Over the last year, the term “DeFi” has caused quite a stir in the decentralized community. Many in the community believe that DeFi, or decentralized finance, can completely turn the global economy on its head by making the finance sector transparent and more easily accessible. The DeFi movement leverages decentralized networks to transform old financial products into trustless and transparent protocols that run without intermediaries:
- The pitfalls of traditional finance.
- What is DeFi, and why do we need it?
- DeFi use-cases and applications.
DeFi has a unique opportunity to craft a unique niche for itself in the space. There are currently 1.7 billion people around the world who don’t have access to essential financial services. However, with a simple internet connection, they will be able to access smart contracts and experience immense financial growth and security with DeFi. So before we look into the nitty-gritty of this revolutionary system, let’s understand what’s going on currently in traditional finance systems.
Traditional Finance and the $1.5 trillion problem
Traditional finance is centralized. We have central banks an authorities taking care of our money for us. Since we don’t have the right to choose the monetary policy that governs us, all that we can hope and pray for is that these institutions are not going to take advantage of us and opt for policies that align with the interest of the majority. However, as history has shown us, a system based on “trust,” is inevitably going to fail.
During the 2020 Coronavirus crisis, the Federal Reserve, USA’s central banking system, made the headlines by stating that they would inject as much as $1.5 trillion dollars into the market to prevent ‘Unusual Disruptions’ and bail out banks that are under immense financial pressure. However, this money isn’t free, and somebody has to pay for it eventually. Ultimately, the ordinary folks have to pay the price and it comes either in the form of increased taxes or higher unemployment rates.
Once again, this underlines the core problem with this sector. There is a massive misalignment between the interests of the people and the interests of the financial institutions. This misalignment was so apparent during the Covid-19 crisis that it led to one of the most infamous headlines of all time:

Image Credit: CNN
Even though millions around the world are losing their jobs, big companies still manage to profit.
The solution to this problem lies in decentralization.
What are DeFi apps?
DeFi or “decentralized finance” is an all-encompassing term that refers to the digital assets, decentralized applications (DApps), financial smart contracts, and protocols that run on top of public blockchains like Ethereum. Public blockchains have several highly disruptive properties.
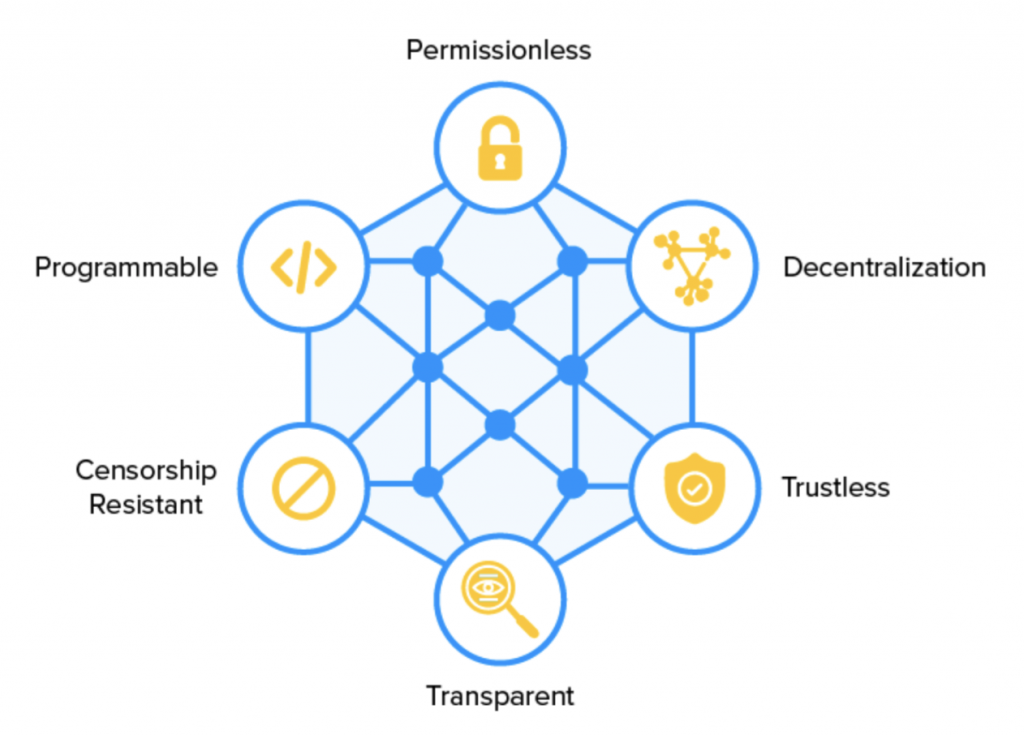
Image Credit: appinventiv
- Decentralization: Every node in the network maintains a copy of all the data stored inside the blockchain, negating the need for a centralized authority. Imagine a decentralized bank or a finance system that’s not dependent on the whims on a central regulator. That’s one of the most exciting promises of DeFi.
