
The application of smart contracts will disrupt the mergers and acquisitions, or M&A, industry. In the process of an M&A transaction, many different parties are involved, like investment bankers, lawyers, and auditors. Those intermediates become at least reduced through the blockchain technology. Furthermore, smart contracts make the transaction programmable and offer many other benefits like accuracy, automation, speed, and cost reduction. How a cost reduction could affect the M&A market is challenging to predict.
One possible outcome is that investors have more capital available for other transactions. This would possibly increase the number of M&A transactions overall. Another likely scenario is that through a cheaper process, investors with smaller capital try to get into the market and increase competition. Eventually, smart contracts reduce the risk for investors because they can build trust beforehand. Finally, smart contracts automate the transactions itself, securing both parties that payments and assets change hands as programmed.
The Nature of M&A Transactions
Since 1985 M&A transactions are rising in number and value. Innovation cycles are shortening, and big companies are forced to buy new ideas strategically as they are not able to keep with smaller but more focused teams.

Therefore, the assumption can be made that M&A transactions will rise in both the number and value in the future and will stay an essential strategic approach for corporations due to the pace of technological development. Despite the general risk in M&A transactions, such as finding the right target, the process itself is expensive as well. A lot of different parties are involved to ensure all sorts of quality measures. Table 1 presents an overview of those involved parties.
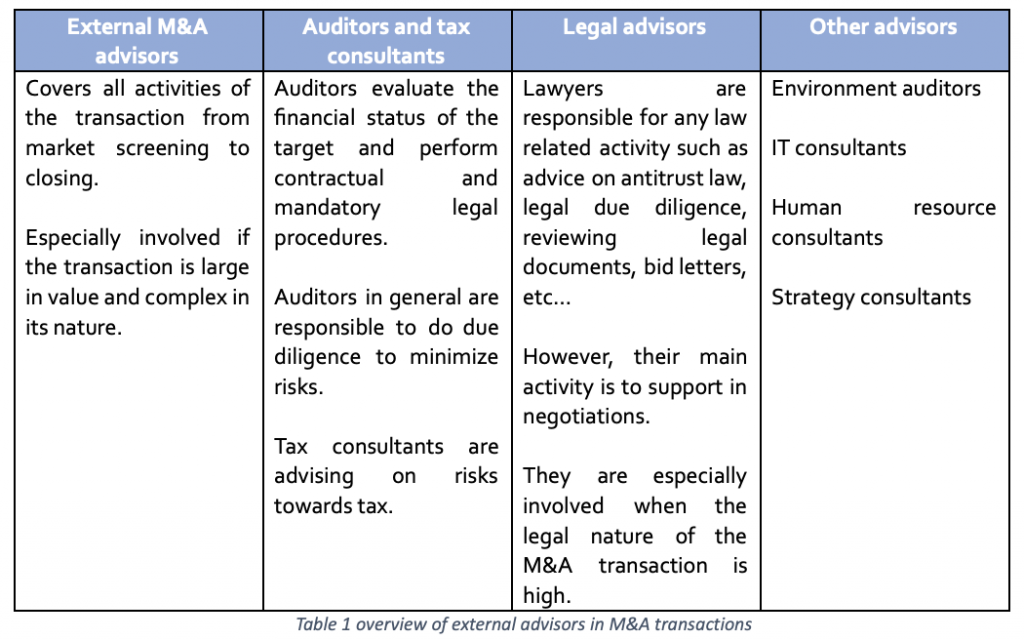
Additionally, to match the regulatory hurdle, M&A transactions swallow a lot of resources. Most of the time the process takes longer than expected and the costs are higher than planned. According to Bain & Company, the scrutiny of M&A transactions is increasing, especially in the tech sector due to their impact on data ownership and their impact on the competition in the market (e.g. monopoly). Therefore, matching the hurdle of trust between all the involved parties is the key to a successful M&A transaction (Figure 1).
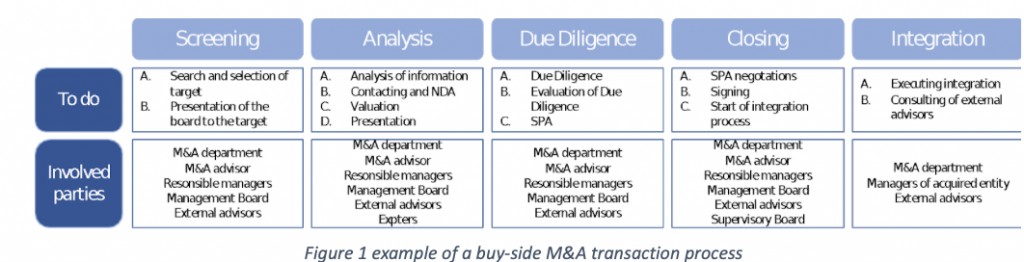
*SPA = Share Purchase Agreement; Letter of Intent = contains information about shares
The Essence of Blockchain Technology
The blockchain technology seems to be the major innovation in the last decade. Although there are and were a lot of critics about the scalability and its practical application the technology has proofed that it will play a major part in the future. There are many use cases for the blockchain technology today, mostly in the financial industry and in any supply-ish scenarios. The blockchain forced its way into the broader technology space because of its advantages and business opportunities outweigh its cost and risk. But still, people have problems to understand what the blockchain is:
“In very simple terms the blockchain is a digital information which is shared by society. This information becomes regularly updated, which adds a new block. Due to this setup, everyone within the society has all the information available and do not have to trust someone else regarding the information.”
