
If you ask people in the crypto space what they think of when you say ‘oracles’, many will likely say “Chainlink”. Chainlink has become the number-one most trusted oracle throughout the crypto space and beyond, boasting partnerships with some of the biggest names in tech and an array of integrations and partnerships with an impressive roster of collaborations.
Specifically, the Chainlink project aims to reinvent how automated financial contracts work and is at the forefront of the fourth industrial revolution. Oracles are the backbone of many DeFi projects and provide the foundation for a multitude of applications.
In this article, we’ll explore how Chainlink works, how the native LINK token works, and why Chainlink has become the oracle of choice for so many cryptocurrency projects and businesses worldwide.
Before you dive into Chainlink, be sure to check out the various blockchain and crypto courses available on Ivan on Tech Academy. Ivan on Tech Academy is one of the most popular online blockchain education platforms, and over 20,000 students have already enrolled in Ivan on Tech Academy. Do it yourself and go from programming zero to blockchain hero!
What is Chainlink?
So, what is Chainlink? In short, Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network, which allows smart contracts to connect securely to external data sources, payment systems, and APIs. Moreover, its native LINK token is the digital asset used to purchase services from the Chainlink network.

Moreover, Chainlink is blockchain agnostic, allowing for seamless interoperability between multiple blockchains. The growing LINK token soared to the number five spot by market cap in August, setting a precedent that could put oracles in the speculative spotlight.
Smart Contracts
After the initial proposition by Nick Szabo in 1994, smart contracts first became widely utilized in 2015 upon the launch of the Ethereum network. Building on Ethereum, developers are able to build smart contracts that are deployable and highly flexible.
A smart contract can essentially be understood as a piece of code that allows currency from one address to be moved to another when certain conditions are met in an if/when/how scenario.
Smart contracts are immutable, meaning they cannot be changed or altered. Smart contracts are publicly viewable and can be observed on the blockchain by anyone. This guarantees trust among users, ensuring that the parameters of the proposed conditions cannot be adjusted.
When smart contracts create an agreement that requires data not held on the blockchain, off-chain data is required and must be converted into an on-chain format that both sources can understand and communicate with. This obstacle has historically been one of the key limitations of smart contracts. Thankfully though, we now have oracles!
Smart contacts can be used for simple peer-to-peer transactions or for enterprise-grade complex use cases. Smart contracts can be used to automate supply chain management and increase efficiency in various industries.
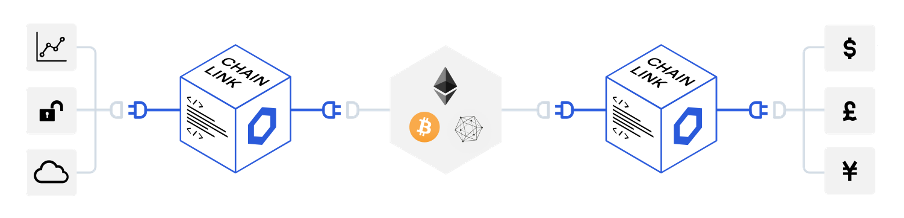
Despite Chainlink being one of the biggest names in the smart contracts space, several other blockchains also support the use of smart contracts – such as NEO, Hyperledger, and Waves. These smart contracts, however, would not be made possible without the use of oracles.
Oracles
Oracles are a type of software, often referred to as ‘middleware’, that play the role of intermediary when data is translated from off-chain sources to the blockchain and communicated between various parties.
Oracles are used to verify and communicate real-world data that is then brought onto blockchains. While smart contracts provide the pipework for transactions to move from one wallet address to another, oracles verify that the conditions within the smart contract have been met and that the information brought into the smart contract is accurate.
Oracles have been a game-changer for blockchain innovation, but the decentralized nature of blockchain and cryptocurrency means that one single oracle that is centralized, creates trust issues if that data source is compromised or is not operating momentarily.
A single centralized oracle is not suitable for most blockchain and DeFi needs, as this would present a single point of failure that could bring down an entire platform, potentially putting users’ funds at risk.