- Transparency: Since everyone in the network maintains a copy of the blockchain, all the data stored inside is open for them to see.
- Permissionless: A public blockchain, as opposed to a permissioned/private one, is open for everyone. By utilizing this property, DeFis will be able to create an open system where people from around the world – who don’t have access to sophisticated financial services – can participate without going through extensive red-tape.
- Trustless: In a decentralized system, individual nodes have an economic incentive to work in the interest of the system. This is in stark contrast to the traditional financial system where you need to trust a centralized governing body to do their job well.
- Censorship Resistance: Blockchains leverage sophisticated cryptographic hash functions to be completely immutable. In other words, once you enter some data into the blockchain, no one can tamper with it.
- Programmable: Public blockchains like Ethereum and EOS are open-source systems and they welcome developers from all around the world to create their own unique applications on top of them. This openness to innovation has led to the creation of some fantastic DeFi applications.
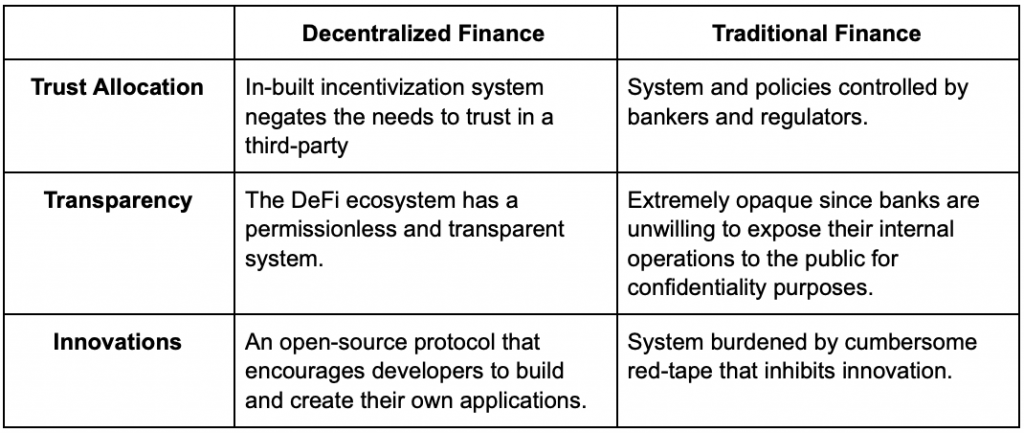
Decentralized Finance vs Traditional Finance
Why do we need DeFi when we have cryptocurrencies?
Since cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are already decentralized and borderless, in nature, why do we need DeFi?
- Comparing pure cryptocurrencies with DeFi is like comparing US Dollars to loans. DeFi is a financial service that can have multiple use cases.
- Old school cryptocurrencies have decentralized the act of issuing and storing money. However, they haven’t decentralized the core financial system in itself.
- Cryptocurrencies are still dependent on centralized exchanges for their use. DeFi brings in decentralized exchanges to make sure that there no centralized point-of-failures within the ecosystem.
- Centralized organizations manage the majority of the cryptocurrencies.