A more advanced definition is that a blockchain contains a network of nodes. Every node has a copy of the blockchain stored locally. If participants want to add transactions to the network, they need at least half of the approval of all nodes. All unconfirmed transactions become stored in the mempool of the nodes. Miners then pick transactions out of the mempool to fill their block which they want to add to the network. Through a mathematical process, also called hashing, the miners are adding the block to the network and get rewarded.
Although the second definition is much more sophisticated than the first, there is still much more to it. However, for the article, it offers a solid ground, but I add some context, where I think, the blockchain technology is currently in comparison to the internet. At the beginning of the internet, there were no motions, maybe some pictures but no videos. This was approximately 25+ years ago, it lacked standards and therefore, development was difficult. However, when the internet entered the second stage (Web 2.0) it started heavily to spread.
In blockchain technology, there are similar developments. First, there was just the possibility of tracking transactions in the blockchain (Blockchain 1.0). Now smart contracts are crucial as they enhance the usage of blockchain technology (Blockchain 2.0) because different protocols can be connected.
With this background knowledge, it is easier to understand the advantages and drawbacks of the blockchain technology, which are discussed briefly in the table below:
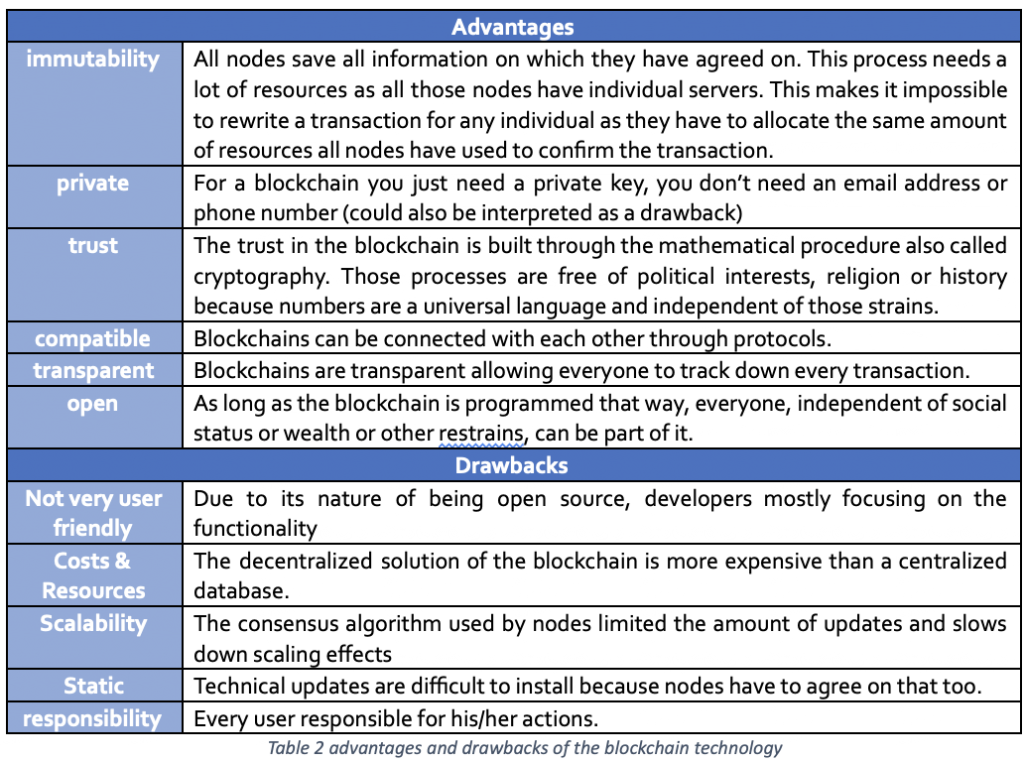
The blockchain is (usually) a public decentralized database which stores all transactions initiated by the participants. Hashing algorithms make it impossible to change already approved transactions. Therefore, no intermediates are necessary to identify the ‘true’ information and to build trust. Trust is built through the mathematical process.
