
Arbitrage is the process of profiting between price discrepancies of assets between different markets. It is often used in FOREX trading and can be a profitable source of passive income when applied correctly. Crypto arbitrage is no different. In fact, the opportunities afforded by the innovation in the blockchain industry has propelled innovation within the space, using arbitrage in complex and nuanced ways.
The price of cryptocurrency on exchanges is set by the price of the most recent trade. As supply and demand fluctuate, so too do the prices of crypto assets. When prices of the same asset vary from one exchange to another, this creates an opportunity for crypto arbitrage.
Arbitrage is used across many different markets, particularly in local currency exchanges. This tool utilizes a small window of opportunity whereby traders have the chance to profit from time-sensitive variations or discrepancies during fluctuations in asset prices.
Fundamentally, arbitrage is about getting the best deal in an exchange of assets by using multiple currencies or exchanges that have a different market value for the same asset. This opportunity could occur over a very brief period, however, it can create many opportunities to make profits.
In this article, we look at some of the key principles of crypto arbitrage, the different ways it can be used, and some of the risk associated. We’ll explore some of the advanced techniques used in this process and look at some of the innovative ways crypto arbitrage is used throughout the crypto space.
Before engaging in any type of crypto trading, however, you should be sure to study the basics of crypto trading. Ivan on Tech Academy has a wealth of courses touching on everything from cryptocurrency fundamentals to crypto trading, blockchain technology and much more.
What is Crypto Arbitrage?
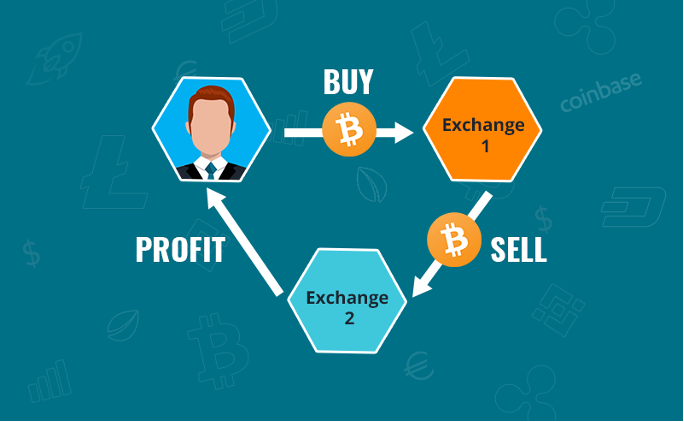
When exchanges list cryptocurrencies at different prices, this provides what is known as an arbitrage opportunity. Arbitrage is the process of capitalizing on price variations between different exchanges, which can happen simultaneously.

As an example, if a coin is available to buy on Kraken for $0.95, but that same coin is being sold on Binance for $1.00, this presents an opportunity to make gains from the difference in price by purchasing coins at a lower price from one exchange and selling them at a higher price to another exchange.
Often these price differences are small, so large amounts of funds are required to cover network fees and actually realize a sizable profit, however, crypto arbitrage has become somewhat of an art form over the years and can yield some significant profits to the eagle-eyed traders among us.
The aim of crypto arbitrage is to make profits. With so many different exchanges selling the same cryptocurrencies, there are often price differences between the platforms due to varying levels of supply and demand. Often, larger exchanges with higher liquidity lead the way for price discovery of an asset, while smaller exchanges often lag behind.
Order Books
Order books are a list of all open orders on an exchange for a particular trading pair, for example, BTC/ETH. An open order simply means a buyer or seller is waiting to make a trade at a specified price.
Cryptocurrency exchanges work using order books. Order books hold buy and sell orders for a particular asset pair at different prices. A trade is fulfilled when a buyer’s order is matched with a seller’s order. At this point, the trade is complete and the fulfilled orders are taken off the order book.
Order books are the backbone of most trading platforms and can vary from exchange to exchange, but essentially they all serve the same purpose: traders place orders in the book to buy or sell, that order can then be matched by another trader willing to buy or sell the same asset at the same price.
How Does Crypto Arbitrage Work?
In cryptocurrency, there are two predominant forms of arbitrage: simple arbitrage and triangular arbitrage. They are both similar in many ways and each requires low-latency high-speed networks.
Simple Arbitrage
Here is a typical example of simple crypto arbitrage:
You have accounts on two different exchanges, let’s say Binance and Hotbit. Both of these exchanges have many of the same asset pairs – BTC-ETH, XRP-USDT, and so on.
The order book of each exchange will have the highest bid price at the top, but the highest bid price is different on each exchange due to varying liquidity. This can cause differences in asset prices between exchanges and therefore, an arbitrage opportunity.
By purchasing the asset at the lowest ask price on one exchange, it can then be sold at the highest bid price on another exchange. Essentially what is happening here, is that the price of an asset is increasing in value on one exchange while remaining stagnant on another.
As long as there is a demand for the asset on each platform, and the ask price on the first exchange is lower than the bid price on the second exchange, an arbitrage opportunity can arise. The difference in the price at which you bought the asset and sold it is your profit, minus any trading fees of course.

Triangular Arbitrage
As the name suggests, triangular arbitrage involves three pairs of assets traded between several markets. Often utilized in currency exchanges by local market makers.
In crypto, triangular arbitrage occurs when three different assets each have different USD prices that can be used as an arbitrage opportunity. This can include both crypto and fiat assets.
It is worth noting that the more parties that are involved in a crypto arbitrage opportunity, the more points of failure that exist in the transaction.
Profiting from crypto arbitrage can seem very tempting. However, keep in mind that any and every investment opportunity comes with risk. Minimize the associated risks by enrolling in Ivan on Tech Academy and learning more about cryptocurrency trading and blockchain technology. Join over 20,000 existing students and supercharge your crypto expertise! Right now, you can get 20% off when enrolling if you use the promo code BLOG20!
Plutus
Plutus, the crypto debit card company, recently ran an arbitrage campaign whereby users of the Plutus DEX are able to sell PLU at a fixed price of $8, during a period when the market value of PLU has been significantly lower on most exchanges.

