
EIP-1559 could offer some good news for those longing to see improvements to Ethereum’s user experience and the current gas fee system. This proposal has recently been accepted into Ethereum’s London network upgrade scheduled to come to the mainnet this summer. This upgrade is now being intensely debated following its recent inclusion in the London fork, even though it has been over two years since EIP-1559’s initial proposal.
EIP-1559 is essentially a proposal to change Ethereum’s fee structure. But it’s also known as “Ethereum’s scarcity engine” or “ETH’s burn mechanism.” The Ethereum faithful should be excited by this since burning ETH will increase the asset’s scarcity.
Burning, however, is only one of its positives. With Ethereum’s Berlin hard fork scheduled for April and the London fork to follow three months later, doing the math tells us that EIP-1559 should kick off in July.
A lot of news headlines have indicated that Ethereum will “go deflationary” with the introduction of EIP-1559, or Ethereum’s fee burn proposal. However, is this really the case? This article takes a closer look at the potential implications of Ethereum’s EIP-1559 proposal, and how it intends to change Ethereum’s gas fee mechanism. Moreover, we explore why some miners are opposed to EIP-1559.
What Is EIP-1559?
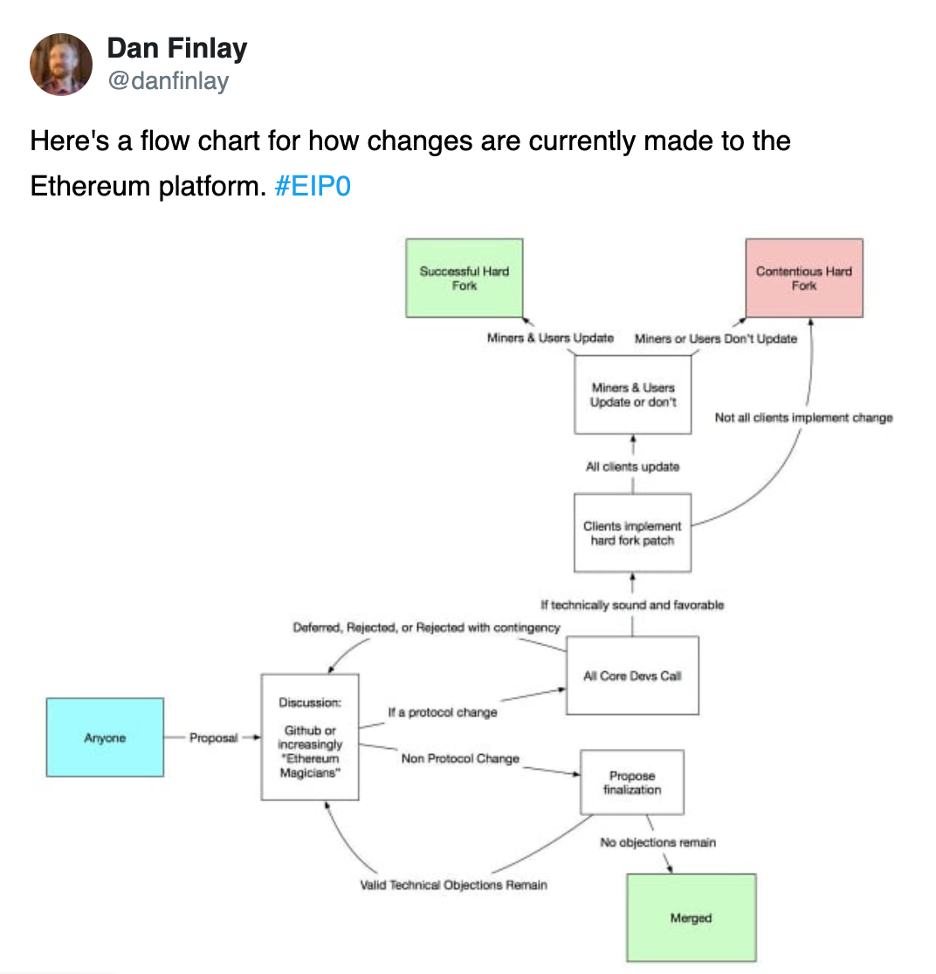
First off, EIP stands for an ‘”Ethereum Improvement Proposal.” When it comes to open-source software development, anyone can add code to a repository. But to have that new code included means getting the proper approval. In the case of Ethereum, such approval must come from the core developers who manage its repository on Github.