The current DeFi ecosystem
A vast majority of the DeFi apps are built on the Ethereum blockchain since it’s the most well-known smart contract platform in the world with a huge developer community. You can think of Ethereum as a global supercomputer that rents out its computational resources to developers around the world who want to build their applications on top of it.
As per DeFi Pulse, this is what the current state of DeFi applications on Ethereum looks like:
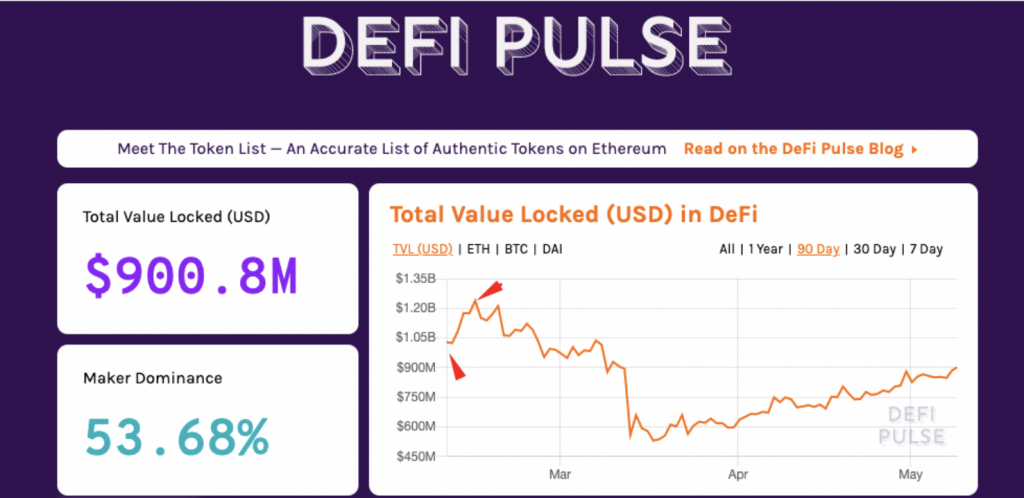
- $900.8 million is currently locked in the DeFi smart contracts.
- On February 11, 2020, the amount of USD locked up in DeFi crossed $1 billion.
- On February 15, 2020, the amount locked up reached a peak of $1.24 billion.
- MakerDAO, a DeFi lending protocol that’s famous for its crypto-pegged stablecoin DAI, has a 53.68% dominance over the market.
DeFi.review gives us a complete overview of the decentralized finance landscape across all platforms.
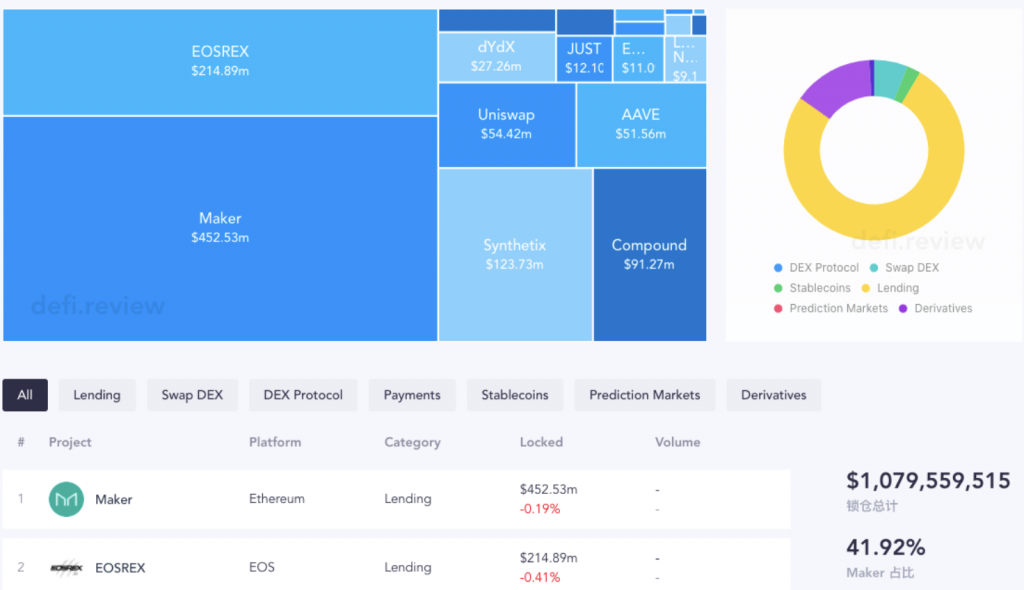
- When you include all the platforms, the total money locked up crosses a billion dollars.