This initiative is aimed to improve liquidity for the Plutus DEX and has been an effective marketing campaign to increase adoption and bring traffic to the platform. The market price of PLU has since risen despite the ongoing campaign, indicating that this could be an effective use of crypto arbitrage beyond trading.
Though transaction limits were imposed, this campaign has given many people their first insight into crypto arbitrage opportunities while encouraging the use of the Plutus DEX. The Plutus monthly withdrawal limit was set at £200, but with gas fees relatively low, Plutus have used crypto arbitrage in an interesting way that could encourage other projects to follow suit by offering similar arbitrage opportunities.
Aave Flash Loans
Aave, one of the biggest names in DeFi, took arbitrage opportunities to the next level with flash loans. With Aave, users can create arbitrage between different assets, without the need to provide the principal amount for arbitrage to be executed.

Flash loans are designed for developers to take advantage of minor fluctuations in prices during market discrepancies using several tools in tandem to make profitable, complex trades in a single transaction.
Flash loans require a good understanding of smart contract programming and can be risky. That being said, flash loans allow users to take out a loan, take advantage of an arbitrage opportunity, repay the loan, and make a profit, all in a single transaction.
Aave flash loans require no initial capital to execute a liquidation. Users can borrow funds from the Aave platform, pay the debt back on the borrower’s behalf, then obtain the deposit and trade it for the best going price using platforms such as paraswap.io, before finally returning the assets to Aave. After any fees are taken care of, the remaining assets become your profit.
The goal is to reduce high-risk, over-leveraged positions considered to be bad for the ecosystem, promoting a safer, more secure platform for decentralized markets that protects against reckless traders.
Flash loans are open source, opening up the ecosystem to developers across the entire crypto community. This has been a catalyst for many of the recent yield farming platforms that have popped up over recent months as Aave continues to innovate the next generation of DeFi applications that could use crypto to change the global economy.
Crypto Arbitrage Considerations
When a coin is listed on a large exchange, there is often a price pump that follows. When smaller exchanges that have already listed the coin have an imbalance of supply and demand, this creates an arbitrage opportunity.
Though this may seem simple, there are inherent disadvantages in crypto arbitrage. Some exchanges inhibit arbitrage by implementing KYC restrictions, and withdrawal limits can prove to be a hurdle when moving large sums of capital. Smaller exchanges with low liquidity might also struggle to fill large orders and leave users unable to complete the arbitrage. Arbitrage can also cause complications when it comes to declaring taxes.

Slippage is another consideration to bear in mind. Slippage occurs when an order made is greater than the size of the cheapest offer on a specific order book. The result is that the order ‘slips’, costing more than initially calculated. Slippage can be extremely problematic when traders are operating on small margins on exchanges with low liquidity and can result in a loss of profit.
Arbitrage opportunities can appear all over the place at any time, so it’s important to keep an eye out for price fluctuations between exchanges. Some exchanges also come with high fees, which should be taken into consideration, particularly when making smaller transactions.
Another important thing to consider is transaction speed. The Bitcoin network is particularly slow, and therefore arbitrage opportunities are limited. By opting to use the Ethereum network instead, and even increasing fees, makes these opportunities more likely to be executed and fulfilled.
Arbitrage Bots
Timing is key with crypto arbitrage, with opportunities presenting themself for very brief periods at random intervals. Traders need to act extremely quickly to avoid missing any potential window of opportunity. This is why arbitrage bots have become so popular.
Trading bots can be programmed to execute orders on specific market conditions being met. These could be tiny movements, but if the bot is good, it can fully automate low-risk, high-volume trades to make consistent gains whenever an arbitrage opportunity arises, without you having to check a hundred charts and screens for hours each day.

Trading bots such as ZenBot are available for free, while other bots such as 3Commas are paid for. There are many different bots available on the market, choosing the right one for you will depend on the complexity of the strategy you wish to implement when trading.
Trading bots can be programmed according to a trader’s risk tolerance and strategy. For crypto arbitrage, bots provide the lowest-risk for executing these orders at the fastest speeds.
Crypto Arbitrage Conclusion
If you are an experienced trader with a strong understanding of technical analysis, and you know your way around several exchanges, capitalizing on price differences between exchanges could be a great way to earn a passive income. But if you are new to crypto and are still finding your feet, then maybe hang-fire with the trading bots until you can see these opportunities for yourself.
Paper trading is a good option for beginners to test out new strategies and techniques with arbitrage bots, without putting your real assets at risk while learning. Many trading platforms offer this service, allowing you to practice the fine-tuning of your bots before putting them to work on the real markets.
Crypto Arbitrage is generally more successful when used by experienced traders with robust strategies and a sizable amount of ‘spare’ capital. If you are new to investing and see a crypto arbitrage opportunity, consider the overall profits you will make including any transaction fees and withdrawal fees. Arbitrage works best at scale, so always be sure to do your own research and never bet the farm when experimenting with new strategies. You should also be prepared to make a large number of trades before realizing any substantial gains.

If you have experience in the crypto markets and a basic understanding of maths, with a little programming knowledge, you can create your own custom arbitrage bots. Ivan on Tech Academy has a dedicated course for algorithmic trading which shows you exactly how to set up your trading bot, use an API, and backtest your strategy on a variety of trading platforms. Want to create your own bot but have no experience at all? No problem – we have plenty of beginners courses to get you started!





