
When it comes to building and hosting DeFi protocols, Ethereum pretty much rules the roost. As per DeFi Pulse, a staggering $872.20 million is locked up in Ethereum-based DeFi. However, as it turns out, Bitcoin has been making impressive leaps in the DeFi department themselves. In this article, we are going to go through some of these Bitcoin DeFi apps. Before we do so, let’s go through the basics first.
DeFi definition
While cryptocurrencies plan on creating an open currency system that gives you complete control over your own money, DeFi aims to take things a little further by building a public, global, and all-inclusive alternative to all the financial services in the world. As ambitious as this sounds, this was previously impossible on the Bitcoin blockchain. However, with the advent of Ethereum and smart contracts, such implementations soon became probable.
Decentralized definition
Smart contracts allow developers to create decentralized applications or dApps. As the name suggests, dApps are applications based on the blockchain, which are not controlled by a centralized entity. This gives them several advantages:
- The rules stated within the smart contracts govern the operations executed within the dApps. Think of smart contracts as self-enforceable and automated contracts between multiple entities. Because of this, DeFi dApps can provide financial services without being controlled by banks or financial regulators.
- The underlying code is public and open-source. This achieves two goals. Firstly, users who are well-versed in coding can understand what’s exactly going on, which fosters trust. Secondly, other developers can use the code to create even better applications.
- As with anything blockchain-related, DeFi apps are present for everyone around the world. The open, permissionless nature also lowers the barrier-to-entry.
- Different DeFi applications – like stablecoins and decentralized exchanges – can club together to form a whole new protocol.

Innovative DeFi with Bitcoin
More and more Bitcoin-based DeFi applications are currently entering the market and have managed to gather a pretty sizeable user base. Let’s go through some of these implementations. Defi pulse lists the following Bitcoin-related DeFi applications:
- Lightning Network.
- Atomic Loans.
- Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC).
#1 Lightning Network

Founded by Joseph Poon and Tadge Dryja, the lightning network is a layer-2 scalability solution for Bitcoin. It’s called “layer 2” because it operates above the Bitcoin blockchain in the form of bi-directional state channels. Before we go into the details, let’s understand why Bitcoin needed this solution in the first place.
Bitcoin’s scalability woes
Few things have been talked about, debated, and documented as extensively as Bitcoin’s scalability problems. Just to give you a brief overview:
- Bitcoin manages 7-10 transactions per second, which is abysmally low.
- Bitcoin’s block size is only 1 MB, which means that it can accommodate only a limited number of transactions.
With the demand for Bitcoin going up in the future with an increasing number of use cases, it will inevitably shoot up. As per Blockchain Capital, the average on-chain Bitcoin transaction fees will reach $100 by the end of 2020. Because of this inflated transaction fee, Bitcoin is very impractical for microtransactions.
What are state channels?
As mentioned above, the lightning network is a two-way payment channel that connects two users directly with each other. These state channels enable you to execute transactions that would typically occur on the blockchain, off the blockchain. Payments channels are a specific form of state channels that deals only in payments.
So, how does a state channel work? Let’s take a look.
A portion of the blockchain gets sealed off via multi-signatures or smart contracts. The participants predetermine the terms of the smart contract. This temporarily isolated portion is known as a “state channel.” The features of these channels are as follows:
- The participants of the channel can interact directly with each other without having to go through the miners.
- These participants can conduct multiple microtransactions without having to commit each and every value to the blockchain.
- The final transaction status of each gets automatically added to the blockchain.
Let’s take a working example to understand how it works. Imagine two entities, A and B. These two need to conduct multiple transactions with each other. However, since these are microtransactions, it’s not that practical to go through the whole headache of sending money via bank-to-bank transfer. So, this is what they do:
- A and B both set aside $10 each and keep their combined $20 inside a safe.
- A and B know half of the access code of the safe.
- Both of them also maintain a ledger that continually documents their individual balances.
- If A pays B $5, it doesn’t need to physically hand over the case to B. A simply deducts $5 from its balance, while B adds 5 to theirs. So, the overall balance remains $20, while A has $5 and B $15.
- Suppose, 7 transactions later, A and B’s balances are $6 and $14, respectively.
Understanding payment channels
At this moment, they decide to end their interaction. A sends over $4 to B to replicate the final state. So, instead of conducting 7 transactions, A just sent over one transaction. This is the core philosophy behind how payment channels work.
