Prediction markets use the “wisdom of the crowd” philosophy to make decisions on future events or outcomes. The events predicted can be extremely diverse, such as – elections, sales of a company, price fluctuations of commodities, etc. In this article, we will talk about DeFi prediction markets. These are prediction markets that use the advent of decentralized finance to drive the prediction systems.
So, first thing’s first….
What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
DeFi stands for decentralized finance. It’s a movement that aims to utilize protocols like smart contracts to create decentralized versions of traditional financial products and instruments. A DeFi can be anything from a digital asset, decentralized applications (DApps), financial smart contracts, and protocols that run on top of public blockchains. Some features of these DeFi applications are as follows:
- Decentralized: There are no intermediaries that take up control of your funds. A central administrative body does not control Defi products.
- Transparency: Since the system is open and decentralized, anyone can see all the stored data inside it.
- Permissionless: An open system where anyone can participate
- Censorship Resistance: Since there are no centralized governance bodies, the protocol is resistant to central censorship.
- Innovative: DeFi products have often been called lego pieces because of their limitless potential for innovation. It is possible to join together multiple DeFi protocols to create a whole new product.
What are Prediction Markets?
Prediction markets are collections of people that are speculating on the outcome of an event. To better illustrate how this works, let’s take a slight detour.
At its very core, what is a market? It is a group of people buying and selling things. Pretty straightforward, right? Similarly, a prediction market is a marketplace where you can buy and sell predictions. Or, to put it more accurately, shares in the outcome of an event. The Iowa Electronic Markets (IEM) is the most well-known prediction market in the world.
Speaking of prediction market shares, let’s take a quick look at how it works.
There are two types of shares in a prediction market – “YES”, or long shares and “NO”, or short shares.
- YES: Gives you a payout if an event occurs and nothing if the event doesn’t occur.
- NO: It gives you a payout if an event doesn’t occur and nothing if it does occur.
The payout given is dependent solely on how much the buyers are willing to buy and how much the sellers are willing to accept.
You can think of prediction markets as event derivatives. The value of these derivatives is directly proportional to the probability of a particular outcome.
To gain a better understanding of how this works, consider the following example.
Example of a prediction market
Imagine a simple dice. Upon a roll, it can show one of 6 results. Suppose the bet is that the dice will display one of three outcomes – 1,2, or 3. So in a prediction market, The weight of “Yes” shares will be equal to the weight of “No” shares. So, if the payout for a correct prediction is one dollar, both the buyers and sellers agree to pay 50 cents each.

However, what if we have a four-sided dice instead of a six-sided one? Now the chance of getting a roll that’s 1,2,3, or 4 suddenly jumps from 50% to 75%. This means buyers will now have to pay 75 cents for Yes and 25 cents for No.
DeFi prediction markets basis – Wisdom of the crowd
Wisdom of crowds is the idea that large groups of people can collectively make smarter decisions than individuals. This is the core concept behind decentralized finance prediction markets. Wisdom of the crowd was first observed by the great philosopher Aristotle. As per his observations, a potluck dinner, wherein people collectively bring food, results in a much more satisfying meal than a feast produced by just one person. The theory gained further prominence in James Surowiecki’s 2004 book, “The Wisdom of Crowds.”

For this theory to work correctly, the following conditions are necessary:
- The crowd itself must be diverse.
- They must have incentives to participate in the market.
- They must come up with their own decision and shouldn’t be influenced by each other.
Wisdom of Crowds – Examples
So, now that we know the theory, let’s look at some practical examples now, shall we? In fact, let’s look at three examples of the wisdom of crowds:
- Imagine we have an object whose weight we have to guess. Taking the average of the individual guesses of a large group will be closer to the real number than those of individual experts who are familiar with the object.
- Studies show that in a major sports event, like the World Cup Final or World Series, a group of people who are knowledgeable about the sport but not fans of the teams involved can accurately predict the result more often than not.
- The last example is the “Ask the Audience” lifeline of “Who Wants to Be a Millionaire.” You are probably aware of how this goes. The studio audience is polled, and the most popular question turns out to be the correct one, 91% of the time.
Why DeFi prediction markets? The limitations of centralized markets
Before we get into the DeFi price predictions markets, let’s understand why we needed them in the first place. What are the problems with centralized prediction markets?
- Borders and regulations silo all the centralized prediction markets. The problem here is that the strength of a prediction market is directly proportional to its size. The more operators and regulators you have, the more you limit access to the markets, reducing its effectiveness.
- Centralized markets also have a low betting cap, preventing the participation of actors who want to make high risk/high reward investments.
- Being an intermediary, these markets usually charge trading fees and take cuts from your profits. If you are a regular user, then all these fees tend to add up.
- Finally, the lack of users leads to reduced participation, which, in turn, makes these markets extremely illiquid.