How Smart Contracts Work
In the first section, I explained that many parties are involved in M&A transactions to solve the problem of trust. A simple example is that a merger can be statutory, meaning that the target is fully integrated and does no longer exist. Or the two entities could join and build a completely new company, or the target company could become a subsidiary of the acquirer. Additionally, they also have to think about the payment which could be in cash, securities, or some kind of mixed offer and when certain payments are due. All of that involves a lot of third parties from investment banks, to audit firms and lawyers. The blockchain technology will have a major impact on those roles and will at least change them. Smart contracts allow participants to hard code contracts. From a technical standpoint those are Aristotelian syllogism which means nothing else than if one party fails to do something, then else happens. A simple example in M&A transactions could be, if the acquisition does not pay X amount of cash to a specific date, then he/she has to pay interest or (else) taken to court. Smart contracts are running on the blockchain making it possible to execute them autonomously.
A simpler explanation of smart contracts helps to gain a deeper understanding of the potential. As with every contract, a smart contract also needs two involved parties. The parties stay anonymous and the contract is stored on the blockchain. The smart contracts entail triggering events like deadlines of a certain payment. Figure two shows all the benefits smart contracts are offering.
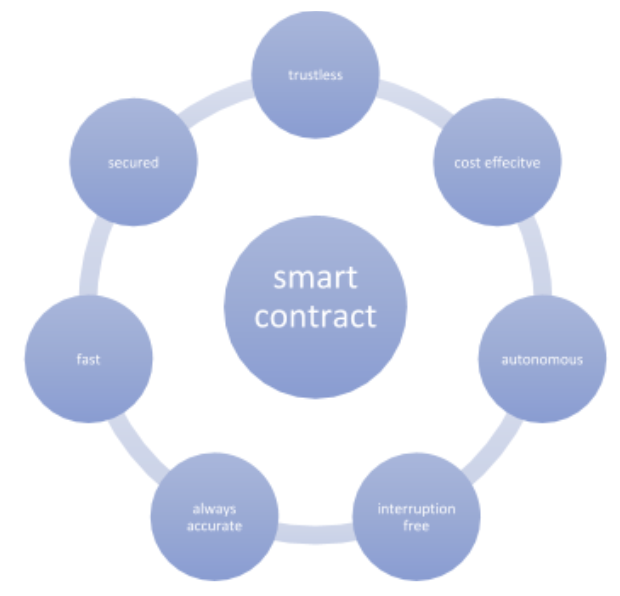
Figure 2 The benefits of smart contracts
Disruption in M&A – The Advantage of Smart Contracts
The application of smart contracts in M&A transactions could lead to disruption as investors have to rethink how they value targets and assets. The automation potential as well as autonomous benefit opens up investors to ensure that there are no hidden liabilities and risks. Here, the programmability of smart contracts is crucial for the decision as investors can program certain rules important to them for the deal. If the condition is not met, the M&A transaction could be postponed or discontinued.
Simply, smart contracts reduce the counterparty risk and allow investors to develop more trust before they even start to negotiate with the target. The technology comes in handy especially when there are not many comparable companies or deals. For example, to evaluate a furniture manufacturer in Uganda is difficult as the country does not provide many comparables. A thesis which suggests that the application of smart contract is useful in M&A transaction involving countries in which macro and microeconomic measures are very difficult to predict.
Another point is the disruption of intermediates in M&A transaction through the blockchain technology. Through the reduction of intermediates, the costs of M&A transactions might lower, allowing investors to secure money for other investments. However, one could also argue vice versa – when the cost of the deal process decreases other investors might enter the market driving the price higher of the target. It is difficult to predict how the market equilibrium of M&A transactions will develop and how that affects individual deals as there are so many different factors influencing success. Overall a few statements can be made about how smart contracts possibly affect M&A transactions.
Conclusion: How Blockchain Will Improve The M&A Industry
- The number of intermediates will be reduced, fewer parties will be involved in M&A transactions
- The reduction of intermediates will make M&A transactions “cheaper”.
- A cheaper price could mean that investors have more capital to execute other deals which might increase the number of overall deals.
- A cheaper price could mean that more investors are competing for the same target because of investors with smaller capital entering the market. This could redo the price reduction after all due to increased competition in the market.
- Smart contracts will reduce the risk for investors of making a wrong decision because trust can be built beforehand.
- The transaction itself becomes much more manageable and secure due to the benefit of autonomous execution.
It can be said that the disruptive power of smart contracts will change this certain industry as blockchain technology does already with the financial industry. Considering where we started with the internet, I am excited to see to what extend the blockchain technology will impact businesses in the future. The internet opened up us to so many opportunities and great challenges and I hope the same will happen with blockchain technology.
Don’t trust – verify.





