![]()
On December 1st, Ethereum 2.0 Phase 0 was officially launched, with the Ethereum 2.0 Beacon Chain launch. This is the first major release in Ethereum’s transition towards a proof-of-stake blockchain through Ethereum 2.0. As such, Ethereum staking has become a hot topic in the past two weeks. This article looks at Ethereum 2.0, the Beacon Chain, and the practicalities of staking ETH.
The relatively recent launch of the Ethereum 2.0 Beacon Chain has once again put the spotlight on Ethereum’s upcoming roadmap. The Beacon Chain effectively brings staking to Ethereum, and paves the way for various future updates to the system. As anyone keeping an eye on Ethereum will know, Ethereum 2.0 is a gargantuan upgrade project which seeks to massively boost the scalability, security and speed of the Ethereum network.
On December 1st 2020, the Beacon Chain shipped and went live at midday (UTC). At this point, the Beacon Chain is more of a foundation for the future of Ethereum than a replacement for the existing Ethereum network. As such, it lacks certain basic functionality, which will be implemented in the coming months and years. Nevertheless, Ethereum 2.0 and ETH staking is a big step towards the future of Ethereum.
If you want to be sure to stay in the loop on updates relating to Ethereum 2.0, ETH staking, or anything else blockchain and cryptocurrency-related, you should take a look at Ivan on Tech Academy. Ivan on Tech Academy is one of the largest blockchain education platforms anywhere in the world. In addition to free daily blog posts on various crypto-related topics, Ivan on Tech Academy also features dozens of in-depth cryptocurrency courses. Kickstart your crypto career with Ivan on Tech Academy!
What is Ethereum 2.0 (Eth2)?
Ethereum 2.0, “Serenity”, or Eth2, is the next major update to the Ethereum network. The Ethereum 2.0 upgrade has been a long time in the making, and will roll out in a series of phases. Perhaps most notably, the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade intends to improve the network’s scalability and security. More generally speaking, this will lead to greater speeds and efficiency, boosting the amount of transactions it can process and resolve existing bottlenecks.

The arguably most important phase of this transition towards Ethereum 2.0 was launched less than two weeks ago, with the “Ethereum 2.0 Beacon Chain”. We go into greater detail regarding the Beacon Chain below, but this chain underpins Ethereum’s imminent shift from a proof of work (PoW) mechanism to a proof of stake (PoS) consensus mechanism.
This is an integral part of Ethereum’s roadmap, and the transition to Ethereum 2.0. To illustrate how important this upgrade is for the Ethereum network, consider that Ethereum 1.0 can only support roughly 30 transactions per second (TPS). This gives rise to network congestion and transaction delays. Ethereum 2.0, on the other hand, aims to be able to support 100,000 transactions per second when it is complete.
A number of testnets have been launched in preparation for Ethereum 2.0, which will roll out in three main phases (Phase 0, Phase 1, and Phase 2). We’ve previously written about the Zinken testnet dress rehearsal launch, following the failed Spadina testnet launch. Now, with the launch of Ethereum’s Beacon Chain, ETH 2.0 Phase 0 has officially been successfully launched.