- Maker still has the most dominant presence in the market, with 41.92%.
- Coming in second is the EOS-based lending protocol, EOSREX with $214.89 million locked up.
DeFi Use Case #1: DeFi Lending
Transparent and open lending protocols have fast become the most popular use-case of DeFi. Let’s hop back to Defi.Pulse and check out the top five most popular DeFi applications on Ethereum:
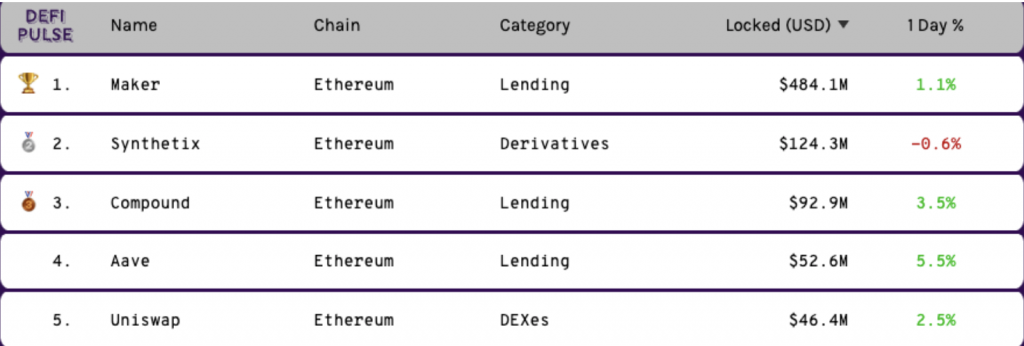
As you can see, three out of the top five are lending protocols. The reasoning behind this is two-fold:
- The immense popularity of MakerDAO and its stablecoin DAI.
- DeFi Lending is a very convenient way of earning passive income.
What is DeFi Lending?
Similar to a traditional bank, a user deposits their money to the platform and earns interest when someone else borrows it. The core difference lies in how the platform handles the money in between.
In traditional credit structure, the loans are issued by financial institutions such as banks or third-party lending services. These institutions conduct a thorough background check of the borrower to judge if they will be capable of paying back the loan or not. This check includes but isn’t limited to:
- Annual salary.
- Credit score.
- Past defaults.
As such, many people get excluded from the process even. Even if they do get in, they still have to pay exorbitant interest rates, making the whole system highly inefficient.
DeFi lending aims to democratize this entire process and connect borrowers to a wide pool of lenders. Instead of having institutes acting as intermediaries, smart contracts directly connect the borrower and the lender with each other. The smart contract is responsible for:
- Dictating the terms of the loan agreement based on predetermined conditions.
- Distributing the interest accordingly.
Both the borrower and the lender can benefit immensely from the open nature of DeFi lending.
Borrowers
- Zero credit checks which make loans available to a wide variety of investors.
- Gain access to different utilities. Eg. A borrower can temporarily loan some EOS tokens and stake them in the EOS ecosystem to take participate in network governance.
- Immediately short the asset they borrow in different exchanges to participate in margin trading.
Lenders
- It’s a solid long-term HODL plan.
- The opportunity to earn passive income via interests.
- Due to the transparency and lack of mediators, the lender earns higher returns and has a clearer understanding of the risks involved.
