Ethereum (ETH) is the second-largest crypto on the market, right after Bitcoin (BTC), and it’s been going through some massive changes recently. After the Ethereum Merge in September 2022, Vitalik Buterin, one of the founders of ETH, introduced an updated Ethereum roadmap. The Merge was an essential milestone in the Ethereum roadmap and entirely changed the Ethereum blockchain’s consensus mechanism. However, Ethereum still has numerous issues, such as high transaction fees and a relatively slow transfer time of several minutes. Also, ETH can only process around 15 transactions per second, which is extremely low compared to the network’s popularity. These issues often cause high network congestion on the Ethereum blockchain, and the various phases of the Ethereum roadmap aim to solve them. The ultimate goal of the Ethereum roadmap is to transform the network into an extremely efficient and lighting fast blockchain ecosystem.
This article will look closely at the post-Merge Ethereum roadmap to determine the subsequent Ethereum development phases. We’ll take a detailed look at the Ethereum roadmap phases and determine what each will bring to the ETH ecosystem. Stay with us at Moralis Academy to find out more about the post-Merge Ethereum roadmap.

Moralis Academy’s Ethereum 101 course will help you learn everything you need about the world’s second-largest cryptocurrency. This course lets you know what Ethereum is, how it works, and its key features.
The Ethereum Blockchain
Before we dive into the particular phases of the Ethereum roadmap, let’s have an overview of the Ethereum blockchain and its key features.
Ethereum was launched in 2015 by a diverse team of blockchain enthusiasts, including Vitalik Buterin, one of the key personalities of the Ethereum project. The Ethereum blockchain was the first crypto project to introduce smart contract functionalities to the crypto market. These contracts are self-executing pieces of programming code that allow developers to automate key application features. The introduction of smart contracts was essential to the Ethereum blockchain’s popularity because it allowed developers to create decentralized apps (dapps). Instead of using centralized programming resources, Ethereum gave developers a decentralized blockchain programming architecture. Developers could host their dapps on the Ethereum blockchain and use the Ethereum programing language Solidity to create dapps.
Instead of just offering digital cash features like Bitcoin or Litecoin, Ethereum was more of a blockchain programming ecosystem. Soon enough, thousands of developers flocked to the ETH blockchain with different dapp projects. Decentralized exchanges (DEX), DeFi protocols, and NFT marketplaces are just some of the many types of Ethereum dapps.
Furthermore, Ethereum enabled developers to launch their cryptocurrencies on top of the Ethereum blockchain. Developers don’t need to invest vast funds and create separate blockchains. Instead, they can use the Ethereum network and launch their crypto projects as ERC-20 tokens. There are thousands of ERC-20 tokens on the market, and numerous popular cryptocurrencies use Ethereum. Projects like Decentraland (MANA), Chainlink (LINK), The Sandbox (SAND), and various others are ERC-20 tokens.
Also, Ethereum introduced non-fungible tokens (NFTs) with the ERC-721 token standard. Ethereum’s NFT token standard paved the way for the massive popularity of NFT collections, marketplaces, and NFT utility.