A state channel can be closed after it fulfills two predetermined conditions:
- A fixed period of time has passed.
- After the completion of a fixed number of transactions.
The most common forms of payment channels are as follows:
- Nakamoto High-Frequency Transactions.
- Spillman-Style Payment Channel.
- CLTV-Style Payment Channels.
- Hashed Timelock Contracts (HTLC)
HTLC is the most well-known form of the payment channel.
What are HTLCs?
The features of an HLTC channel are as follows:
- Allows participants to open up payment channels and share funds before a predetermined deadline.
- Cryptographic hash functions.
- Cryptographic hash functions validate the payments between the participants involved.
- It can allow a party to forfeit their payment, which would be infeasible in a standard blockchain transaction.
- It enables the projects to conduct cross-chain, atomic swaps, which can allow users to swap one cryptocurrency for another.
The Lightning Protocol is an example of HTLC.
Lightning Network – Behind the scenes
Alice and Charlie want to transact with each other, and they both have a common connection with Bob. To do so, they take the following steps:
- Bob opens up two channels with Alice and Charlie. Alice declares that she plans on interacting with Charlie.
- Charlie then randomly chooses a secret number, hashes it, and passes along the hash to Alice.
- Alice sends x BTC to Bob along with the hash that she received from Charlie.
- The only way anyone can unlock the BTC sent by Alice is if they produce a number that generates the same hash as send over by Alice.
- Bob then passes along the transaction and the hash to Charlie, along with the condition.
- Since Charlie has the number, he can generate the hash that will be equal to the one sent over by Alice and unlock the funds.
Lightning Network benefits
- This first thing to note here is that users don’t need to commit every single transaction to the blockchain if they choose to transact with the lightning network. This allows them to conduct multiple microtransactions, which inevitably increases the speed of the transaction.
- Once again, since the miner-interaction is minimal, the transaction fees are on the lower side.
- As mentioned before, the lightning network opens up the avenue for cross-chain atomic swaps.
- The transactions are not taking place over the blockchain, which means that they are not open to everyone. This brings in a high level of privacy.
- Layer-2 transactions lower the bloat and stress in the base blockchain.
#2 Atomic Loans

Atomic Loans is creating the first-ever decentralized Bitcoin-backed loan offering. It uses P2P and cross-chain debt agreements that are open, borderless, and resistant to centrlaized censorship. We have briefly touched upon the technology at the heart of the protocol in the previous section – atomic swaps.
What are Atomic Swaps?
An atomic swap is a P2P exchange of cryptocurrencies that don’t need to go through a third-party service like a cryptocurrency exchange. Some interesting facts about atomic swaps to keep in mind:
- You have full control over your private keys.
- Direct implementation across chains with different native coins
- They can also take place off-chain.
How do Atomic Swaps work?
Suppose Alice wants to swap her BTC for some LTC and has found Bob as a willing partner. The core idea is that they both will agree on a shared secret, which they will use to interact with each other. Now, let’s see how it works:
- Alice and Bob link up via a payment channel. Alice, the initiator, creates a contract address. This address is akin to a multi-lock safe which takes care of both their funds.
- Alice generates a secret value and hashes it. She sends the hash and her BTC to Bob.
- Bob uses the hash to create the temporary, contract address, where he sends his LTC.
- Only Alice can unlock the litecoin in this address because she has the value which generates that particular hash.
- The moment she unlocks the contract address, she reveals the secret value to Bob, who can use it to unlock the Bitcoin given by her.
The goals and principles of Atomic Loans
- The system should be as interoperable as possible and breaks through silos between different blockchains and assets.
- Atomic loan agreements don’t require you to custody funds at any point. All the funds are locked up in user-defined Bitcoin scripts and smart contracts and won’t need to go through any centralized entity.
- Borrowers and lenders can customize their debt agreement and loan terms specific to their needs. This is entirely different from traditional loan systems where one central party determines the rates and terms on their own.
Atomic Loans users
Atomic loans allow bitcoin holders to get stablecoin and fiat liquidity through loans, which they can use to pay off personal and business expenses. On the flip side, this also presents an excellent opportunity for individuals and organizations who want to put their money to work and provide liquidity as a lender.
Looking at both sides of the equation, Atomic Loans identifies two user types who will be a perfect fit for their program.
- Borrowers: Struggling to acquire enough business capital to ensure the smooth functioning of their operations is a prevalent headache for all businesses, irrespective of their space. Speaking specifically about the crypto space, miners struggle to keep their business afloat during a bear market. They could benefit immensely from opting for a loan during a crisis and keep the lights on until the market swings around.
