
Hegic is a decentralized options trading platform on Ethereum. With Hegic, you can buy or sell put and call options for ETH and WBTC. Options in decentralized finance (DeFi) work best for those looking to speculate, hedge their positions, or provide liquidity. Hegic Protocol is an on-chain trading protocol which is powered by liquidity pools and hedge contracts.
If you’re an options trader from the traditional world of finance, you’ll notice some differences when trading options in DeFi. Here are some of the features of on-chain options trading with Hegic:
- No KYC or email registration required
- Non-custodial, censorship-resistant trading
- Verified on-chain settlement for options contracts
- Choose your strike price and exercise at any time during the contract period
- Earn yield as a liquidity provider
To trade options on Hegic, you just need to connect with an Ethereum wallet like MetaMask and you’re good to go. We’ll explore the rest of these features later, but first, let’s look at traditional options trading so you can see how it relates to DeFi. (If you’re an experienced trader you can skip past this part). If you need more basic information relating to decentralized finance, Ivan on Tech Academy is your go-to source. Ivan on Tech Academy is one of the premier blockchain education platforms and offers dozens of in-depth blockchain courses!
Options Basics
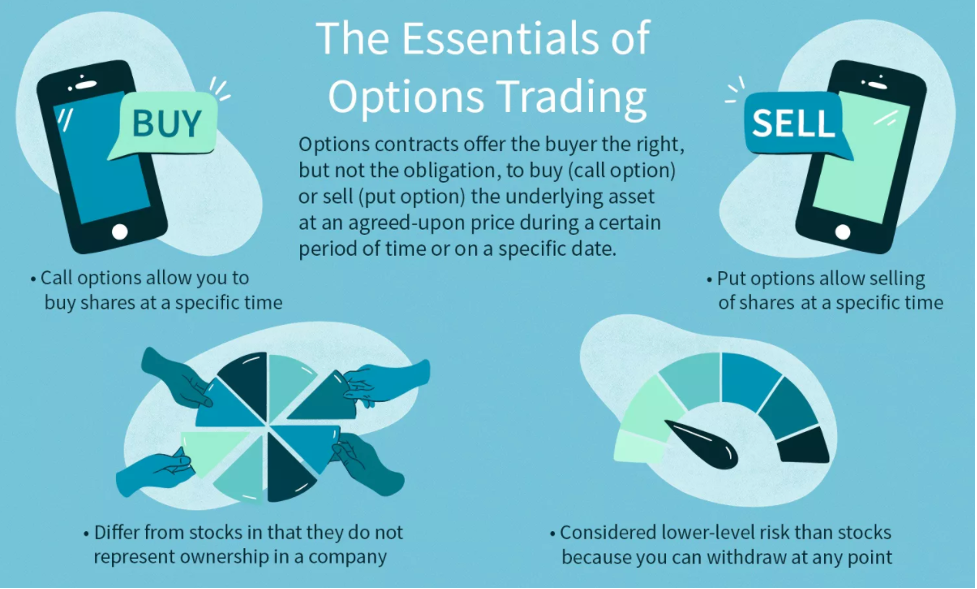
An option grants its holder the riHght, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) the underlying asset at a specific price on or before a certain date. So a trader could buy a stock outright or they could instead buy an options contract on the underlying stock for a lot less money.
What is a Strike Price?
This is the set price at which you can buy or sell an option. For call options, the strike price is the purchase price and for put options, the strike price is the selling price.