So, passing an EIP is like passing a bill through congress. It can’t become law until it goes through the proper inclusion process. Someone must first propose an EIP. Next, the devs evaluate the EIP, edit, and test it before including it.

This particular EIP is a big deal because it’s a huge upgrade and change to the second-largest cryptocurrency’s monetary policy – that being Ethereum. If you want to become an expert in Ethereum and all things crypto, join Ivan on Tech Academy today. A great place to start is the Ethereum 101 course.
Why EIP-1559?
With all the network issues Ethereum has been experiencing lately (like congestion and high gas costs), many are expressing doubts. Whales can afford the high cost of transactions, but these premiums are causing a lot of pain for the average user. Because of it, other projects are springing up to capitalize on Ethereum’s shortcomings.
Avalanche, Polkadot, and Cardano are a few that come to mind. But we also have the Binance Smart Chain (BSC) and all its players like PancakeSwap and Venus popping up.

PancakeSwap is BSC’s answer to Uniswap and Venus is its version of Yearn Finance. Each of these projects is wooing customers away from Ethereum with microscopic fees in comparison. With Ethereum 2.0 still looming somewhere off in the future, the network needs solutions in the interim to alleviate the pressure and that’s where EIP-1559 comes in.
Ethereum’s Auction Mechanism
First, let’s look at how Ethereum currently operates. It uses a mechanism called “first-price auction,” whereby users submit their bids to include their transaction in the block. This competitive bidding causes congestion and increased gas prices across the Ethereum blockchain. Not to mention, some users often end up needlessly paying more than others who have transactions included in the same block. It’s far from fair or efficient.
Do you want to learn how to program smart contracts on Ethereum? Start your educational journey today at Ivan on Tech Academy! The higher fees aren’t such a big deal for the whales. But it is a big deal for everyone else, and it also increases uncertainty as to the proper amount of gas required to send a transaction. It’s not easy, especially when bidding against an army of investors with deep pockets moving millions of tokens around to farm yield.
EIP-1559 Base Fee
So, how will EIP-1559 fix these issues? It won’t fix them all, but it will be a start. By deploying a Base Fee, it will target the market rate gas price and adjust on the fly on a block-by-block basis. That way, users can easily send their transaction without having to guess which gas option to choose like they do now.
There will also be an option to tip the miners to incentivize them to include a transaction in the block quicker. This feature will be similar to giving a waiter a tip for good service. The only difference is that the tip will come before the service and hopefully expedite it. However, tipping the miners will not impact the fees to be paid.
EIP-1559 Quicker Transaction Inclusion
Under the current system, transactions can end up in the “pending” status for long periods. That’s because with the network congestion these days, blocks are always full, with the highest-paid transactions quickly filling the next block. With the kind of action on Ethereum right now, users must pay a very high gas fee to get a transaction immediately included.
While crypto veterans and DeFi Degens have learned how to navigate the current system, it’s not ideal for onboarding new users. It’s too complex and filled with uncertainty.
The EIP-1559 Solution
With the new EIP, users need to send transactions with a fee higher than the Base Fee, along with a tip for the miner to include them in the block.
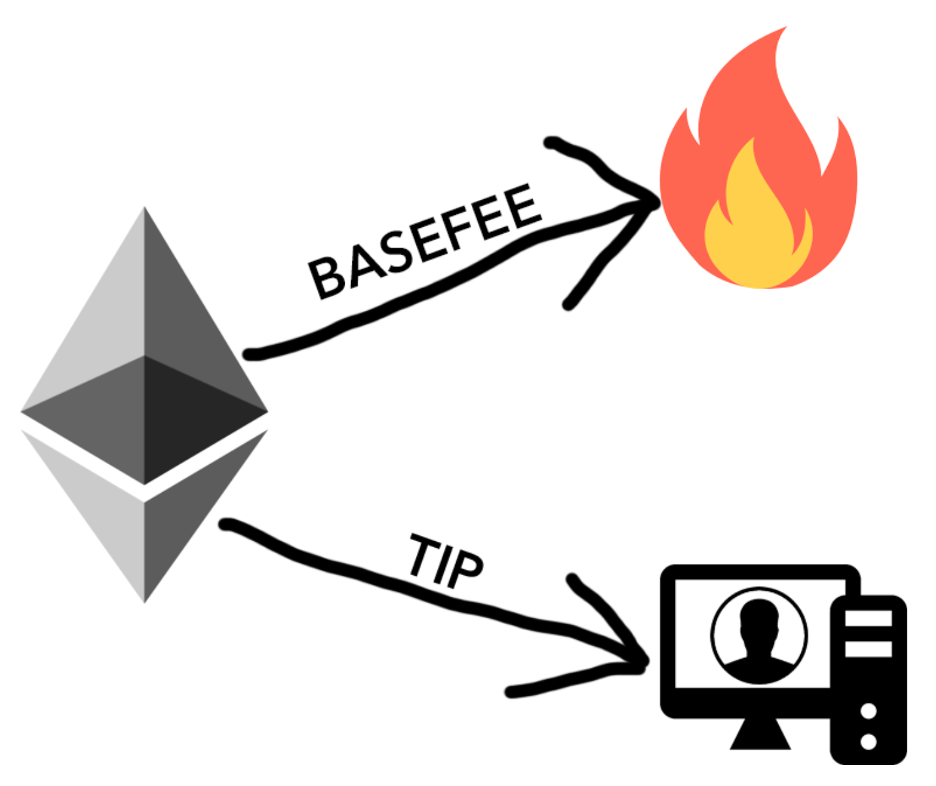
However, the Base Fee can fluctuate between the time when a user sends a transaction, and a miner includes it in a block. To counter this, users can specify a Fee Cap. This is the maximum they want to pay. After inclusion, they are refunded the difference between the final Base Fee and their Fee Cap, and don’t forget the tip!
