
The simplest way to describe Ren is that it’s a decentralized interoperability protocol. What it means for decentralized finance (DeFi) is that permission-less value transfers between blockchains can now take place. This is huge where the subject of liquidity is concerned because Bitcoin hodlers can move their BTC over to the Ethereum blockchain to participate in things like DeFi.
Ren is a unique project that seeks to create a decentralized exchange (DEX). Sure, there are plenty of DEXs out there (and we’ve covered many in previous articles), but what makes Ren unique is that it is both private and interoperable.
With Ren, users can exchange crypto assets on different chains without the need for an intermediary. So, by cutting out the middleman, users can save money in reduced fees without having to trust a central authority to take custody of their assets throughout the process.
Ivan on Tech Academy is the best place to learn about exciting DeFi projects like Ren. Enroll in our world-class blockchain academy and join over 20,000 students in learning blockchain, cryptocurrency and decentralized finance. What are you waiting for?

What is the Ren Virtual Machine?
The Ren Virtual Machine is the engine that powers this decentralized interoperability solution. And it can scale to meet demand. It is the Ren Virtual Machine that lets developers bring cross-chain functionality to their dApps. Privacy and interoperability seldom unite, but that is precisely what Ren seeks to combine.

Is Ren Virtual Machine Trustless and Permissionless?
Ren Virtual Machine is a Byzantine fault-tolerant network. This means that even if some of the nodes go down, the network will still function effectively. So, Ren Virtual Machine serves as a decentralized, permissionless, and trustless custodian of users funds in transit.
It locks digital assets on one chain and mints pegged representations of them on others. So, Ren Virtual Machine affords users the chance to interact with multiple assets, multiple chains, and multiple dApps in a single transaction. This means a user can utilize Ren Virtual Machine to send any amount of tokens to any application on any chain.
Is Ren Virtual Machine Secure?
Ren Virtual Machine uses large bonds, large Shard sizes, and “random shuffling.” This makes it a hard target for both rational and irrational adversaries. However, should an attack meet with success, Ren Virtual Machine can restore lost funds.
Also, as more funds flow into its custody, the algorithm’s adjusted fee system allows for the protocol to scale automatically to meet demand. So, the Ren protocol is both secure and scalable. But we’ll dive deeper into their security model with Shards and Darknodes later in the article.
Why Use the Ren Virtual Machine?
Ren Virtual Machine (or RenVM) supports complex and composable cross-chain transactions with a simple design. RenVM seeks to solve the illiquidity problem with billions of dollars tied up in other ecosystems. There are vast amounts of liquidity on other blockchains (mainly Bitcoin) that can’t interact with the Ethereum blockchain. That’s billions of stagnant assets that could be put to work in DeFi.

RenVM was over a year in development and was released on the mainnet back in May 2020. Therefore, like many things in DeFi, it is relatively new. The main reason to use RenVM is to put Bitcoin to work in DeFi. If a user sends Bitcoin to RenVM, it will mint the BTC into the ERC-20 equivalent renBTC token. And each renBTC token is backed by an equal amount of BTC in the RenVM.
Tokenized Representation and renBTC
Tokenized representation occurs when a user locks up an asset with a custodian. The custodian then mints a one-to-one representation of that token on another chain.
WBTC vs. renBTC
If you read our previous article, What is Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC)? then you will already understand how the process of moving assets cross-chain works. Conceptually, RenVM is similar to WBTC but technically there aren’t that many similarities.

With WBTC, a user must send their BTC to BitGo, which is a centralized Custodian. BitGo holds the funds and then creates a 1:1 representation of that BTC on the Ethereum blockchain in the form of WBTC, an ERC-20 token.
With WBTC, the Bitcoin is stored with BitGo. Hence, Bitgo is the central point of potential failure. As the Custodian, Bitgo mints the ERC-20 counterpart, WBTC, to match the stored BTC. And it also burns the WBTC when users are ready to redeem their BTC.
RenVM is Trustless
RenVM does the same thing but much faster. Instead of storing the BTC with a central custodian, RenVM stores it on its network of decentralized nodes, called “Darknodes.” These Darknodes cannot censor anyone or deny a user the ability to mint or redeem their BTC. That’s because, unlike the central Custodian model, code governs the Darknodes, not a central body.