Puts and Calls
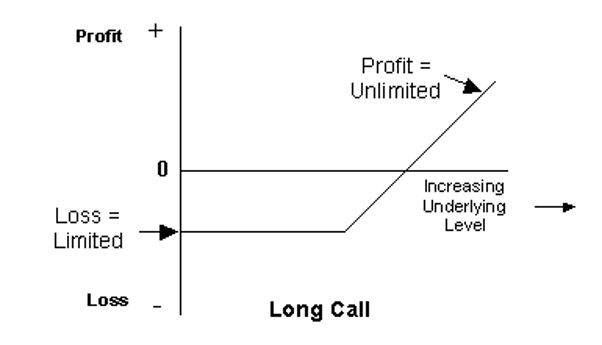
So, an option is a contract between two parties. With a call option, the buyer is betting that the price of the underlying asset will rise higher than the strike price before the option’s expiration date. If the bet is right, the call option buyer can exercise the right to buy that underlying asset from the option seller at the strike price and resell it for a profit.
For example, let’s say that stock X is trading for $200 a share but you think the price is going to rise to $250 in the next month. You could shell out $200 for 1 share of X stock, or, you could buy a call option for around $10 with a strike price of $200.
Now, you have the option to buy 1 share of X stock for $200 within the next 30 days. If the stock rises to $250 within that period, you can exercise your call option to buy the stock for your strike price of $200 and resell it for the market rate of $250. So, $250 – $200 earns you a gross profit of $50. Notice that you didn’t have to put up $200 to buy the share of stock outright.
To buy a call option, though, you must pay an option premium. In the case above, the seller is betting that the stock price won’t rise in the next 30 days. If the seller is right, he gets to keep your $10 premium as his profit.
The Power of Options
Options are powerful because they offer leverage. Risking $10 to make $50 is more cost-effective than tying up $200 to make the same profit. So options can provide profits, hedge protection, and leverage.
Options are called derivatives because they derive their value from an underlying asset. So with an options contract, you can buy or sell that underlying asset at a specified price by a certain date. (If you want to get a deeper understanding of derivatives, check out our article on What is Synthetix?).

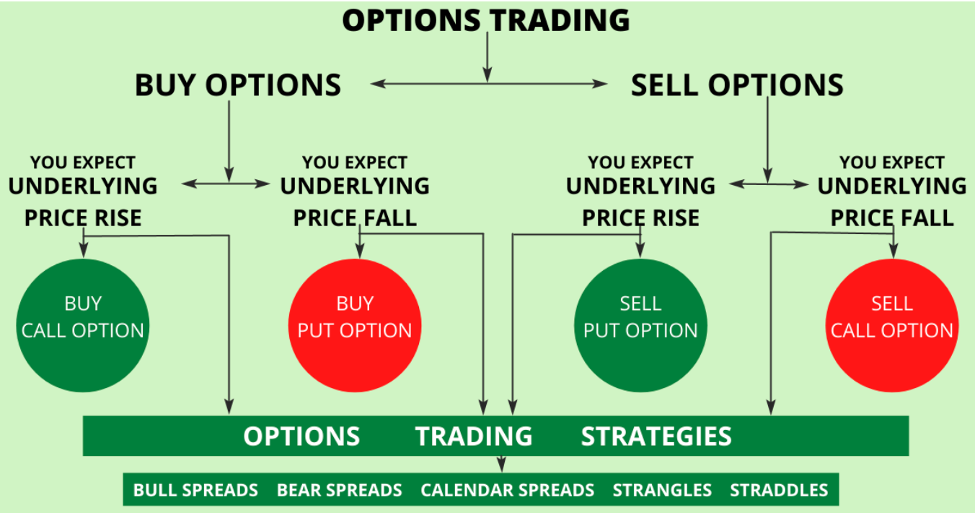
There are essentially 4 ways to trade options:
- Buy calls
- Sell calls
- Buy puts
- Sell puts
Buying Puts and Calls
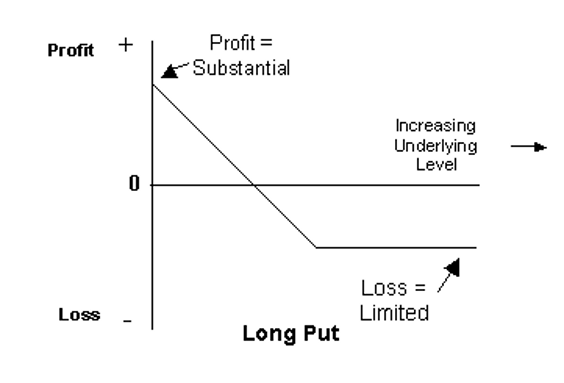
The simplest way to trade options is to buy a call or put. You can profit off the call if the price of the underlying asset rises. And you can profit off the put if the price of the underlying asset falls. The only risk a buyer incurs is the price of the option premium.