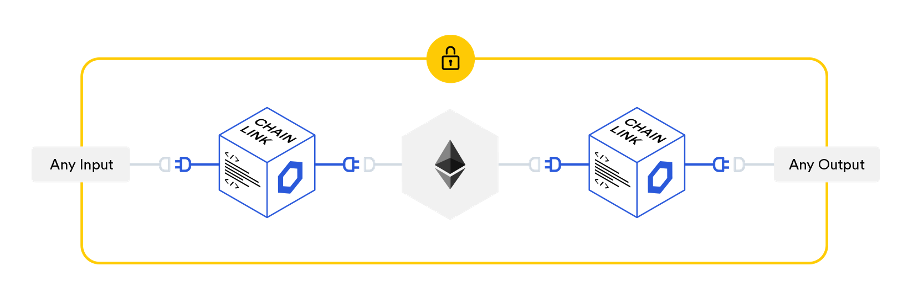
Chainlink’s decentralized oracles require consensus from the node operators to validate data feeds. If someone tries to add inaccurate data to the blockchain, the Chainlink network would reject this feed and the node operator responsible would be penalized. This is what makes the Chainlink decentralized oracle system so powerful and secure.
Chainlink Smart Contracts
A smart-contract-enabled blockchain can request data for their smart contract by putting out a request (Requesting Contract) for data. This ‘event’ is then registered by the Chainlink network and generates a smart contract known as the Chainlink Service Level Agreement Contract (SLA) to allow users access to off-chain data. From here, the SLA contract then creates three further sub-contracts:
Chainlink Reputation Contract
The Reputation Contract checks and tracks the performance history and authenticity of a node, refusing any node operators that may appear to be unauthentic, disreputable, or suspicious.
Chainlink Order-Matching Contract
This is the contract that sends the requests to nodes for data for smart contracts. The Order Matching Contract will take any bids made by requesting contracts that do not specify a preferred set of nodes, then allocates the appropriate nodes to meet the request.
Chainlink Aggregating Contract
The Chainlink Aggregating Contract collects data from the chosen oracle. This data is then either validated or reconciled to provide an accurate result. Data requests from smart contracts are then translated between on-chain and off-chain parties using the “Chainlink Core” software. Once translated, the newly formatted request is sent to an application programming interface (API) to collect data from the specified source. Once collected and translated, it is sent back to the Chainlink Aggregating Contract.
The Chainlink Aggregating Contract can collate, validate, and reconcile data from single sources and multiple sources. If either source is incorrect or dishonest, their data can be reconciled or denied from the data feed supplied. This can be repeated for multiple sources which eventually creates a single averaged piece of data.
All-in-all, Chainlink smart contracts are among the most advanced and sophisticated in the space and are a must for any DeFi project worth their salt.
The LINK Token
The native currency of the Chainlink ecosystem is LINK, a token built using the Ethereum ERC-20 standard. LINK is used to pay Chainlink node operators, with the price of the token determined by the node operator according to the demand for the data that they can provide.
The LINK token is staked by node operators on the Chainlink network, this is required to ensure that node operators are incentivized to provide an honest and efficient service, as not doing so can incur penalties. Several data points, including the size of a node’s stake, is observed by the Chainlink Reputation Contract. This contract efficiently matches data requests with relevant nodes. The larger the stake of the node, the higher the chance of that node being chosen to fulfill data requests and earn LINK tokens as rewards.