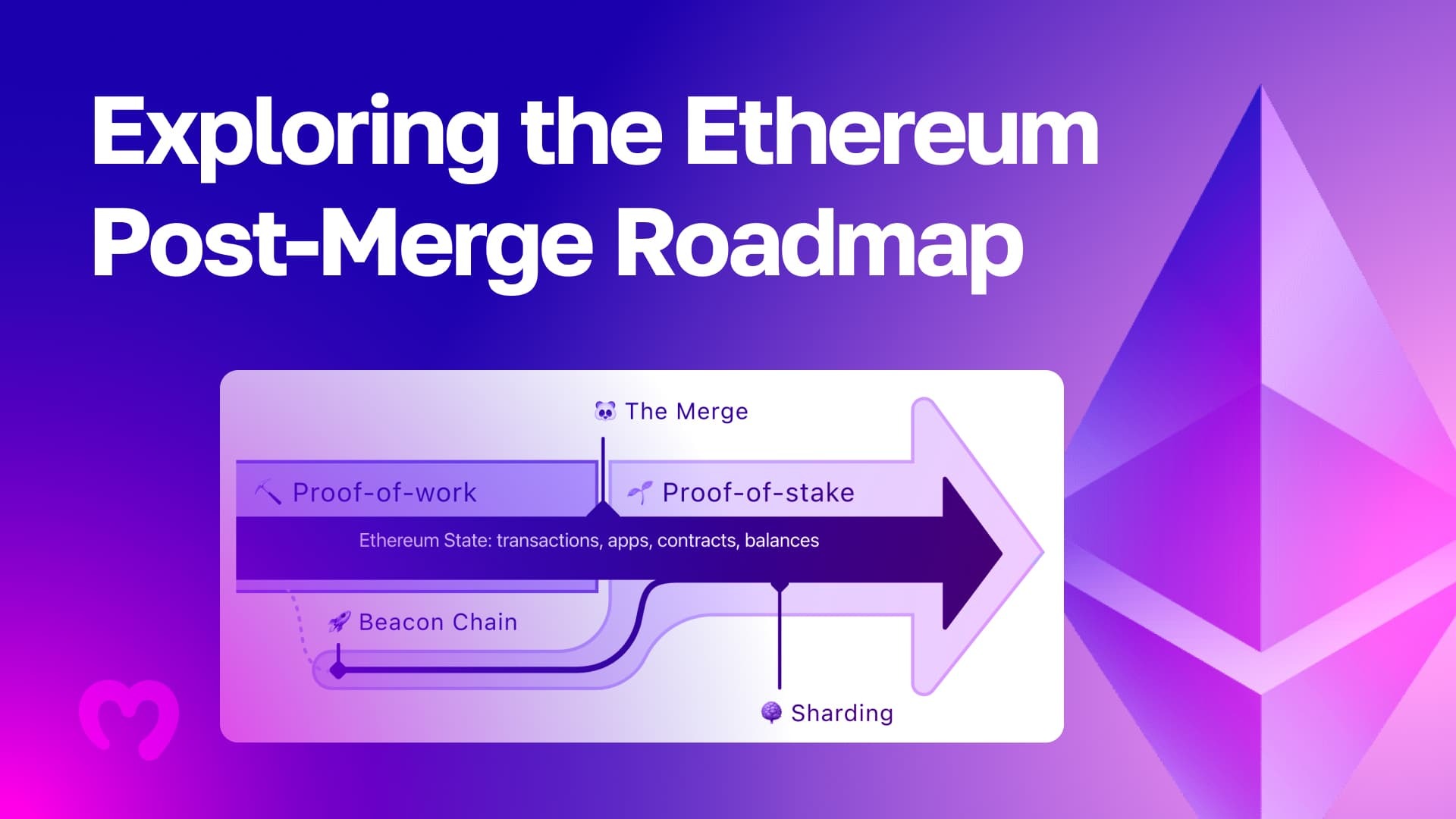
The Merge
The Merge is an essential development phase of the Ethereum roadmap that took several years for the developer team to implement because of its complexity. Ethereum initially used a Proof-of-Work (PoW) blockchain mechanism similar to Bitcoin until September of 2022, when the Merge happened. The Merge phase of the Ethereum roadmap moved the blockchain to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism.
The PoW blockchain architecture relied on the use of Ethereum miners to process and approve transactions. Miners used their mining hardware to find the correct hash for each ETH transaction, which required a vast amount of electricity. Also, mining ETH was expensive because efficient mining hardware was very pricey.
At the same time, Ethereum transaction time was pretty slow compared to some new blockchains. Competitors like Avalanche (AVAX), Polygon (MATIC), Solana (SOL), and others process transfers within a few seconds, and their transaction fees are a fraction of a US dollar. Unlike Ethereum gas fees that can cost several tens of USD regularly.
The Merge was the first step of the Ethereum roadmap to making Ethereum far faster, more efficient, and cheaper in the long run. The Merge moved ETH to a PoS mechanism, eliminating miners’ roles. Instead of miners, Ethereum network nodes with a stake of at least 32 ETH became responsible for validating transactions. Everyday crypto users can now stake their Ethereum through various crypto exchanges, wallet providers, and DeFi platforms that offer these services. In return, users can earn Ethereum staking rewards.