So, you can go long on a stock by buying a call. Or you can short sell a stock by buying a put. On the flip side of that coin, you could sell a put option that gives you a long position in the underlying stock or sell a call that gives you a short position.
It can seem a little confusing at first, but those are the four basic ways to trade puts and calls. Also, users who buy options are called holders and those who sell options are called writers. Here is the difference between option holders and writers:
Call holders and put holders are not obligated to do anything. They have the choice to exercise their right to buy or sell the underlying asset or not. So their risk is limited to the price paid for the option premium.
Call writers and put writers, however, do have obligations to buy or sell if their option expires “in-the-money.” So, option writers have more risk exposure. They can potentially lose a lot more than just the option premium paid. That’s why though it may seem that buying a put and selling a call is essentially the same thing, they do have different risk/reward scenarios.
Puts and Calls Examples
To put this into perspective here’s how the four scenarios could play out at the expiration date:
- Strike Price: $200
- Stock Price: $250
- Premium $10
- Call Holder
He profits $40 because he has bought the right to purchase a share of stock at $200. He sells for $50 gross profit minus the $10 premium fee.
- Call Writer
He loses $50 if the call holder exercises his right to purchase. That’s because the call writer will be obligated to sell 1 share of stock at the $200 strike price even though the market price is now $250.
- Put Holder
He loses because he bought the right to sell the stock at $200. He’s not obligated to sell, however, otherwise he would lose $50. Fortunately, the put buyer can close out the contract and only has to pay the $10 premium.
- Put Writer
He profits the $10 premium from the put holder who bought the right to sell at $200 but didn’t exercise that right.
Although writers risk losing more, the good news is that only about 10% of buyers ever exercise their options. Most close out their positions or let their options expire.
How to Value Options
When it comes to valuing option contracts, it boils down to predicting future price movements. Also, there is the time factor. The less time there is until an option contract expires the lower the option’s value will be. That’s because the probability of the stock’s price making a big move diminishes as the expiration date approaches. Hence, an option is a “wasting asset.”
Volatility is another component that can increase an option’s price. That’s because a volatile asset is more likely to make a larger price move. So the greater the volatility of an underlying asset, the greater the price of its options contract will be.
Looking to learn more about the more technical aspects of trading? If so, join over 30,000 students already enrolled in Ivan on Tech Academy! If you enroll in the Academy, you get access to courses like Technical Analysis and our Algorithmic Trading course!
Trading Options On-Chain with Hegic
So, there are numerous options strategies that can be employed for speculation or hedging, but in DeFi you can also earn money by being a liquidity provider. As mentioned, you can trade options with two assets on Hegic, WBTC, and ETH.

What Is an ETH Call Option on Hegic?
An Hegic ETH call option is an on-chain contract that gives the buyer the right to swap DAI for ETH at the strike price. ETH call option buyers get to choose the amount, the period, and the strike price for the options contract. The strike price is the price at which the holders can swap their DAI for ETH.
Example ETH Call Option:
Price of ETH: $450
Strike Price: $500 (out of the money)
Premium $10
Strike Price: $420 (in the money)
Premium: $35
Period: 4 weeks
Notice that the “in the money” option has a higher premium than the “out of the money” option. That’s because the probability of the current price staying above $420 is more likely than it is to rise above $500.
Max Profit:
This can be as high as the price of ETH rising above the strike price in four weeks.