Best DeFi Lending DApps #1: MakerDAO

MakerDAO is, far and away, the most dominant project in the decentralized finance space with a whopping $484 million locked up in it. MakerDAO allows you to lock up your Ether in a smart contract called Collateralized Debt Position of CDP, in exchange for DAI, a stablecoin that’s pegged by a basked of cryptocurrencies. In the Maker ecosystem, there are no Lenders. The DAI you receive is a loan that’s collateralized by the ETH you locked up in the CDP contract. Along with DAI, MakerDAO has another native token called “MKR.” MKR is used to pay interest fees and for participating in Maker’s decentralized governance.
The DAI and CDP relationship
- CDP generates DAI after the user locks up Ether in the contract.
- The Ether gets locked up in the form of Pooled Ether or PETH.
- The CDP calculates the interest accrued on the locked PETH over time. This interest is also known as the “stability fee.” This fee can only be paid by the MKR tokens and it’s immediately burnt upon use.
- The user can withdraw their ETH from the CDP any time they want by paying back an equivalent amount of DAI.
- Since cryptocurrencies are unstable, the loans provided are “over-collateralized,” to ensure the stability of DAI tokens. Over-collateralization means that the value of the asset exceeds the value of the loan. This makes sure that the price of DAI remains stable through market fluctuations.
- The current collateralization ratio is 121.5%. So, if you send $121.50 worth of Ether to the CDP, you will get 100 DAI, in return.
Interacting with CDP
Users can interact with CDP using a four-step process.
- Creation: The user triggers CDP creation by sending a transaction to Maker. They then send another transaction to fund the CDP with ETH.
- Generation: The user now sends a transaction to generate and retrieve the amount of DAI they want from the CDP. The CDP automatically calculates the collateral accrued based on the collateralization ratio and locks in the amount.
- Debt Payment: The user can retrieve the locked Ether only after the CDP becomes debt-free. The user will need to pay off both the debt and the stability fees accrued (in MKR) for their CDP to be entirely debt-free.
- Closing: Following the debt payment, the CDP user can send a final transaction to Maker to retrieve all or some of their collateral back in their wallet.
Best DeFi Lending DApps #2: Compound

Compound is another promising DeFi Lending protocol that aims to build an algorithmic money market protocol on Ethereum. Users can lock up their assets in Compound’s liquidity pool and earn passive income via a continuously-compounding interest.
Compound currently supports BAT, DAI, ETH, USDC, REP, and ZRX. Each of these tokens connects to Compound via its native token “cToken.” cToken allows users to earn interest on their money while also enabling them to transfer, trade, and procure services in other applications.
Points to note:
- Compound maintains excess liquidity through a moving interest rate that’s dependent on the real-time supply and demand of each crypto asset.
- The Interest rate gets compounded as soon as a block is mined.
- You have the freedom to pay back your loans and unlock your locked assets, any time you want.
Users can mint or create cTokens using an Ethereum friendly wallet like MetaMask, Coinbase wallet, or Huobi wallet.
DeFi Use Case #2: DeFi Derivatives
“Derivative” is a pretty well-known term in traditional finance. It refers to a contract that derives its value from the market performance of an underlying entity such as an asset, index, or interest rate. The terms of the contract are executed by a third-party called “broker.”
Decentralized derivatives are pretty similar, save for one crucial factor – instead of a centralized broker, they use a smart contract to. There are several advantages to this approach:
- Eliminates the need for a third-party.
- Automated, on-chain settlement.
- Users can create instruments on virtually any underlying asset.
So, why use derivatives in the first place? There are two main reasons:
- It protects you from future price fluctuations since you signed a contract to buy an asset for a fixed price.
- Gain by correctly predicting how the price of the entity is going to change in the future.
The four types of derivatives
- Swaps: Allows counterparties to exchange cash flows between each other. The swaps derivative contract defines the dates of the pay-outs and its calculation.
- Options: The buyer can purchase or sell the underlying asset governed by the contract if they want to.
- Futures: Buyer must purchase the underlying asset at the predetermined price on a fixed date in the future.
- Forwards: This is a more customizable version of the futures contract.
Importance of DeFi derivatives
Synthetic assets, like derivatives, form a huge and vital part of the global financial landscape. As per the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), for the first half of 2019, around $640 trillion in financial derivatives are currently outstanding. This easily makes the derivatives market the largest in the world.
