In this "Polkadot vs Cardano" article, we'll examine the differences between Cardano and Polkadot based on their mission, architecture, tokenomics, governance, and ease of product development. However, before we compare the two, let's break them down individually.
What is Cardano?
Cardano is a blockchain that uses a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm. We won't dig too deeply into this feature since we've covered it extensively in the Moralis Academy blog. For now, understand that Bitcoin uses a proof-of-work (PoW) algorithm. PoW is computationally intensive and consumes lots of energy. On the other hand, PoS consensus mechanisms use validators and are more friendly to the environment.
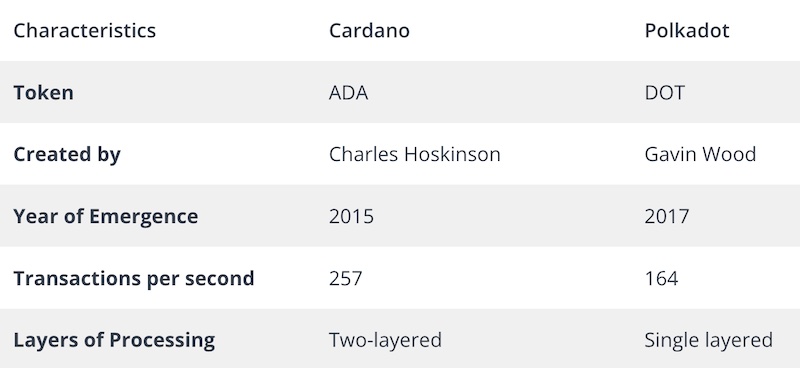
Cardano founder Charles Hoskinson was initially a co-founder of Ethereum. In September 2015, Hoskinson launched Cardano as an open-source, decentralized blockchain. Cardano is a third-generation blockchain and enjoyed a significant rise in capitalization through 2021.
To clarify the generations, Bitcoin is first-generation blockchain technology. More importantly, while Bitcoin is powerful, it has limited transaction capabilities. Ethereum, on the other hand, has revolutionary features that land it in the second-generation blockchain category. Its innovative smart contracts allow users to transact safely and automatically.
Cardano offers a solution to the bottlenecks common in first and second-generation blockchains. Therefore, it falls in the third-generation blockchain category. Cardano developers discovered mathematical solutions to overcome some of blockchain's security vulnerabilities. They accomplished enhanced productivity by separating the computational layers from the accounting layers, reaching a level of scalability that neither Ethereum nor Bitcoin can rival.
So, let's take a deeper dive into some of these third-generation technologies.
Cardano's Technology
Cardano's blockchain architecture is two layers deep:
1. Cardano Settlement Layer (CSL)
CSL is the first layer of architecture where peer-to-peer transactions occur. It uses the Plutus and Marlowe scripting languages to transfer value. Cardano also uses the "Ouroboros" consensus mechanism, which is different from what previous blockchain generations used.
2. Cardano Computation Layer (CCL)
CCL assists in replicating "Rootstock" from the Bitcoin ecosystem and helps scale specific protocols.
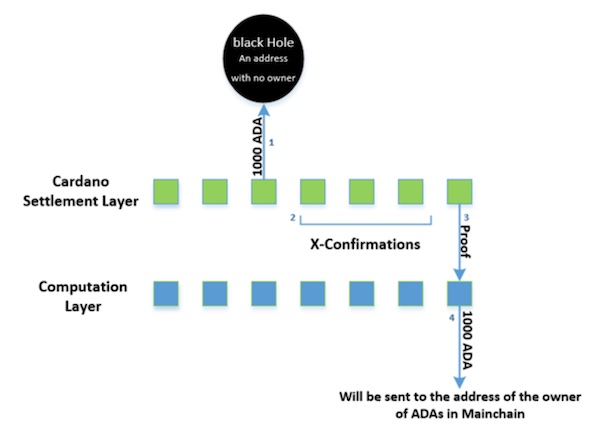
Because these two layers remain separate, smart contracts can execute independently without getting shackled by transaction verification requirements.