Wallets can set this value by default, so users won’t have to set it manually each time.
Price Transaction Inclusion
EIP-1559 operates similarly to Bitcoin’s PoW difficulty adjustment. With Bitcoin, the difficulty for mining a block automatically adjusts upwards when blocks are mined faster than the established one block per ten minutes. On the other hand, it adjusts downwards when blocks are mined slower than ten minutes. Hence, Bitcoin blocks can maintain their steady ten-minute average. EIP-1559 also does this but with price for transaction inclusion.
So, when Ethereum blocks get more than 50% full, the gas costs for inclusion will increase. When blocks get to less than 50% full, the gas costs decrease.

EIP-1559 effectively doubles the Ethereum block space, but then it targets blocks only to be 50% full. The block size will still average out to the same size over time. However, the built-in flexibility allows for extra capacity for transaction inclusion.
How EIP-1559 Affects Ethereum
While EIP-1559 is a major upgrade and will provide vast improvements to the Ethereum network, it is not a cure-all. The upgrade will make transactions more efficient, but it will not fix network bloat because it is not a scaling solution.
What it will do, however, is improve UX by making fee prediction easier. Nor will users have to worry about transactions getting stuck in the mempool for long periods. This EIP aims to smooth out Ethereum gas fee volatility while helping users better estimate their transaction rates and times.
EIP-1559 Burn Mechanism
One of the most important features of this upcoming EIP is its effect on ETH’s supply. What happens is that the Base Fee is burned. Since this fee is paid in ETH, more ETH gets burned as more transactions occur. This is good news for ETH hodlers since there is the possibility that these fee burns could counteract future ETH inflation. However, this doesn’t strictly mean that Ethereum will definitely go deflationary. Rather, EIP-1559 merely introduces a theoretically deflationary mechanism, something Ethereum has hitherto lacked.
Moreover, Ethereum has a “Minimum Viable Issuance” monetary policy. That means it only issues enough ETH to ensure network security and no more. This deflationary measure is important as Ethereum moves from Proof of Work to Proof-of-Stake, (POS). That’s because with POS, the cost to attack it is a function of how scarce the staking asset is. With the introduction of this proposal, ETH could become more scarce. This is how EIP-1559 intends to improve Ethereum’s security.
Miner Extractable Value (MEV)
Another factor is MEV. At present, Ethereum miners can set the order of transactions on-chain in ways to benefit themselves profit-wise. So, the MEV is the profit miners can extract by reordering and censoring transactions. Because of arbitrage bots and their bidding wars, they can incentivize miners not to mine on the longest chain. This can be a destabilizing factor for any blockchain.
Consequently, EIP-1559 reduces miner’s incentives to try to mine older blocks. It accomplishes this by burning the ETH rewards paid to miners, which reduces their incentives to focus on older blocks after new ones have already propagated.
Layer 2 Solutions
For those constantly predicting doom and talking about all the upcoming Ethereum killers ready to devour it, don’t forget that the Ethereum we see today is not in its final form – far from it. Devs are working hard on Ethereum 2.0, but even though implementation is still a ways off, there are other solutions to help it scale in the meantime.