With WBTC users have to trust that BitGo is securely storing their BTC. Furthermore, they have to trust that BitGo will let them redeem when they’re ready to transact back to Bitcoin. It’s unlikely but technically possible that WBTC’s Custodian could deny a user’s request.
So, what RenVM does is replace the trusted custodian with a decentralized one. This decentralized custodian improves upon WBTC’s centralized custodian model. RenVM, therefore, can run its platform in a trustless fashion.
So, RenVM has a superior decentralized model, but WBTC still holds the liquidity advantage at present.
RenVM, Darknodes, and the REN Token
As ominous as they sound, Darknodes are not controlled by any central authority. What Darknodes do is communicate with each other around the world to keep the network running smoothly.
Thus, Darknodes operate as independent computers on the network. For a regular user to advance to become a Darknode, however, requires putting some “skin in the game.” Darknodes must put up 100,000 REN tokens as a bond to align their economic incentives with the protocol’s best interest and to discourage malicious behavior.
RenVM uses a bond value 3x greater than the locked value. This bond binds the Darknode to a promise of honest behavior—otherwise, their bond gets slashed. The loss of the bond will be greater than any gains a malicious actor could hope for. Therefore such attacks are considered to be irrational.
The two no-no’s that can get a Darknode slashed are:
- The Darknode behaves maliciously.
If a malicious Darknode steals assets, RenVM can slash the bonds of the responsible party to restore the one-to-one peg with its underlying asset.
- The Darknode irresponsibly loses assets.
In this case, the protocol can slash the Darknode’s bond to help restore the lost assets (even though the act wasn’t malicious).
Darknode Fees
RenVM incentivizes its Darknodes with a reward system that compensates them for contributing computational power along with bandwidth and storage capacity. Their pay is based on the volume of transactions that take place through the network. So, if a user transfers their BTC to Ethereum (from one chain to another), Darknodes earn a percentage of the fees charged.

Do you want to learn more about regular nodes, or the inner workings of blockchain programming and the cryptocurrency sector, we highly encourage you to check out Ivan on Tech Academy. Best of all, right now you can get 20% with the exclusive promo code BLOG20!
RenVM Shards and Shuffling
RenVM shuffles its Darknodes into random groups each day known as Shards. These Shards contain at least one hundred Darknodes.
Each Shard generates a secret, private key via an algorithm. This secret key is hidden from everyone including Darknodes in the Shard. This key cannot be used to sign any transactions without 1/3rd of the Darknodes cooperating. This is how Shards securely lock assets in their custody.
All of this randomness and shuffling makes things like Sybil Attacks difficult. That’s because to carry out such an attack, the malicious actor would need to own a large portion of the whole network before they could corrupt a Shard.
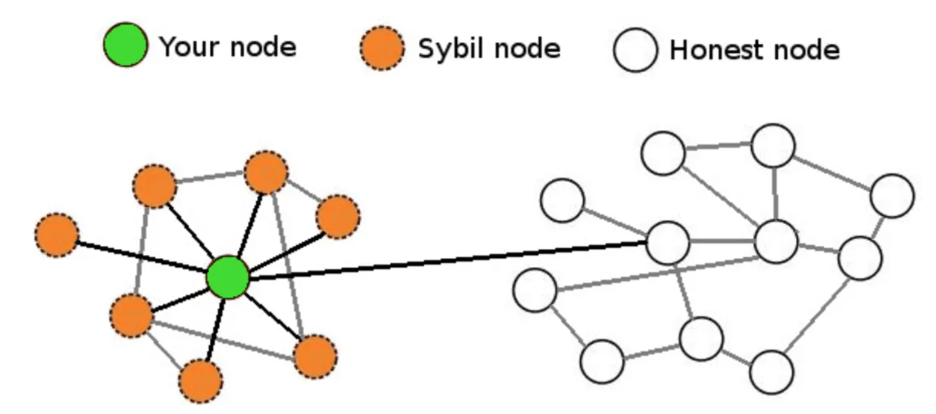
It also makes a Bribery Attack extremely difficult. That’s because an attacker would have to figure out a way to conspire with a large number of anonymous Darknodes in a short time.
These security measures help make RenVM more resistant to both rational and irrational attacks. To distinguish between the two, rational attacks are carried out by those seeking profit. Adversaries with no interest in profit carry out irrational attacks.
Regardless, even if either type of attack were to succeed, RenVM can always restore its one-to-one peg.