If the study of Polkadot vs Cardano feels too advanced for you, please take the Crypto for Beginners course at Moralis Academy. This class will give you a strong foundation in how blockchains work.
What Makes Cardano Different?
First, Cardano uses a form of the POS consensus mechanism making it more energy-efficient and "greener" than other blockchains such as Bitcoin that use the POW algorithm.
Second, Cardano has two layers. The settlement layer handles transactions with ADA, its native coin. The computation layer enables smart contracts and works identically to Ethereum. Thus, Cardano offers a double-layer alternative to the strained Ethereum ecosystem.
Third, KMZ sidechains let users bridge to Cardano and other cryptos. This protocol allows ledgers to communicate with the CSL without exposing a user's sensitive information. Secure transfers from the CSL to a CCL or any blockchain using KMZ are possible because of the KMZ sidechain protocol.
Lastly, Cardano uses the Plutus language for smart contract development and Marlow for non-programmers. These options bring a user-friendly approach making it more accessible for businesses.
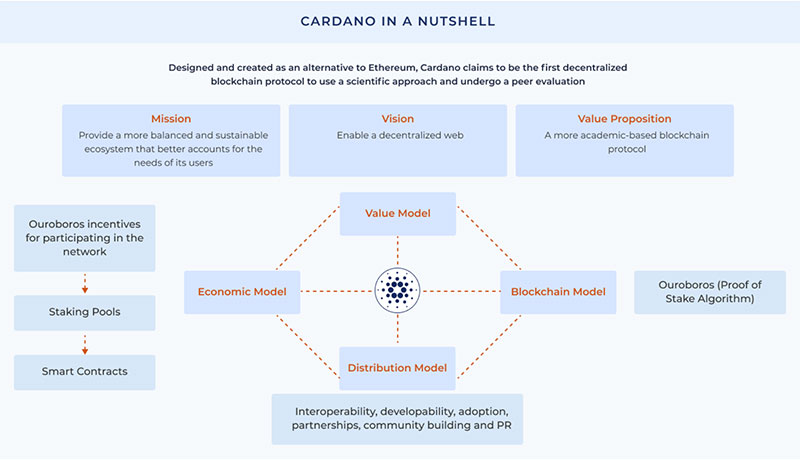
Cardano's Scalability
As the number of network validators grows, Cardano's scalability also grows. Charles Hoskinson developed the "Epochs" system that divides validators into blocks and assigns slot leaders to each. Slot leaders have the authority to mine, validate, and post transactions to the appropriate blocks.
Further, Hydra is Cardano's layer-2 solution that helps scalability. The goal is to lower fees and overcome insufficient storage issues. These features are appealing, especially for larger firms.
Find out how Ukrainian citizens are surviving the Russian invasion with crypto. Learn more in our "Ukraine and Cryptocurrency" article.
Cardano's Governance
Cardano's governance mechanism (Cardano Foundation and Input Output Hong Kong) is off-chain like Ethereum's. Charles Hoskinson is also the CEO of Input Output Hong Kong (IOHK), an R&D company committed to the development of peer-to-peer blockchain innovations.
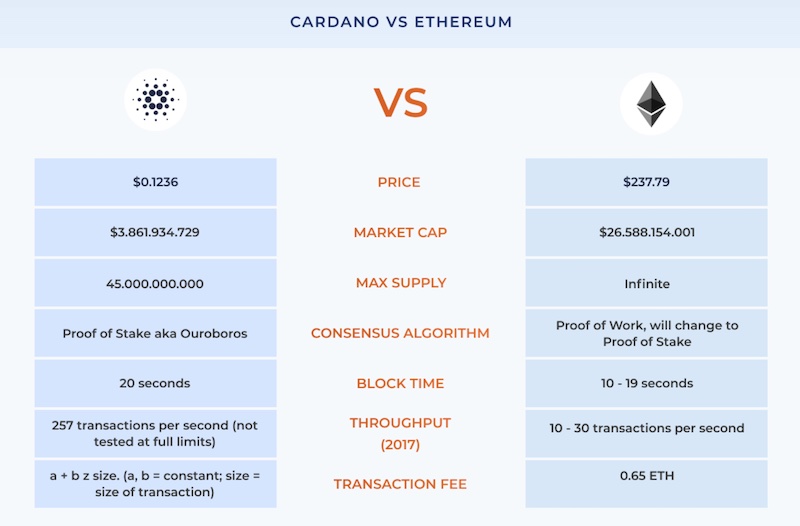
Cardano vs Ethereum
Ethereum and Cardano are similar in how they help their users build tools and protocols. However, Cardano has better scalability potential and advanced security measures that Ethereum will probably never attain.