Advantages of DeFi prediction markets
The core component of decentralized finance is the lack of centralized ownership. This gives it several advantages over their centralized counterparts.
- The lack of a central overseer opens up the markets for free and open participation. Anyone anywhere can bet on any outcome, anytime they want. Do you want a free and open market with zero friction? This is how you get it.
- Assets that were formerly closed to you are accessible via DeFi prediction markets. For example, certain countries can’t usually access American stocks. However, decentralized finance applications can allow you to do so.
- Users can also create their own markets if they want to.
- DeFi prediction markets lack intermediaries, which is why it eliminates counterparty risk, and the fees collected are noticeably lesser.
- Open and free participation increases the liquidity available in the pool, drastically improving the potency of DeFi predictions markets.
DeFi predictions – The rise of decentralized finance
The core innovation crucial for the creation of DeFi prediction markets is smart contracts. A smart contract is an automated agreement between two parties. These smart contracts are a bunch of instructions that execute using the IF-THEN-ELSE logic. In other words, instructions can only be executed after the completion of the previous ones. This ensures that two people can enter a binding agreement that’s governed by code, instead of a third-party, like a lawyer.

Predictions Markets are becoming a central part of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
However, smart contracts themselves aren’t enough to properly execute these prediction markets. Another vital piece of this puzzle is oracles. Decentralized prediction markets like Augur and Gnosis have smart contracts that decide how much the participants get paid if a particular event occurs. However, how do they know that the event has indeed occurred, or not? For this, we require oracles.
Enabling DeFi predictions via blockchain oracles
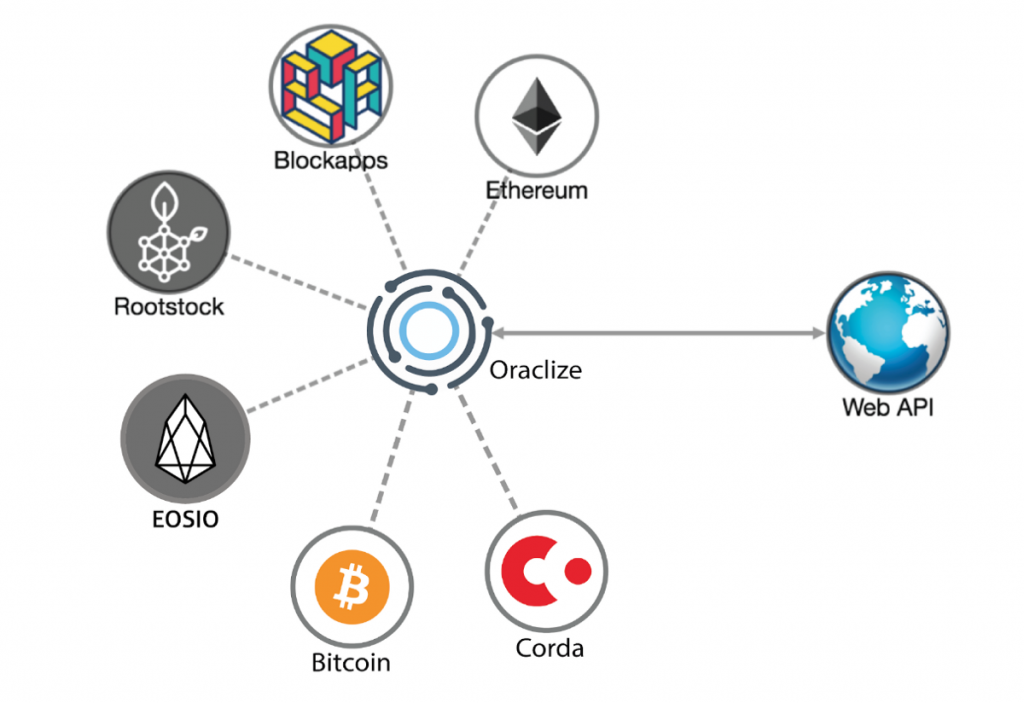
An oracle is a third-party service that provides smart contracts. DeFi prediction markets capture knowledge about a particular event via multiple oracles. Think of them as a bridge between the fiat world and the decentralized world. The relationship between the smart contract and oracles works like this:
- Smart contracts and the blockchain, in general, live in an isolated reality. As such, they are oblivious to the rest of the world.
- Therefore, the oracle’s job is to sign off and validate the state of the world and upload it periodically to the blockchain.
- More than one oracles can obtain the required information from more than multiple sources.
Alright, now let’s bring everything together and see how smart contracts and oracles work together to create a prediction market.
- Imagine a hypothetical market with just two members – Alice and Bob.
- In a match between Manchester United and Arsenal, Alice believes United will win while Bob is with Arsenal.
- The two of them enter into a smart contract and lock up their payments.
- Upon getting the results, the smart contract releases the funds to the victor.
- The oracle queries a trusted API to find out which team won.
- Finally, it then relays the information to the smart contract, releasing the funds to Alice or Bob, depending on who won.
DeFi Predictions Markets Examples – Augur and Gnosis
DeFi Prediction Markets #1: Augur