Suppose you want more information regarding Ethereum and Ethereum 2.0. In that case, Ivan on Tech Academy features a great beginner’s course to Ethereum, as well as courses on Ethereum smart contract security, smart contract programming, and Ethereum game programming.
What is the Ethereum 2.0 Beacon Chain?
The beacon chain, which is sometimes referred to as a coordination layer for Ethereum 2.0, is a central element of the ETH 2.0 architecture. Specifically, the Beacon Chain contains the core functionality that will constitute Ethereum 2.0’s Proof-of-Stake blockchain. As such, the Beacon Chain can be regarded as the beating heart of the upcoming Ethereum 2.0 network and is what will coordinate the actors using it.
Consequently, the Beacon Chain is primarily in charge of managing this proof-of-stake protocol, as well as all of the shard chains – which will be added at a later stage in the development of the Ethereum 2.0 system. We will go over all the details of Ethereum 2.0 shard chains, ETH 2.0 staking and much more in this article. Nevertheless, it is worth going through the various tasks that the Beacon Chain will have to handle.
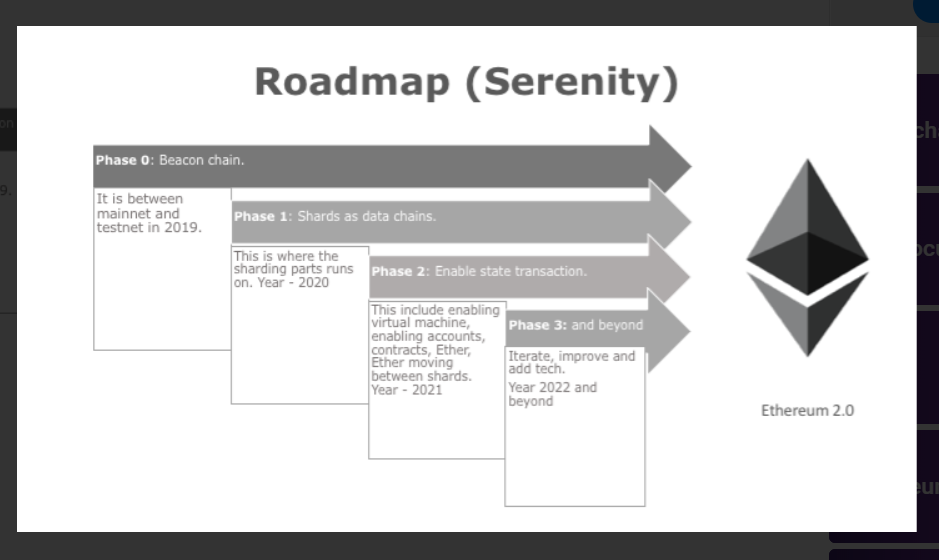
The Beacon Chain will handle validators and their respective stakes, nominate block proposers for shards, sort validators into block proposal voting committees, enact consensus rules, manage validator rewards and penalties, and much, much more. For example, the Beacon Chain will also act as the anchor point for shard chains in the future. This highlights the central role the Beacon Chain will play in Eth2, or Ethereum 2.0’s, future.
Nevertheless, it is important to note that the launch of the Beacon Chain does not fundamentally change anything for the Ethereum network most people use today. Additionally, the Beacon Chain is currently missing some of Ethereum’s fundamental functionality. For example, it currently does not manage smart contracts or accounts. Nevertheless, the introduction of the Beacon Chain is a crucial step towards eventually realizing a scalable, secure and stable release of Eth2.
Ethereum 2.0 Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake
As previously mentioned, the Beacon Chain introduces proof-of-stake functionality to Ethereum. Avid readers of the Ivan on Tech Academy blog will be familiar with proof-of-stake, which is one of the main consensus mechanisms found in the cryptocurrency industry. Proof-of-stake is often compared to the other major consensus mechanism, which is proof-of-work.
Whereas proof-of-work requires active crypto mining through solving cryptographic puzzles, proof-of-stake instead relies on a validator’s relative stake in the network. Although this difference can seem minuscule at first, it is a crucial factor to understand in order to appreciate the benefits and differences proof-of-stake will bring to Ethereum 2.0.
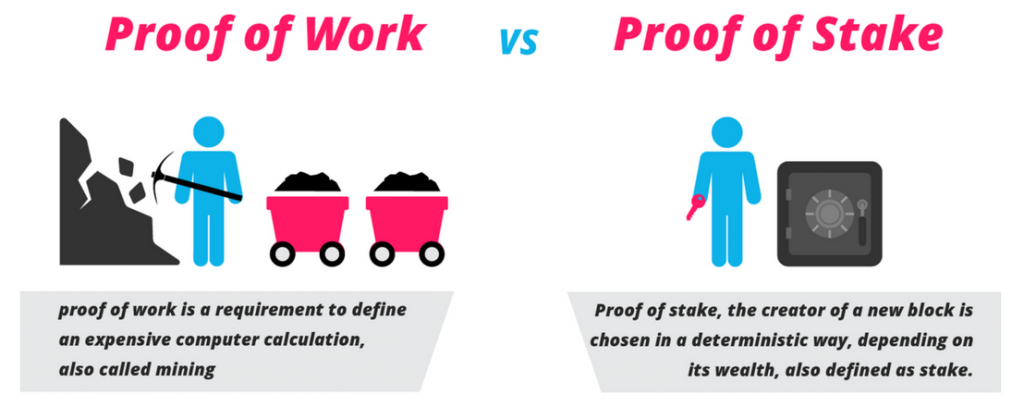
Proof-of-work (which Bitcoin uses) and proof-of-stake (which Ethereum 2.0 will use) both have their own advantages and drawbacks. However, there are a number of advantages brought about by a proof-of-stake network, which is why the Ethereum team has decided to go this route with the Eth2 Beacon Chain. This is in addition to the clear advantage of enticing users to hold a stake in the network, rather than just contributing with raw compute power.
According to the Ethereum team, this proof-of-stake Beacon Chain upgrade will boost the security of the Ethereum network. Essentially, proof-of-stake will mean that validators’ votes are weighted based on their stake in the network. Some of the arguments in favor of proof-of-stake note that this can make 51% percent attacks more difficult, it is more sustainable in that it does not lead to excessive electricity consumption, and lowers the risk of centralization.
For reference, some of the estimates put both Bitcoin and Ethereum at currently using over $1 million worth of electricity and hardware daily to secure their blockchains.
Ethereum 2.0 Staking
Consequently, it’s clear to see why Ethereum 2.0 staking and proof-of-stake offers certain benefits over a proof-of-work system. Network users will likely want to stake their ETH attest to correct blocks in exchange for receiving ETH staking rewards. In addition to this, Ethereum 2.0 staking can also allow the staker to receive a portion of Ethereum 2.0 network transaction fees.