Cardano offers two architectural levels to Ethereum's one. Further, Cardano's consensus mechanism allows for far more transactions per second (TPS) than Ethereum.
Everyone is complaining about the downturn in the crypto market. Learn how to survive a bear market in our Moralis Academy blog article.
Is Cardano the Next Ethereum?
Will the widespread use of Ethereum suddenly transition to Cardano because of these improved features? It's unlikely. Since thousands of blockchain developers are already familiar with Ethereum, they're less likely to migrate. But, Cardano has some compelling advantages that can serve to carve out a niche in the blockchain development market in the future.
Cardano likens itself to being the equivalent of Ethereum 2.0 ahead of Ethereum engineers who are still making the necessary changes on their march to version 2.0. Cardano is already there with its two-layer architecture. Now, let's move on to Polkadot.
Ready to dig deeper? Learn about Ethereum at Moralis Academy!
What is Polkadot?
Polkadot is a Web3 Foundation project led by Gavin Wood, another Ethereum co-founder. At this point, you've probably noticed that the founders of Cardano and Polkadot are from the original Ethereum team.

Web3 Foundation exists to disrupt Web2's big-tech monopolies with individual empowerment. Polkadot founders consider it to be a third-generation blockchain. This protocol can link numerous chains into a single global network with "DOT" functioning as the network's token.
From the outset, Polkadot's architecture ensures that core programming work for dapp development remains as simple as possible. So, what features make Polkadot another potential Ethereum killer? Furthermore, can it revolutionize and transform blockchain development?
Some predictions estimate that the Polkadot blockchain will be able to handle over 1,000,000 TPS one day. That would be quite an improvement from Ethereum's present rate of approximately 30 TPS. It's no wonder that businesses comfortable with fintech solutions will naturally feel more affinity with Polkadot because of the innovative network infrastructure.
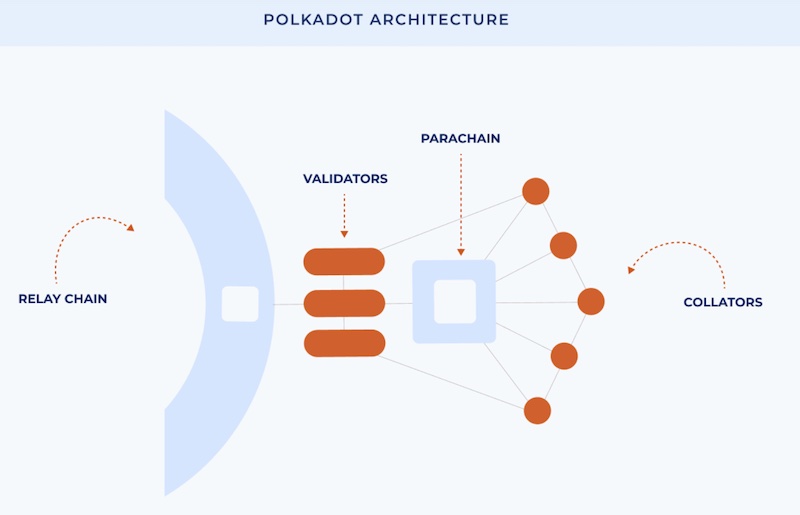
Polkadot's Relay Chain
Polkadot's Relay Chain is its hub that ensures flawless interoperability and security for its linked blockchain products. These include multiple parachains, dapps, exchanges, and services.