- Lenders: Any financial advisor worth their salt will give you the same advice – “make your money work for you.” Currently, the majority of the people have their money stored in saving banks, which provide a negligible interest rate. The crypto equivalent will be people who store their wealth in the form of stablecoins.
Atomic Loans potential
Atomic Loans looks like a great DeFi use case for Bitcoin. It allows users to lock up Bitcoin as collateral in a non-custodial escrow and draw out loans against it. These loans can be drawn in the form of stablecoins like Dai or USDC. The cool thing about this concept is that it allows users to drawn the full value of their present BTC investment without falling victim to its volatile whims.
Another amazing thing to keep in mind is that its the only viable decentralized service around that provides bitcoin-focused lending. Morgan Creek Digital co-founder Anthony Pompliano said about Atomic Loans:
“There’s a new alternate financial system being built around Bitcoin, with a focus on decentralization. Atomic Loans is building the decentralized financial infrastructure that uses Bitcoin how it was intended.”
#3 Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC)

Another interesting class of Bitcoin-based DeFi offerings is Bitcoin-collateralized ERC-20 tokens. The idea is pretty straightforward – a user deposits Bitcoin into a smart contract that delivers a BTC-pegged token to the user’s Ethereum wallet. The contract leverages an oracle to monitor the real-time value of Bitcoin continually. The core idea is to bring Bitcoin’s liquidity into the Ethereum network. The most popular implementation of this token is WBTC.
Wrapped Bitcoin or WBTC is the first ERC20 token backed 1:1 with Bitcoin. The project is the joint effort between decentralized exchanges Kyber Network and Republic Protocol and BitGo, a crypto custody company. BitGo will handle the initial custody, while Kyber and Ren will use their own Bitcoin holdings to provide the initial liquidity.
A decentralized autonomous organization, or DAO, made up of 16 projects, including DeFi protocols like Dharma, Compound, MakerDAO, and Set Protocol, runs the WBTC initiative.
How can I swap WBTC for BTC?
- Through the eight initial merchants who act as sources of token distribution, users can exchange their BTC for WBTC through the eight initial merchants – Dharma, Kyber, Set Protocol, GOPAX, AirSwap, Prycto, Ren, and DiversiFi.
- Prior to swapping, the user must go through the KYC/AML process with the merchant of their choice.
- The merchant mints WBTC by supplying the user’s BTC to the custodian.
- The merchant can also redeem their BTC by burning an equivalent amount of WBTC tokens.
- The users can thoroughly verify whether or not their WBTC is fully-backed via on-chain proof of reserves.
- The DAO members maintain a multi-sig contract that adds or removes valid merchants and custodians. This entire process is very open and transparent.
Reasons behind WBTC’s recent popularity
The biggest reason behind WBTC’s recent popularity is that the MakerDAO community has voted for it to be one of the coins in its collateral basket. This inclusion alone caused WBTC’s cumulative on-chain value to cross $22 million.
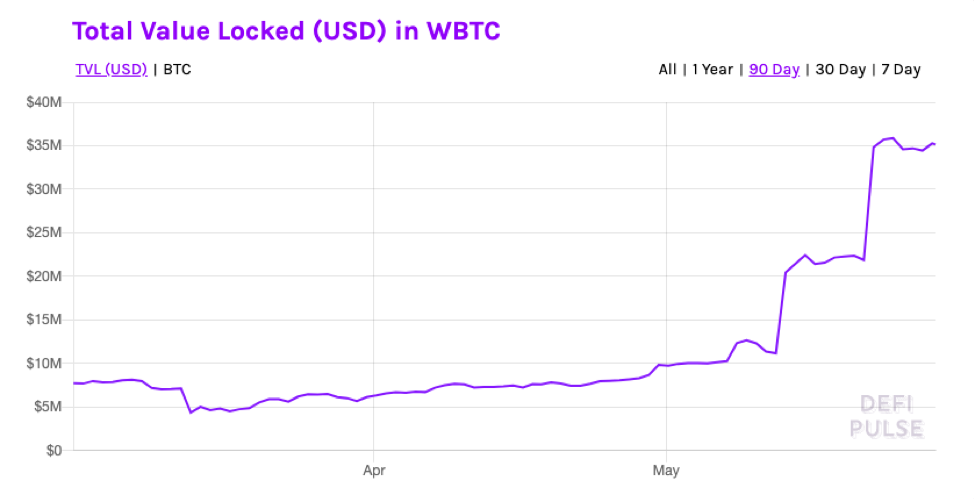
Currently, the total amount of USD locked up in WBTC has crossed $35
The majority of the trades happen via centralized exchanges. One of the biggest reasons why DEXs haven’t entirely changed the game yet is because of the severe lack of liquidity. However, WBTC brings in the functionalities of the most liquid cryptocurrency in the world – Bitcoin. DEX allows you to trade for other ERC-20 tokens with BTC. Another exciting feature is that it will enable developers to write smart contracts that integrate Bitcoin transfers. However, despite its growth in popularity, Ether remains the dominant DeFi coin.