Max Loss:
If the price of ETH stays below the strike price, the most the trader could lose would be the premium paid for the call option.
With Hegic, premiums and settlement fees are calculated based on the amount, period, and strike price for the ETH call option contract. Call buyers will have to pay the premium and settlement fee in ETH with their MetaMask wallet.

How to Exercise an ETH Call Option?
Buyers can exercise the ETH call option as long as the option contract hasn’t expired. To exercise the option, the call buyer unlocks their ETH in the contract by sending the prescribed amount of DAI.

Exercising is 100% guaranteed because the contract size in ETH is locked in a contract for the holding period. Also, Hegic does not offer auto settlements at expiration, so buyers will always need to exercise ETH call options by themselves. Furthermore, buyers can exercise ETH call options at any time during the period they have paid for.
ETH call options contracts time range:
- 1 Day (24 Hours)
- 1 Week (7 Days)
- 2 Weeks
- 3 Weeks
- 4 Weeks
Hegic ETH Put Options
Hegic’s version of a put option is an on-chain contract that gives a buyer the right to swap their ETH for DAI at a specified price before the expiration date. Like the other Hegic option contracts, an ETH put option buyer selects the amount, the period, and the strike price.
Example ETH Put Option:
- Strike Price: $500
- Expiration Cost: $450
- Gross Profit: $50.
- Premium Cost: $10
- Net Profit: $40
The put holder could exercise this option contract before the expiration date and swap 500 DAI for 1 ETH. So if the price of ETH had dropped to $450, the calculated profit would be $40. However, let’s say the expiration price of ETH was $550. In that case, the put buyer would be out the premium cost of $10.
Here are some pricing examples for ETH put options contracts:
- 1 Day: 1.9%
- 7 Days: 4.9%
- 14 Days: 6.9%
- 21 Days: 8.5%
- 28 Days: 9.8%
So, if the put holder bought a contract for 7 days, his premium would have been $500 (strike price) x 4.9% (7 days premium) = $25.50
How to Exercise a Put Option on Hegic
To exercise, a holder must send ETH to the contract to receive the locked DAI. So, if a holder buys a put option for 1 ETH with a strike price of $500, then $500 worth of DAI will be locked in the contract for this holder. There are no automatic settlements at expiration, so users must take care to exercise their ETH options before expiration on Hegic.

Selling ETH Calls and Puts on Hegic
Option premiums are the fees buyers pay to hold puts or calls. These premiums are the income received by option writers and are distributed amongst all the liquidity providers based on their share in the pool.
Call Option Writers
Call writers provide ETH to the Hegic liquidity pool and begin earning an estimated 29% annual percentage yield (APY) on their money. The ETH provided will be used for selling call options.
After providing ETH, a liquidity provider receives writeETH tokens. These are ERC-20 tokens that can be converted back to ETH whenever a liquidity provider wants to leave the pool.
Put Option Writers
Put writers provide DAI to the Hegic liquidity pool and begin earning an estimated 29% APY. DAI tokens from liquidity providers are used for selling put options. It essentially works the same as with call writers. After becoming a liquidity provider, the put writer receives writeDAI tokens. These can be converted back to DAI when the liquidity provider decides to leave the pool.
Hegic is a DeFi protocol, so the liquidity pools are non-custodial. That means no other user will take custody of your funds.
Hegic Conclusion
Before you enter any options trades in DeFi make sure you know the risks. DeFi protocols can get hacked, so you never want to risk more than you can afford to lose.

Also, as an options seller, the value of your writeDAI or writeETH tokens can increase each time a new buyer pays a premium. However, their value decreases when a buyer exercises a contract. Just know that you can lose up to 100% of your funds as a seller so exercise proper risk tolerance.
Having done the necessary homework though, if you’re interested in DeFi options trading, visit Hegic’s website.
And if you’re ready to become a better trader or learn about blockchain development, make sure to visit Ivan on Tech Academy today!
Author: MindFrac