How to Mint renBTC with RenVM
Let’s say you want to put 1 BTC to work in DeFi. To do so, you’ll first need to exchange your BTC for an ERC-20 token like renBTC. To make the swap, you will need to send your BTC to a Bitcoin address in the following steps.
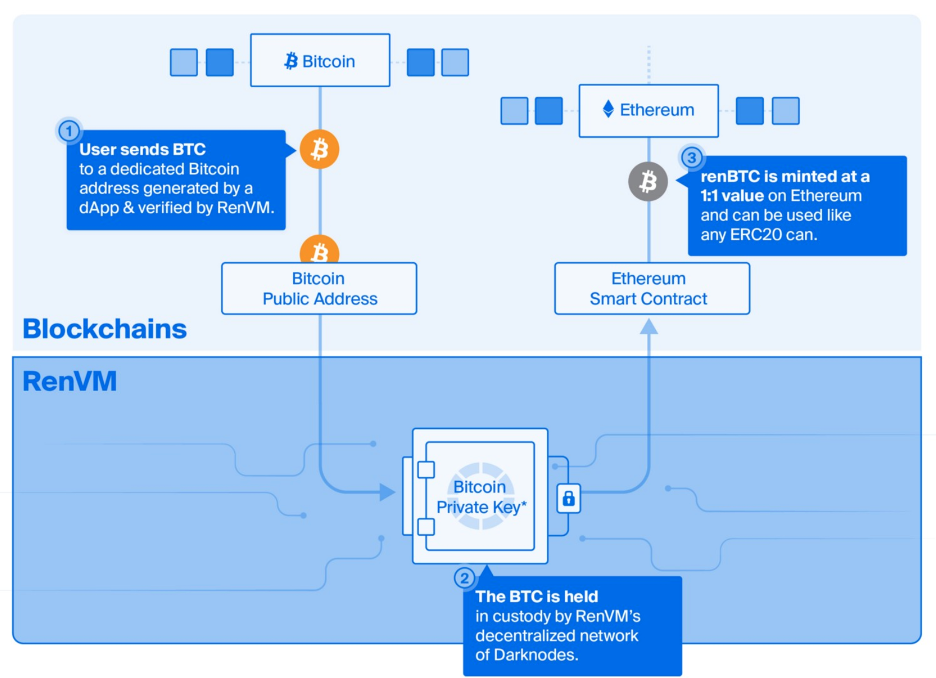
- This article is not about promoting any products, so, you will need to find an app with RenVM integration. The app will generate a Bitcoin address.
- You would send 1 BTC to the address and wait for six confirmations to pass. The UI will take over and RenVM will use one of its secret, private keys to produce a minting signature. With this signature, it can mint 1 renBTC and designate it to your Ethereum wallet. You must also pay the RenVM fees.
- You can then take your new renBTC and put it to work in the DeFi space.
Redeeming Your BTC
This process is as simple as minting. Your 1 renBTC is redeemable for 1 BTC, so when you’re ready to switch back into BTC, you can redeem the same amount.
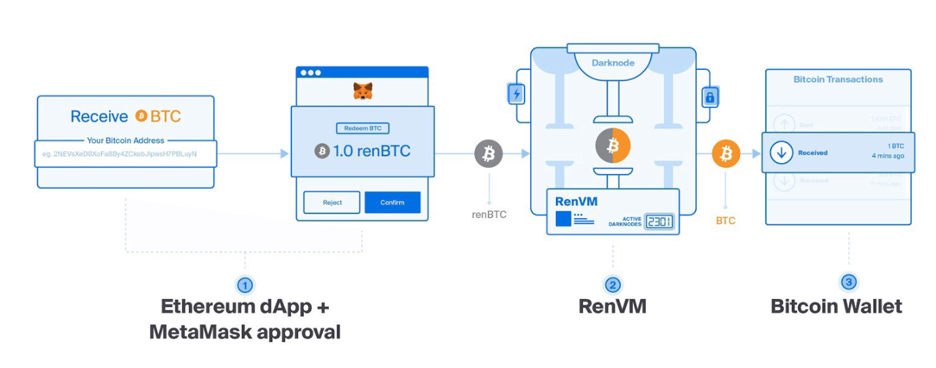
- Again, use an app with RenVM integration. The UI will prompt you to provide your Bitcoin address.