Blockchain technology can be challenging to understand because of the numerous types of blockchains and specific crypto terms. Moralis Academy has numerous blockchain guides and a handy guide on crypto terminology to help you enter the world of blockchain technology.
Post-Merge Ethereum Issues
Although the Merge lowered Ethereum energy consumption by more than 99 percent and successfully shifted to the PoS mechanism, it highlighted some key issues. Since running an Ethereum PoS node requires a stake of 32 ETH, only users with considerable funds can run nodes. Data shows that five entities control as much as 60 percent of all staked Ethereum. A few top centralized crypto exchanges manage about 30 percent of staked ETH.
Furthermore, two addresses processed around 40 percent of post-Merge ETH transfers at the end of September 2022. About 73 percent of Ethereum blocks comply with the US Office of Foreign Asset Control (OFAC) standards. In short, this means that a considerable portion of Ethereum transactions is subject to screening. Transactions whose senders or receivers don’t comply with OFAC standards can be blocked.
These statistics raise the question of network centralization and censorship in the post-Merge phase of Ethereum.

The Moralis Academy’s Crypto for Beginners course is a great way to learn the basics of cryptocurrencies. This course teaches you key crypto concepts and how digital currencies work.
The Updated Ethereum Roadmap
Due to the post-Merge issues regarding centralization of transaction processing and censorship concerns, the Ethereum team decided to update the Ethereum roadmap. Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin recently announced the introduction of a new phase of the Ethereum roadmap called the Scourge.
By introducing the Scourge, the total number of remaining Ethereum development phases grew to five remaining milestones.
Surviving the crypto bear market can be difficult if you don’t have a plan. Moralis Academy’s guide on how to invest during a crypto bear market will introduce you to several trustworthy tactics for making it through crypto winter.
The Surge
The next phase of Ethereum’s development after the Merge is called the Surge. The main goal of this development phase is to dramatically increase the Ethereum transaction per second (TPC) capacity. The network’s TPS capacity will grow from the current 15 to a projected 100,000 TPS. This will immensely increase the scalability of Ethereum and make it fitter for mass use by millions of users around the world simultaneously. One of the critical issues of Ethereum is network congestion. At the time of Ethereum’s launch in 2015, no one could anticipate how popular Ethereum would become in the future. However, now thousands of developers use Ethereum, and millions of users utilize Ethereum dapps. Because of this, the increase of the TPS capacity is the top priority of the Ethereum developers.
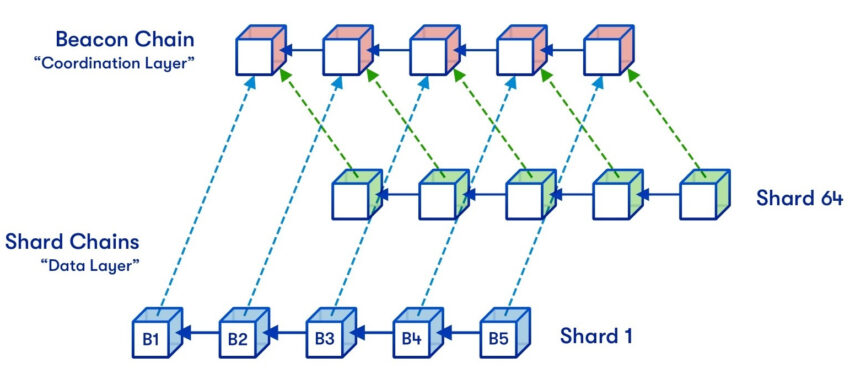
The Surge will use sharding to improve Ethereum scalability. Sharding splits transaction data across multiple shard chains that act as secondary Ethereum blockchain layers. The total TPS will dramatically increase by taking a considerable portion of the weight off the Ethereum blockchain’s primary layer.