Polkadot is unique because it blends a network of parachains and parathreads which are blockchains themselves. Moreover, Polkadot's RelayChain connects and secures these chains. These parachains can also join external networks through bridges. Because of this design, Polkadot adds lots of flexibility to its mission to connect blockchains.
Notably, with its blockchain solutions, Polkadot delivers a hassle-free project launch to developers without overloading the performance of other projects. Also, projects built on Polkadot can first test on Kusama to emulate real-life conditions and nip any problems in the bud before launching.
Finally, its advanced scalability and security features put Polkadot in the running to be the most robust platform in the blockchain sector.
Blockchain gaming is booming with loads of new exciting projects on the horizon. Learn about the top gaming tokens at Moralis Academy!
Polkadot's Primary Components
1. RelayChain
RelayChain is the main chain where Polkadot validators stake their tokens. In addition, RelayChain validators can validate parachains (see below). At all times, RelayChain exchanges information quickly with parachains.
2. Parachains and Parathreads
These "para" names derive from chains running parallel to RelayChain. Furthermore, their parallel nature enables more significant transaction processing and scalability for the ecosystem.
A parachain is a single blockchain that resides in Polkadot's ecosystem. Parathreads, on the other hand, provide value because of the lack of availability of parachains. Parathreads are more economically feasible because their fixed registration price is lower than obtaining a parachain slot.
In addition, a Polkadot DeFi parachain will reside on top of these parachains to accommodate applicable DeFi projects. Likewise, an NFT parachain will contain associated digital assets like games.
3. Bridges
Another significant Polkadot component is its bridges. Parachains and parathreads can communicate with other external networks such as Bitcoin using bridges.
Polkadot's Governance
When considering the Polkadot vs Cardano debate, we must note that, unlike Cardano, Polkadot uses an on-chain governance mechanism where the community can stake DOT tokens to participate and vote on initiatives.
Moreover, many crypto projects use decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) to provide community governance. If you'd like to learn how to create a DAO, be sure to read the relevant article on our blog!
Polkadot vs Ethereum
Since both Polkadot and Ethereum share founding members, let's see how they differ. Both projects have an identical mission and promote dapp development. Ethereum's primary tool is smart contracts, and Polkadot focuses on helping developers build and integrate entire blockchains into the mainnet.
Further, Polkadot's parachain structure makes it much faster than Ethereum. However, we'll see how that holds up as Ethereum's layer-2 solutions evolve and the march to ETH 2.0 upgrades winds down.
Polkadot vs Cardano - Notable Differences
An exciting caveat about the projects is that both founders are former Ethereum co-founders. So, inevitably, it seems logical that both projects will seek to remedy whatever shortcomings these two perceive in Ethereum.
First, Gavin Wood was interested in research and development. On the other hand, Hoskinson wanted to monetize Ethereum's innovative technology and change it to a for-profit organization. Regarding the similarities, both Gavin Wood and Charles Hoskinson wanted to solve Ethereum's bottleneck issues. However, they went about it in different ways. Below are some of the differences:
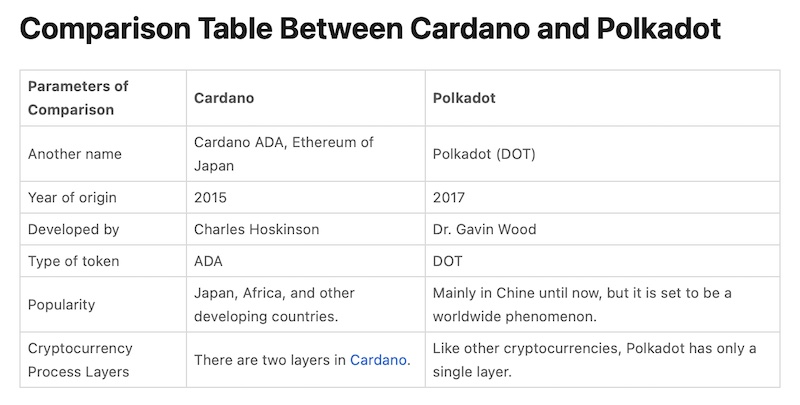
1. Infrastructure
Cardano has a double-layer infrastructure, while Polkadot enables multiple blockchains connected to a single mainnet.