Chainlink VRF
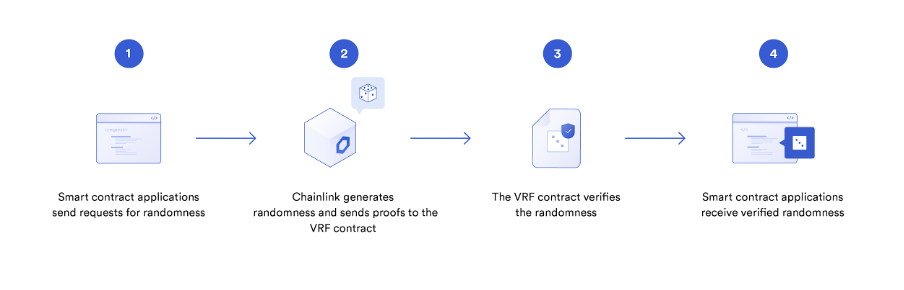
The Chainlink VRF uses verifiable randomness functions to produce provable, verifiably random outcomes that can be seen on the blockchain. This is particularly useful for blockchain gaming, security, and layer-two protocols. The VRF provides cryptographic proof that randomness is unpredictable, that can be verified on the blockchain. This has the potential to make gaming more fun, and generate provably random assignment of tasks or assets. The proof verification properties of the blockchain make it well suited to this application. This is how the VRF works:
For example, if a smart contract provides a seed to Chainlink to request randomness, the seed is used to generate a random number. This seed should be unpredictable to any oracle it is provided to. The random number that is generated is then sent to the smart contract on the blockchain. Oracles have their own unique secret key used for generating this randomness, which is used to verify the outcome of the event on-chain along with the application’s seed.
Nodes
Nodes are how the Chainlink ecosystem remains decentralized. Chainlink nodes are oracles that allow smart contracts to operate on the Ethereum blockchain and interact with external data sources and APIs. Chainlink nodes are rewarded with LINK tokens for validating requests. Nodes can provide off-chain data to smart contracts directly, allowing smart contract uses to be more flexible and fluid.
DeFi
The explosion of decentralized finance this year has been incredible, with new DeFi projects and dApps popping up nearly every day. Most of these dApps require some sort of price feed that needs to be brought on-chain from an external source. Moreover, if a DeFi price feed is not accurate, the result could be huge monetary losses and a loss of faith in the platform by new users.
This is where Chainlink comes in. Though most crypto projects will use several oracles in case of an error or outage, this is largely for due diligence. Chainlink is the number one oracle of choice for the vast majority of cryptocurrency projects and DeFi applications.
Moreover, Chainlink is regarded as one of the most trustworthy and reliable oracle providers for platforms sector-wide and has become the benchmark for bringing real-world data onto the blockchain.
Link Marines
As far as crypto communities go, Chainlink’s so-called “LINK Marines” are arguably unrivaled. This Chainlink fanbase is reportedly over 50,000 strong, and crypto Twitter, Reddit and Medium are fertile breeding grounds for LINK enthusiasts, with an ever-welcoming community and positive approach.

Some of the node operators and early investors of Chainlink provide an abundance of data and resources to keep the LINK Marines squad informed and excited. Much of the unwarranted FUD spread about Chainlink is relatively quickly quashed by the LINK guard, ready to protect their prized asset.
Whether we are referring to roadmaps, infographics or partnerships, the LINK community is one of the most active and engaging in all of crypto. The LINK Marines are also highly acclaimed for their innovative approach to meme-culture.
Partnerships & Integrations
As we’ve already mentioned, practically any credible DeFi project that requires price feeds will use Chainlink. That being said, the benefits of Chainlink oracles are being implemented across various sectors, as industries outside of the crypto-realm begin to acknowledge the advantages presented by the technology.
Already a staple in every decentralized finance protocol, Chainlink has announced partnerships with the likes of IBM, Microsoft, Google, and Coca-Cola, plus a host of huge global entities. Just see a sliver of Chainlink’s countless partnerships in the graphic below!

Zeus Capital
It can, however, be a good idea to look at some of the actors spreading fear, uncertainty and doubt (“FUD”) regarding Chainlink. The supposed research firm Zeus Capital spent a considerable amount of time, energy, and money promoting several FUD campaigns against Chainlink during the peak of it’s August bull run. For example, adverts claiming that the project was a Ponzi scheme, a pump and dump scheme, and an out-right scam, were circulating crypto Twitter with paid adverts. Many crypto influencers even shared screenshots of messages from Zeus offering payment in Bitcoin for publishing bearish price predictions.