Augur is a DeFi price prediction market based on Ethereum. Augur traders use ETH to buy and sell shares in the different prediction markets. As per DeFi Pulse, Augur has over $620k in USD.
Augur accommodates for markets of various complexity. The simplest market is a simple YES/NO. These markets give the following results:
- YES: The outcome has occurred.
- NO: The outcome hasn’t occurred.
- INVALID: The outcome is unverifiable (explained more in the Augur V2 section below).
Augur has a native ERC20 token called “REP.” While users use ETH to trade (as explained above), they will require REP to create markets. It allows them to:
- Post no-show bonds.
- Dispute market outcomes.
- Buy participation tokens.
Augur’s actions that positively impact the ecosystem, such as making correct predictions, creating markets, and honestly reporting on off-chain events, are incentivized. This makes sure that the interests of the market actors and the market itself are aligned.
Speaking of creating markets. How exactly do you do it?
Augur has made this a pretty, simple, step-by-step process. Let’s take a look:
- A chosen oracle reports on the outcome at appropriate times.
- Post a no-show bond, to ensure that the designated reporter is economically incentivized to act correctly.
- Post a validity bond (in ETH).
- (Optional) A creator fee that’s a percentage of settlement fees (in ETH)
- If participants are not happy with the outcome, they can invoke Augur’s in-built dispute process.
Is Augur a standard DeFi price predictions market?
Augur is a set of open and public smart contracts that run on top of the Ethereum chain. They are not a prediction market in themselves. Instead, they are just a protocol that users can use to create their own markets. In other words, the users are responsible for the creation and maintenance of these markets.
Augur V2

Augur V2 was released on July 28, 2020. Its main aim is to address several issues like UX, onboarding, market-making, etc. Some of the features that Augur V2 will be bringing in are:
- Mobile-focused user interfaces.
- Market-making tools: Improves overall liquidity via 0x and enables cheaper and faster orders.
- Market settlements are now possible with DAI, instead of ETH.
- Finally, and most importantly, INVALID markets will receive more explicit specifications. This, in turn, will lead to the creation of markets that are better worded and more well-defined.
Augur V2 improves overall user-experience by leaps and bounds.
DeFi Prediction Markets #2: Gnosis

Gnosis is another Ethereum-based, open-source protocol for the DeFi predictions market. The core ideas behind Gnosis is as follows:
- Firstly, it allows users to trade cryptocurrencies that are representative of event outcomes on an open market.
- Secondly, the native GNO tokens gain or lose value depending on the predictions made by the user.
- Finally, it aims to build a decentralized infrastructure that the users can use to create prediction markets.
Gnosis attempts to achieve its vision via the use of the following platforms:
- Apollo: A platform where users can create their own tokens.
- Gnosis Ecosystem Fund (GECO): Allows teams to increase the adoption of dapps by leveraging the full potential of Gnosis’ products and protocols
- DutchX: A DEX or decentralized exchange for users to trade and auction their tokens.
- Gnosis Safe: The native wallet that allows you to interact with Ethereum applications.
So, how does Gnosis tie all these together?
For that, we need to look at these three layers.
- Core Layer: The whole foundation of the Gnosis DeFi predictions platform is the core layer. This layer has all the smart contracts responsible for powering events, outcome tokens, settlements, and various platform mechanics.
- Service Layer: The main interaction layer of the whole ecosystem. This layer has chatbots, payment processor integration, stablecoins, etc., and anything else that improves ecosystem interaction.
- Applications Layer: This is the customer-facing layer of Gnosis. It has all the prediction market dapps that are built by third-parties using the underlying protocol.
Gnosis – The dual token ecosystem
Gnosis has two tokens in its ecosystem – GNO and OWL. Let’s take a closer look at how these two tokens interact with each other.
- GNO: The ERC20 token sold during the Gnosis ICO (Initial Coin Offering). Gnosis users stake GNO tokens to generate OWL tokens. Users can lock up GNO for up to one year. The amount of OWL received is proportional to the length of the staking period. The total supply of GNO is 10 million.
- OWL: These tokens are used to pay fees on the Gnosis platform. These are stablecoins pegged 1:1 to the US Dollar. In other words, each OWL is worth $1. Transaction fees not paid in OWL are collected, sold for GNO, and burned.

DeFi Prediction Markets – Conclusion
So, there you have it. The truly wonderful thing about DeFi is that it allows for more innovative and decentralized versions of legacy financial structures – like prediction markets. Decentralized finance prediction markets can circumnavigate the shortcomings of centralized markets and allow for more participation and higher liquidity. While Augur and Gnosis are definitely the market leaders, there are several other interesting DeFi predictions protocols like Helen and Omen.
We hope that you learned a lot about DeFi price prediction markets from this article. Having said that, do keep in mind that prediction markets are just one aspect of the DeFi-verse. It has a lot more to offer, such as lending, derivatives, decentralized exchanges, etc. There is a reason why DeFi currently has so much hype in the market. It is revolutionary in every sense of the word.
Speaking of which, do you want to learn more about DeFi, besides DeFi prediction markets? If yes, then check out our blockchain courses at Ivan on Tech Academy. We have some of the industry’s best experts on the subject, giving you hours of valuable content on DeFi. Come join our academy and open yourself to the world of blockchain and decentralization.