WBTC criticisms
WBTC has attracted quite a lot of criticism in recent times. According to Reddit user u/Trizeropz:
“Calling this new ERC20 BTC thing a wrapped coin and ‘innovative’ is bullsh*t. What they sell you is a worthless new ERC20 token, while getting your BTC […] Nothing different to a scammy ICO, exchanging your ETH and BTC with worth, into newly printed worthless ERC20. If they exchange it 1:1, why not just exchange to ETH itself? Nothing different but HEY printing money.”
#4 Money on Chain

Finally, let’s look at another implementation of Bitcoin DeFi that has seemed to grow immensely in popularity in recent times. However, before we do so, let’s give you some background context.
Sidechains on Bitcoin
Quick question for you.
Which is the most secure, used, and decentralized blockchain in the world?
Yup, it’s Bitcoin.
If that’s the case, then it might just be the best possible smart contract platform out there! This is why several projects like RSK and Liquid are building sidechain functionalities on top of the Bitcoin blockchain.
What is RSK?
Rootstock is one of the most well-known projects in the space that’s connected to Bitcoin via a two-way pegged sidechain. It maintains its security via a special consensus protocol called “merge-mining.”
Rootstock fuels its internal ecosystem with Smart Bitcoin or SBTC. Users can swap their BTC for SBTC at a 1:1 ratio through the peg. RSK has a technological stack built on top of it called Rootstock Infrastructure Framework Open Standard (RIFOS). RIFOS acts as a third layer on top of Bitcoin, and it brings in several developer frameworks into Bitcoin to enable them to build DeFi applications. RIFOS has the following properties
- Developers can easily integrate their products with the RIFOS ecosystem as long as it is compatible with the underlying protocols.
- The Bitcoin Network’s inherent security protects all the apps made on RIFOS.
- RIFOS has its own token called “RIF” which will be fuel the services running inside it.
- RIF protocols have mechanisms that can trigger network effects and economies of scale. RIF developers are presently working in three areas – Storage, Payment, and RNS.
What is Money on Chain?
Money on Chain has collaborated with RIF to create the world’s first stablecoin collateralized by Bitcoin. The protocol utilizes a dual-token system to ensure price stabilization. The tokens are – Dollar on Chain (DOC) and BitPRO (BPRO). Let’s look at what they have to offer.
- DOC: DOC is the main stablecoin, which is pegged to the USD. The BTC fully collateralizes it, however, its dollar peg ensures that it is safe from Bitcoin’s volatility. You can use DOC to conduct quick transactions, store of value, and unit of account.
- BPRO: BPRO takes on the volatility risk associated with the Bitcoin association. While BPRO will be subject to the whims of the market, it can provide a way for its holders to earn passive income on their coins. BPRO holders get awarded from a percentage of platform-collected fees, an interest rate, and small leverage on the price of Bitcoin.
Conclusion – Bitcoin DeFi

Bitcoin is slowly, but surely, making its presence felt in the DeFi landscape. As per DeFiPrime, a DeFi aggregator site, out of the 245 projects listed, 23 are Bitcoin-based.
When you keep in mind that Bitcoin is the biggest project in the space, you can only expect this number to go even higher in the future. However, will it become the premier DeFi platform of the future? While it’s hard to bet against Bitcoin, it isn’t easy to see them overcome Ethereum’s lead. It is tough to see Bitcoin overcoming these odds with more promising projects coming in like Cardano and Algorand. However, can we expect super high-quality Bitcoin-based DeFi dApps in the future, which could be potential game-changers? Absolutely. This is why it’s easier than ever to increase your software engineer salary by becoming a blockchain developer at an online blockchain school. The time is now!