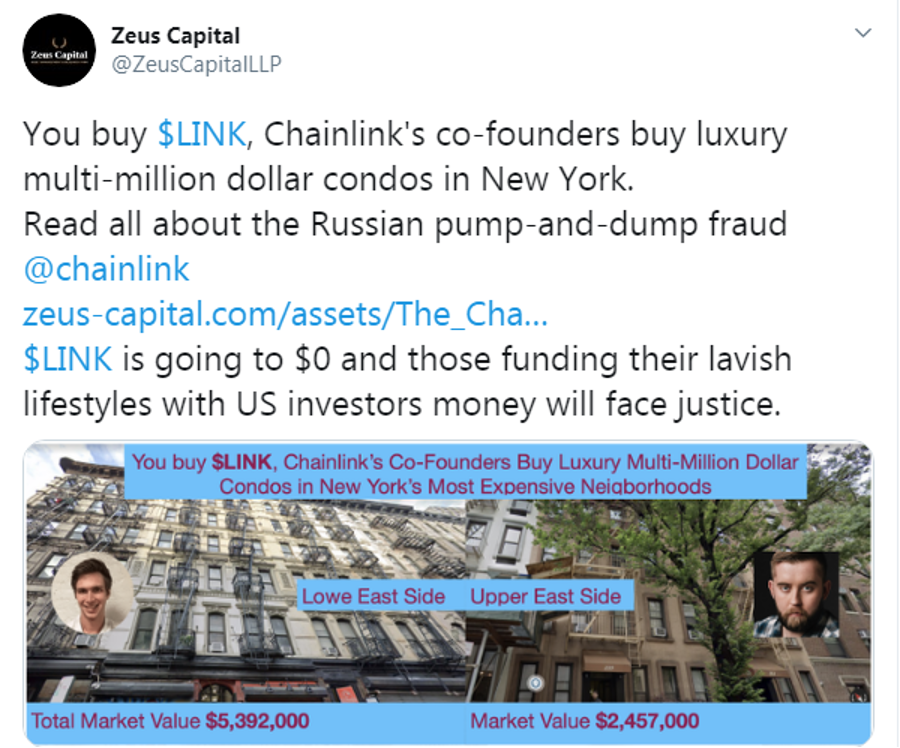
Though this FUD scandal was eventually quashed, the price suppression of LINK has resulted in the token struggling to recover from a 50% loss, currently hovering around the $10 mark.
Competition
Though Chainlink is the go-to choice of oracle in the crypto space, data sources need to be cross-referenced for due diligence. As such, many crypto-oracle projects are emerging, claiming to offer things that Chainlink can’t. Below are a few of the most popular up-and-coming oracles in the space and how they compare to Chainlink.
Band Protocol
- Established in 2019, Band Protocol has become a prominent player in the oracle space. With a strong team and a recent Binance integration, Band Protocol looks set for great things in the coming years.
DIA
- DIA, which stands for Decentralized Information Asset, is a Switzerland-based not-for-profit organization. DIA is fully open-sourced and transparent and has become popular among an increasing number of Dapps.
DOS Network
- The DOS network focuses on scalable, cost-effective oracle solutions. Though relatively new to the scene, DOS Network has the ability to increase data query throughput and computation capacity as more nodes join the network.
What is Chainlink: Conclusion
Chainlink is undoubtedly the oracle of choice for many blockchain projects. With use cases ranging across many industries and underpinning the colossal growth of the recent DeFi craze, Chainlink is becoming a major institution, changing how we view contracts and transactions in all walks of life.
Following the recent SmartCon DeFi developer convention, Chainlink announced the acquisition of DECO from Cornell University. One key piece of this acquisition was Dr. Ari Juels, the former Chief Scientist of RSA, one of the largest security companies globally. Juels is responsible for formalizing the consensus mechanism Proof of Work, which is now used to secure over $300 billion in cryptocurrency.
Despite FUD attempts and extreme price volatility, many see LINK as a permanent top five token. The recent integrations, acquisitions, and partnerships with world-leading companies suggest that big things are happening for Chainlink. As the demand for high-quality off-chain data increases among blockchain projects, Chainlink’s growth could be unprecedented. With the technology working its way into every sector, the Chainlink brand has become the benchmark for oracle providers.
For those looking to learn more about blockchain, Chainlink, crypto and decentralized finance, Ivan on Tech Academy is the go-to platform for blockchain education. Best of all, right now you can get 20% off when enrolling in Ivan on Tech Academy if using the exclusive promo code BLOG20!





