is due to its immutability, which means that fraud becomes exceptionally harder to get away with. Banks are just as interested as other actors in reduding the risk for fraud, theft or other malicious forms of attack.
Trade finance processes are shifting from paper to electronic ones
As trade finance processes increasingly shift from their current paper-based, manual state to electronic ones, DLT trading will become more common. This is partly due to the
Moreover, a report from Boston Consulting Group also states that one single transaction using legacy techniques can involve roughly 5,000 different data field interactions.
Different actors and systems currently work together to provide input on e.g. insurance policies, order forms, bills of exchange, letters of credit, certificates of origin, payment confirmation and much more.
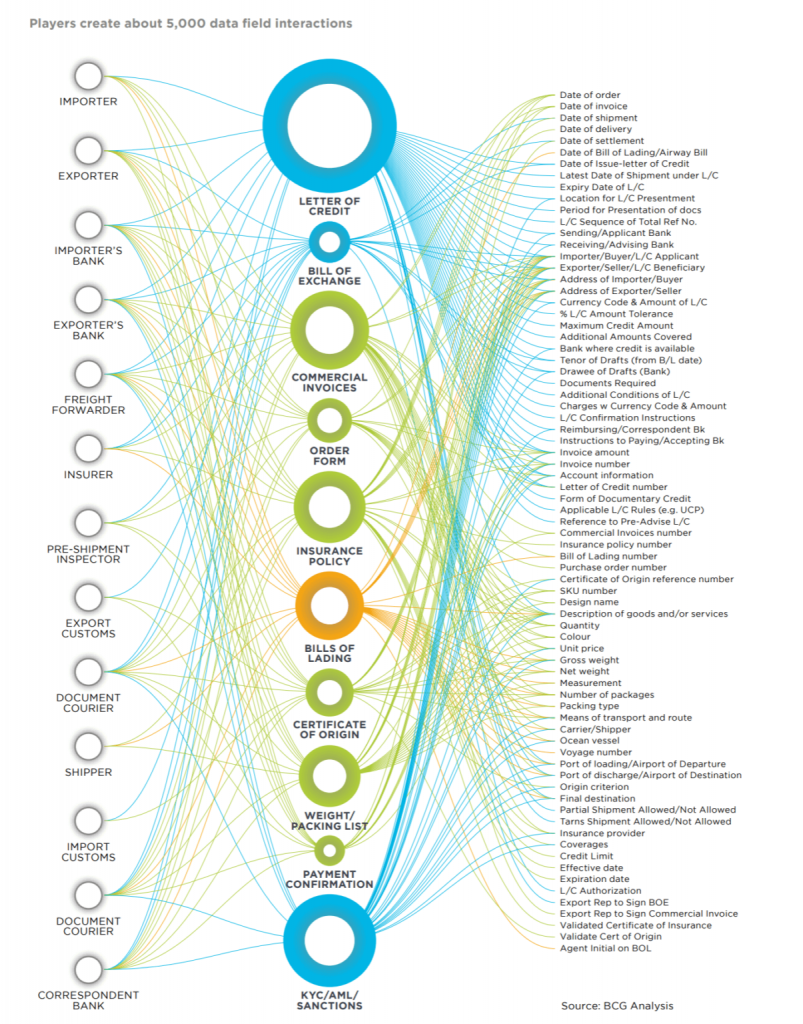
The previous image shows the various different factors that work together in legacy systems.
This clearly demonstrates the extreme complexity relating to financial documentation and trading. A blockchain system or DLT trading could solve this through massive reducing the number of participants who input data.
DLT trading summary
These examples illustrate some of the many advantages of using distributed ledger technology to do trade. In fact, DLT trading could provide comprehensive trade systems driven by the blockchain that bring about a tipping point in greater blockchain adoption.
In fact, trade processes are an excellent example of how blockchain technology can be introduced in order to simplify and unify sub-par systems. This type of shift towards blockchain and DLT will likely be seen in virtually every industry – but is perhaps most readily visible in trade finance processes.