- You will wait for the Ethereum confirmations. Once your renBTC has been burned, your BTC will be released to your specified Bitcoin address. Expect some Ethereum gas fees and RenVM fees for this transaction to conclude.
- Now your real BTC is back in your wallet.
Types of Transactions Available on RenVM
- Lock and Mint
Lock-and-mint transactions are cross-chain transactions that occur between an origin chain and a host chain. For example, this would occur when a user decides to send BTC to the Ethereum blockchain.
- Burn and Release
Burn-and-release transactions occur when a user sends assets from the host chain back to their origin chain. In this case, the smart contract would burn the pegged asset from the host chain and return the underlying asset to the origin chain. For example, this would happen if the user wanted to redeem his/her BTC off the Ethereum blockchain.
- Burn and Mint
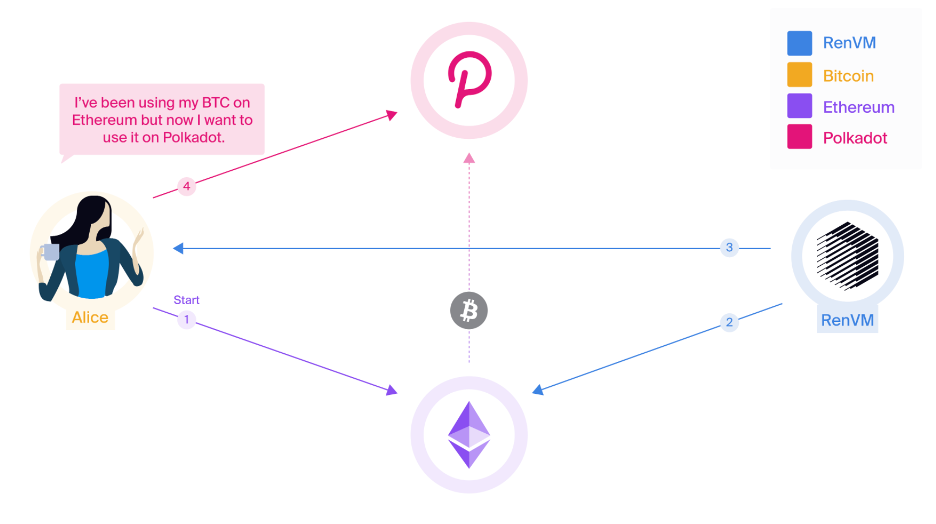
With burn-and-mint transactions, smart contracts can burn pegged assets from one host chain but also mint the same amount of pegged assets on another host chain. Amazingly, RenVM accomplishes this without ever touching the origin chain. A simple example of this would be a user wanting to send BTC from Ethereum to Polkadot without having to first transfer back to the Bitcoin origin chain.
What Can Devs Do with RenVM?
RenVM isn’t just for moving Bitcoin to Ethereum. It is a plug-in for DeFi. That means that any DeFi app can incorporate RenVM into their existing smart contracts. Devs can benefit from integrating with RenVM anytime their project needs cross-chain liquidity.
And that’s exactly what RenVM seeks to do. It wants to provide devs the ability to build private and trustless dApps that can interact with other protocols on other blockchains.
Conclusion
When it’s all said and done, the easiest way to imagine RenVM is to think of it as a trustless custodian that holds your digital assets as they move between blockchains.
RenVM currently supports Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, and Zcash and is capable of supporting any assets that use ECDSA private keys. The cool thing about this is that it opens up a potential sea of liquidity from the Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, or Zcash ecosystems. Billions of dollars can now pour seamlessly into DeFi.
From a tokenomics perspective, should DeFi continue to grow, the greater the potential fees Darknodes can earn. More Darknodes means more REN tokens staked at the rate of 100k a pop. There is a cap of 1 billion REN. Therefore as more Darknodes lock up REN tokens, the price of REN should increase with all other things being equal.
No one knows what the future price of REN will be, but one thing is for sure—developers should not have to continuously reinvent the wheel. Once an app is battle-tested and adopted, devs shouldn’t have to build it again on a different blockchain. And that’s what innovations like RenVM are accomplishing.
Do you want to become a blockchain expert? Sign up at Ivan on Tech Academy and start your education today! Ivan on Tech Academy is the go-to platform for all things DeFi or blockchain related. Join us!
Author: Mindfrac