Moreover, Ethereum 2.0 staking has the potential of taking off solely due to the relatively low requirements. In fact, the minimum requirements for staking are simply 32 ETH per validator, an internet connection, and a computer with sufficient hardware. There are several different combinations to choose between for what software to run when staking. Specifically, these include the following:
- Beacon node
- Beacon node and a validator client
- Beacon nod and multiple validator clients
In addition to this, Eth2 stalkers will be incentivized to keep a validator client online, or penalized if it goes offline. This boils down to how it is advantageous for the network if a validator is consistently available for block votes, which makes the system safer. You can read all about the details of this penalty on EthHub, but most importantly, it means you can lose “X%” of your deposit over a year if blocks finalize and you are offline. In this case, X=current_interest.
So, practically speaking, how can one go about staking Ethereum using the Beacon Chain? For the uninitiated, “staking” is the process of essentially locking up a deposit of the relevant asset. In Ethereum 2.0 staking, this means locking up an ETH deposit, so that the staker can act as a network validator. In effect, ETH 2.0 staking is done through depositing 32 ETH so the validator software can be activated until your validator term is over.
Earn ETH by Staking
One of the most popular questions relating to Ethereum 2.0 staking, or any staking for that matter, is how much ETH someone can earn by staking. Ever since ETH 2.0 Phase 0, or the Ethereum 2.0 Beacon Chain, successfully launched on December 1st, interest in Ethereum 2.0 staking has been on the upswing.
Those acting as validators, or nodes in the Ethereum 2.0 network, can – as previously stated – earn ETH by staking. As we’ve previously discussed, this can be a good way to make a passive income with Ethereum. However, how much can you expect to earn by staking on the Ethereum 2.0 Beacon Chain? Let’s break it all down.

Before we take a look at the actual staking reward, however, it is important to note that the Ethereum 2.0 Beacon Chain has not replaced the proof-of-work Ethereum network you normally use. All the “traditional” functionality still works, and is still online. What’s more, the classic Ethereum network will continue to function until it officially merges with the new Ethereum 2.0 blockchain under construction.
This merger is not expected to happen until late 2021 or early 2022. As such, the Beacon Chain will not entirely replace Ethereum 1.0 for some time. This complicates things somewhat for stakers, as the ETH rewards cannot immediately be withdrawn. Instead, this will take until Ethereum 1.0 becomes a shard of Ethereum 2.0, when Ethereum 1.0 and Ethereum 2.0 actually merge, after Ethereum 2.0 Phase 1.

Although one should note that staked Eth2 tokens will remain on the Beacon Chain, this does not stop people from realizing the goal to earn ETH by staking. The only thing this means is that stakers should stake according to a long-term horizon. Kraken notes the ETH 2.0 staking rewards are between 5% and 17%.
ETH Staking and Ethereum 2.0 Beacon Chain Summary
In short, the launch of the Ethereum 2.0 Beacon Chain and the advent of ETH staking presents a number of interesting possibilities. What’s more, Ethereum’s transition towards a proof-of-stake blockchain through the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade is also an interesting prospect on a technical level. Improving Ethereum’s scaling and security is an important issue if Ethereum is to be able to support a wider user base.
What’s more, the countless number of DeFi applications available, NFT tokens, and new smart contract platforms shows that interest for Ethereum is on the rise. Consequently, although ambitious, the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade is an important step for boosting the network’s ability to handle mass adoption. Granted, the Beacon Chain is not yet an outright replacement for “Ethereum 1.0”, but it is an encouraging step in the right direction.
Do you want to learn more about Ethereum, DeFi, crypto or blockchain technology in general? If that is the case, Ivan on Tech Academy has got you covered. If you enroll using the promo code BLOG20, you get 20% off. Become another person in the growing list of people who have found a new career in the blockchain or cryptocurrency field after enrolling in the Academy.