With DeFi, it will be possible to bring these derivatives contracts in the decentralized space. Let’s look at just some of the derivatives use cases in the crypto world:
- Futures derivatives can allow investors to mitigate the risk of price fluctuations.
- Allow users in developing countries to invest in stocks in first-world countries.
- Bet on a coin’s future performance.
DeFi derivatives app example – Synthetix

Synthetix is a peer-to-contract trading platform that allows users to mint various synthetic assets, including derivatives. The platform’s native Synth (SNX) token provides access to 20 different assets such as bitcoin, USD, gold, TSLA (Tesla stocks), etc.
So, how does this system work? Let’s take a look:
- A user creates synthetic assets by putting collateral in the form of SNX tokens.
- The user can now swap their synthetic asset for another.
- Synthetix’s pooled collateral mechanism ensures that all the SNX collectively take on counterparty risks of other users’ positions.
DeFi Use Case #3: Decentralized Exchanges
Exchanges serve one of the most critical functions in the crypto ecosystem, serving as a bridge between the fiat and crypto worlds. Having said that, it’s hard to ignore its many problems and the way it has plagued the crypto space over the last several years.
- First, let’s address the elephant in the room. Time and again, centralized exchanges have proven themselves to be an obvious target for hackers. Such repeated attacks have damaged the public perception of cryptocurrencies.
- Since exchanges are centralized entities, they can be subject to mismanagement. The infamous Mt. Gox hack happened directly as a result of gross mismanagement.
- Finally, the operations of the exchange can be affected by the policies of the country it is registered in.
What are decentralized exchanges?
Decentralized exchanges or “DEX” enables trustless trading without being intermediary-dependent by running on top of a shared ledger. A DEX directly connects two parties with each other and allows them to share assets without having to go through an intermediary. Let’s look at how the process works:
- Suppose you want to convert your BTC to ETH.
- You send in a request to the DEX to convert your BTC to ETH.
- The DEX smart contract will first check if you have sent them the required amount of BTC or not.
- Now the DEX will go through its other requests to match you with an appropriate order.
- Once the transaction is complete, you’ll receive the appropriate amount of ETH in your wallet.
Advantages of DEX
- The lack of an intermediary ensures that there is no single point of failure.
- Not dependent on centralized management.
DEX Example #1: Uniswap

Uniswap is an Ethereum-based DEX that allows for the trading of ETH and ERC20 tokens. It uses liquidity reserves in facilitating the exchange of digital assets on its platform. These reserves are provided for by a network of “liquidity providers.” Individuals can use the protocol as long as they have the MetaMask wallet installed.
Uniswap consists of two Vyper-coded smart contracts:
- Exchange contract.
- Factory contract.
Exchange contract
- Each exchange contract supports exactly one ERC20 token and holds a reserve of ETH and its supported ERC20 token.
- You can conduct ERC20 to ERC20 exchange using ETH as an intermediary through these contracts.
Factory contract
- Used to deploy new exchange contracts.
- Serves as a registry for exchange contracts.
DEX Example #2: Kyber Network

Kyber Network is one of the most well-known DEXs out there. Kyber works using pools of over 70 different ERC20 tokens called “reserves” that are controlled by Different parties. If you send an order to the Kyber protocol, it looks through all the reserves available and returns the best price possible.
The native token of Kyber is called Kyber Network Crystals (KNC). The reserves need to pay fees in KNC to continue their operations. The fees collected are either burned or awarded to integrated dApps.
Conclusion
The DeFi movement is one of the most promising offerings of the decentralized space. Not only is the tech involved intriguing, but it truly has the unique opportunity of revolutionizing the global financial landscape. If you want to be a part of this movement, then at Ivan on Tech Academy, we have the perfect course for you.
Our DeFi course will give you the fundamental knowledge needed to dive deeper into the wonderful world of Decentralized Finance. The course provides you with the fundamental building blocks required to provide you with a holistic view of the entire DeFi space. Join us and understand the true potential of this space.