2. Strengths
Polkadot's strengths are endless scalability and sustainability, while Cardano's upside is high transaction speed with low (or zero) transaction fees.
3. Mission
Cardano seeks to build an upgraded network essential for dapp development, while Polkadot strives for better functionality and interoperability between blockchains.
4. Tokenomics
Cardano's ADA token supply is capped at approximately 45 billion, while Polkadot's DOT token has an unlimited supply. However, DOT holders lose 10% from inflation each year. Thus, wealth preservation strategies include staking their tokens on the Polkadot network for a 10-15% APY to offset inflation.
In sum, Polkadot and Cardano are pursuing different strategies for the long run.
Polkadot vs Cardano - Which is Better?
"Better" is a challenging claim to prove because it's a subjective term in many cases. Developer and user preferences will come into play along with tribalism amongst community members when determining which one is better.
First, both perform well as third-generation blockchain solutions. Cardano fans believe its infrastructure is better with its two-layer design, while Polkadot supporters consider its ecosystem more friendly for developers.
Polkadot has technical features that some consider superior to Cardano. For example, both use a version of the PoS consensus mechanism, but Polkadot has a network of unified, multiple blockchains under one network. This feature makes its infrastructure more flexible.
Polkadot has more projects currently functioning, but many believe Cardano is more friendly to the environment. Furthermore, they think its operations are more resilient and sustainable in the long run in terms of functionality and infrastructure. So, they feel that Cardano has the chance to become the all-in-one blockchain solution.
Polkadot, Cardano, and Ethereum
Two of the masterminds behind Ethereum created Polkadot and Cardano to resolve Ethereum's limitations. So, it's only natural to include Ethereum in this comparison mix.
Polkadot and Cardano have better throughput and lower fees than Ethereum and some innovative features that Ethereum lacks. However, both are still new, so it's hard to predict future sustainability and how tolerant these chains will be to increased demand.
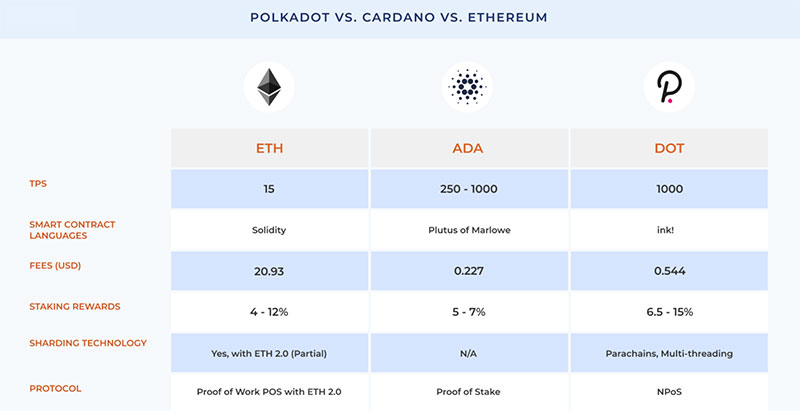
Also, it's unlikely Cardano or Polkadot can ever catch up to Ethereum's years of widespread adoption. More importantly, the Ethereum 2.0 upgrades seek to resolve the problems that Polkadot and Cardano remedy. So, will all of the hard work that went into Polkadot vs Cardano be for nothing?
Polkadot vs Cardano - Conclusion
Both Cardano and Polkadot show promise for blockchain integration with their inexpensive transaction costs and consensus mechanisms. Polkadot leads Cardano in its current progress, with Cardano playing "catch-up" by allowing its users to pay transaction fees in whatever token they're transferring.
While Cardano and Polkadot are still relatively new projects, adoption rates will vary depending on how quickly each project manages unforeseen challenges. Both networks are faster than Ethereum but are still quite a ways away from any semblance of global adoption. Further, to compete with traditional payment systems such as Visa or Mastercard, they'll need to bump up speeds up to 5,000 TPS.
If blockchain technology interests you and you'd like to dive into a newly emerging field, learn how to start a blockchain career by joining Moralis Academy today!