The Scourge
Initially, the Scourge wasn’t a part of the Ethereum roadmap. However, the Ethereum team decided to introduce this additional development phase because of the post-Merge censorship and centralization issues. The main goal of the Scourge is to ensure that the Ethereum blockchain stays decentralized and to disable any potential discrimination of transactions. Censoring transactions based on sender and receiver data is fundamentally against the principles of Ethereum. The Scourge will introduce credibly neutral transaction inclusion protocols to prevent network nodes from censoring specific transactions. The nodes won’t be able to discriminate against or for certain parties and will have to process all transfers that fulfill network requirements.
The Scourge will also stop prioritizing transactions with higher fees by network nodes. In turn, this will make it pointless for users to compete with each other by adding high gas fees to transactions. The network will process transactions according to the order of their initiation.
JavaScript is a crucial Web2 programming language for learning more advanced Web3 programming languages such as Ethereum’s Solidity. Moralis Academy’s JavaScript Programming 101 course will help you start your Web3 developer career.
The Verge
Currently, running an Ethereum node is very demanding regarding hardware. Full node operators need to download a full copy of the Ethereum blockchain, which takes up vast amounts of hard drive space. Node operators must have a lot of network bandwidth and keep their computers operational 24/7 to process transactions and update their copies of the blockchain constantly. The Verge will considerably lower the hardware requirements for running Ethereum nodes. Users will validate Ethereum transactions without downloading a complete copy of the ETH blockchain on their devices. Node operators will process transactions primarily with their RAM, contributing to the network’s decentralization.
The Verge will achieve this by introducing Verkle Trees, which will optimize blockchain data storage and the size of nodes. Additionally, the Verge will introduce the Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge (SNARK) upgrade to increase user anonymity.

Ethereum is one of the leading blockchains for building decentralized applications. Moralis has a thorough guide on how to build an Ethereum dapp in 5 steps to help you set up your Ethereum Web3 project.
The Purge
During the Purge phase, the Ethereum team, will go through all aspects of the blockchain to eliminate everything contributing to network congestion. This phase will simplify Ethereum gas mechanics and eliminate most gas refunds that unnecessarily take up storage space. Also, the developers will delete useless historical data and irrelevant data tied to transactions. There are numerous layers of unnecessary data on the Ethereum blockchain, and it will be pretty challenging to locate and delete all of it. New node operators will no longer need to store historical data after the Purge. Instead, they will only keep blocks from the most recent checkpoint block. Users who wish to access historical data will still be able to do so, thanks to specialized full-sync nodes that keep data from the Ethereum genesis block.
The Purge will make the Ethereum blockchain lighter and more versatile. In terms of scalability, the Purge will improve network speed and capacity.
The Splurge
The final stage of the Ethereum roadmap is the Splurge. During this phase, the Ethereum developers will patch up all persisting issues from the earlier development phases. Also, the team will implement more minor upgrades that weren’t a part of the earlier roadmap phases.
The Splurge will be the ultimate test ground to wrap up the Ethereum roadmap and ensure all of the network’s features work well. If some Ethereum upgrades have issues or the developers get new ideas, they will implement them during the Splurge.
At the end of the Splurge, Ethereum aims to become a super-fast blockchain with extremely high TPS capacities and nearly instantaneous transaction finalization. Additionally, the developers claim that the famously high gas fees will drop to a fraction of a US dollar by the end of the Ethereum development roadmap.
Exploring the Ethereum Post-Merge Roadmap – Summary
The Ethereum roadmap is very ambitious and one of the most thorough roadmaps on the crypto market. It will be difficult for the developers to go through all the roadmap phases and deliver on their promises. However, up to this point, the Ethereum developer team managed to stay on track with their roadmap and consecutively deliver network improvements. The newest update to the Ethereum roadmap is the inclusion of the Scourge phase, and there may be additional roadmap phases in the future.
The Ethereum blockchain is the largest smart contract and dapp development ecosystem on the crypto market, and it still has a lot of space for development. Hopefully, the team will fulfill the roadmap milestones and make the Ethereum network more efficient, affordable, and scalable.

Web3 technology is becoming increasingly popular because it’s bringing complete decentralization to the internet. Moralis Academy’s Web3 ebooks will help you learn more about the key innovations of Web3. If you plan to start your Web3 project but don’t know how to launch your web page, we have a practical guide on how to make a Web3 website.