If you’re not familiar with Ethereum Layer 2 solutions, understand that Layer 1 is the main Ethereum chain layer. The upgrades coming with Ethereum 2.0 pertain to Layer 1. Layer 2 refers to interim solutions that help scale applications by handling certain transactions off the main chain.
Network congestion and slow transaction times negatively affect the UX for dApps on Ethereum. So, while waiting for Ethereum 2.0, these Layer 2 solutions can bring some relief.
Layer 2 solutions typically revolve around a cluster of servers called nodes. Developers can move transactions off of the congested main chain and submit them to Layer 2 nodes instead. There they are batched and sent back to Layer 1 to be secured.
Rollups
These Layer 2 solutions are good for reducing Ethereum gas fees and acquiring fast transaction throughput. Rollups execute transactions off of Layer 1 but post transaction data back to it. Their defining characteristic is that they perform executions outside of Layer 1 while inheriting security properties from it.
Zero Knowledge (ZK) Rollups
ZK Rollups bundle hundreds of transactions off-chain and generate a “SNARK” that’s known as a validity proof that’s posted back to Layer 1. For a deep dive, please read our article on ZK Rollups and ZK Snarks.
Optimistic Rollups
Optimistic rollups offer as much as 100x in scalability improvements and will get even better with the introduction of shard chains.
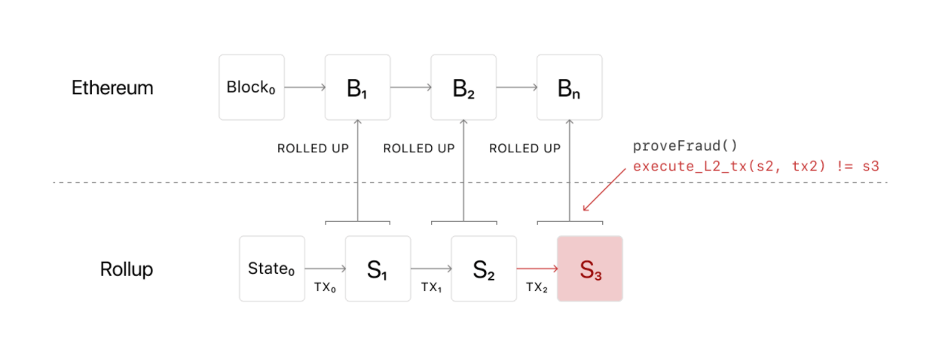
With this kind of Rollup, a side chain runs parallel to Ethereum’s main chain, and transactions are written to it as call data. This reduces gas costs. Also, Optimistic Rollups offer improved scalability because they don’t do computations. They merely notarize transactions. Since they don’t do computations, fraud proofs must ensure that transactions are legitimate.
For more information on Layer 2 solutions, please read our article “Breaking Down ETH 2.0 – Ethereum Layer-2 and Scalability Explained.”
Rollups Pros and Cons
ZK-Rollups don’t suffer delays since their proofs are already validated when submitted to the main chain. Nor are they subject to the kinds of economic attacks that can plague Optimistic Rollups. But they are not compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and are limited to simple transfers.
Optimistic Rollups are compatible with EVM and Solidity and are more secure and decentralized than ZK Rollups. Albeit, they are prone to suffering long wait times due to fraud challenges. Optimistic Rollups will help decongest the main chain reducing fees and expediting transactions in the process. This makes them a valuable option for developers. Nonetheless, in a recent interview, Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin expressed more confidence in ZK Rollups for the longer term.

Vitalik Buterin
EIP-1559 Conclusion
Now that we have some Layer 2 solutions in the works and the long-awaited EIP-1559 to serve as a medium-term solution before Ethereum 2.0 brings Ethereum staking, there is a lot to be optimistic about.
However, EIP-1559 doesn’t come without risks or security considerations. One that is taking center stage is the miner’s reaction to all of this. With the London hard fork slated for July, we’ve already learned that with EIP-1559, a portion of every transaction fee is burned and removed from circulation permanently.
Since over 40% of the miner’s revenue comes from transaction fees, EIP-1559 will likely decrease revenues. Also, the tips may not be enough to placate them. Nonetheless, with everything else going on, even if they do so begrudgingly, the miners will likely go along peacefully with this update. We shall see.
Along with the other solutions to ease Ethereum’s growing pains, EIP-1559 is all about working towards long-term sustainability. There’s still much work to do. But even with the risk of the miner’s negative reaction, it’s even riskier to count Ethereum out. Learn all about the Ethereum blockchain, smart contracts, and how to get a job in crypto at Ivan on Tech Academy!
Author: MindFrac





